Updated April 1, 2023

Introduction to DBMS Relational Model
DBMS provides the different types of model to the user; the relational model is the one type of model that is provided by the DBMS. The relational model is used to represent how we can store the data in relational databases. Basically, relational