Updated July 10, 2023
Introduction to Dependency Injection in Spring
Dependency Injection (DI) is a design pattern that implements the Inversion of Control for resolving the dependencies at run-time, i.e., injecting the dependency object to the dependent object to use at run-time. The most important module in the Spring Framework is Core Container & Dependency Injection (DI) acts as the heart of Spring’s Core Container.
Conventionally, Developers will have control over the code in creating the objects & injecting them at run time. Here, the Spring framework takes control of doing the activities mentioned above at run time; that’s why the term is coined as ‘Inversion of Control’ (IoC), i.e., the control is inverted!
How to Perform Dependency Injection in Spring?
Before we investigate the ways of performing Dependency Injection, it is important to know the different types of Dependency Injection Configurations. There are two different ways of Dependency Injection Configurations.
- XML based Configuration
- Java Annotation-based Configurations
This article will focus on Java Annotation-based Configuration, which is the most advanced, easy to implement, and used widely across the software industry. Also, it is important to know the definition below before diving deep into implementing Dependency Injection.
- Beans
- Autowiring
In Spring Terminology, Objects that act as your application’s backbone and are managed, i.e., instantiation, Configuration & assembly by the IoC Containers, are referred to as Beans.
Spring Framework helps us by providing a way to detect the relationship between the beans by reading the XML Configuration file or scanning the Java annotations when booting up the application. The IoC Container – Bean Factory takes up this task, which will create the objects & wire the dependencies. Since Spring Framework does this process automatically, it is called Autowiring, i.e., Automatic Wiring!
With Java Annotation Configurations, developers wire beans by using the @Autowired annotation.
Different Ways of Dependency Injection
As per Java Annotation Configuration, Dependency Injection can be performed in three different ways. They are as follows.
- Constructor-based Dependency Injection
- Setter-based Dependency Injection
- Field or Property-based Dependency Injection
Let us see one by one in detail with real-time examples & code snippets.
1. Constructor Based Dependency Injection
Constructor-based Dependency Injection refers to the use of the @Autowired annotation on top of a class constructor. Let us witness the usage of Constructor-based Dependency Injection with a real-time example.
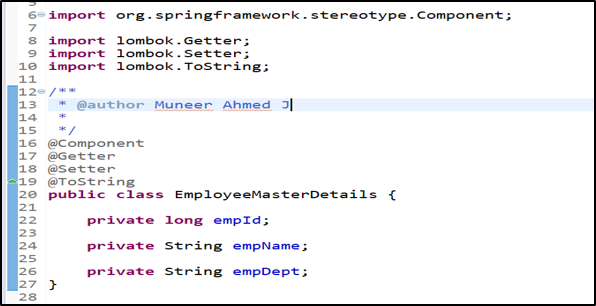
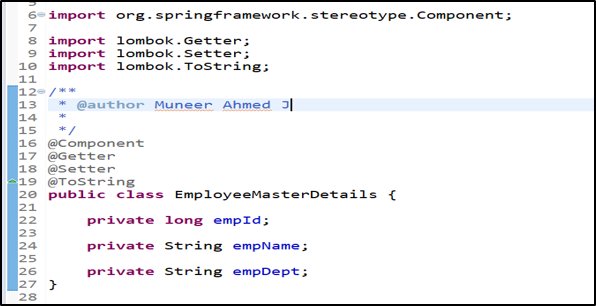
POJO Class: EmployeeMasterDetails class
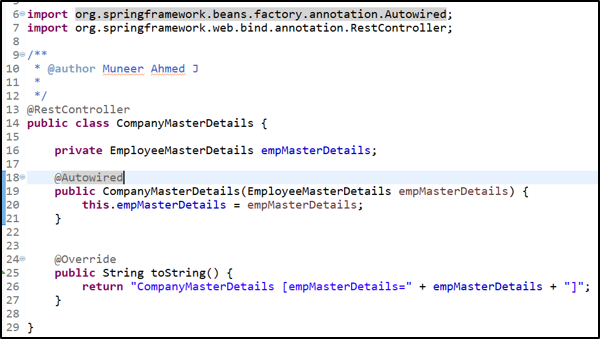
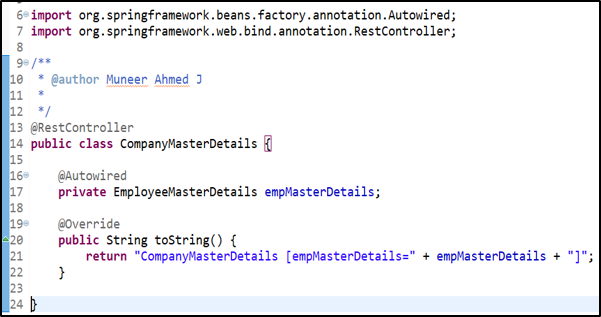
Controller: CompanyMasterDetails class
The code creates the EmployeeMasterDetails class as a component using the @Component annotation on line 16. Spring will automatically recognize this during the initialization/booting up of the application & will make a bean object using Bean Factory for EmployeeMasterDetails class.
After this, when Spring detects that the EmployeeMasterDetails bean object has been Autowired (using @Autowired) into the CompanyMasterDetails class constructor (line 18), the bean object created for EmployeeMasterDetails will be injected into CompanyMasterDetails class via constructor.
In this way, the Spring Framework will perform the Dependency Injection automatically. So, if you notice here, the developer has not created an object by using the “new” keyword in CompanyMasterDetails class, thereby removing the tight coupling between the CompanyMasterDetails class & EmployeeMasterDetails object.
2. Setter Based Dependency Injection
Setter-based Dependency Injection refers to the use of the @Autowired annotation on top of the setter method of a class. Let us witness Setter-based Dependency Injection’s usage with a real-time example.
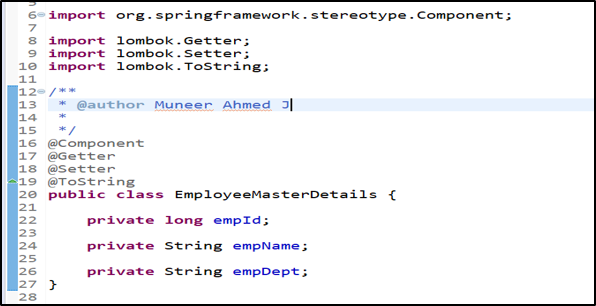
POJO Class: EmployeeMasterDetails class
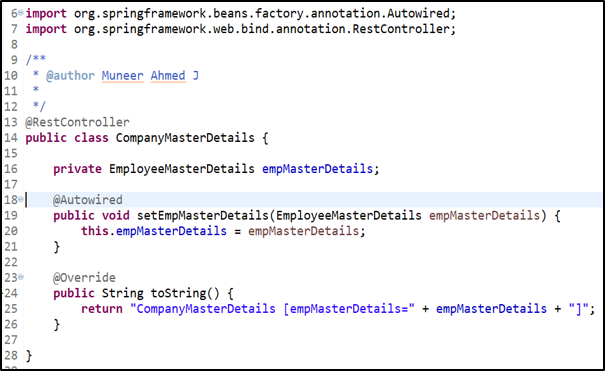
Controller: CompanyMasterDetails class
Similar to constructor based Dependency Injection, here the Autowiring takes place using the setter method at line no.18. The bean object created for EmployeeMasterDetails class will be Autowired & injected via the setter method in CompanyMasterDetails class.
3. Field or Property-Based Dependency Injection
Field-based Dependency Injection refers to the use of the @Autowired annotation on top of a field or property in a class. Let us witness the usage of Field-based Dependency Injection with a real-time example.
POJO Class: EmployeeMasterDetails class
Controller: CompanyMasterDetails class
Similar to Constructor-based Dependency Injection, here the Autowiring takes place using the field ‘empMasterDetails‘ at line no.16. The bean object created for EmployeeMasterDetails class will be Autowired & injected via the field ’empMasterDetails’ in CompanyMasterDetails class.
Fallback or Error Handling Cases.
Suppose there is more than one bean of the same type; the Spring Framework will get confused to inject the appropriate dependency. At this point, we will be running into the NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException.
To properly handle this, annotations from either @Primary or @Qualifier and the @Autowired annotation should be utilized.
- @Primary annotation: Gives priority to the other beans of the same type.
- @Qualifier annotation: Differentiates between the other beans by providing a unique qualifier name.
Advantages of Dependency Injection
Some of the advantages are as follows.
- Primarily Dependency Injection helps achieve loosely coupled architecture by removing the tight coupling/dependency between a class & its dependence.
- As the dependency between objects is loosely coupled, it helps the developers test the module by injecting the dependent Mock Objects (for example, using Spring Mockito).
- Dependency Injection removes unnecessary dependencies between the classes.
- As the modules are independent of each other & can be injected, the scope of making the component reusable is very high.
- Maintenance of the System becomes easy.
Disadvantages of Dependency Injection
Some of the disadvantages are as follows.
- Dependency Injection makes it difficult to trace the code as the developer needs to refer to more files (such as XML Configurations) to understand how the system behaves.
- As the Spring Framework takes care of the control rather than the developer, it will be difficult for the developers to understand how things work in the background & also to have customization.
- Dependency Injection allows loose coupling, increasing the number of Interfaces & classes.
Conclusion
So, in a nutshell, Dependency Injection helps the developers to achieve loose couplings between the classes. In this article, we have covered in-depth of Dependency Injection, its advantages & disadvantages & different ways of performing dependency injection with real-time examples & code snippets.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Dependency Injection in Spring. Here we discuss the introduction, How to perform dependency injection in Spring, along with advantages and disadvantages. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –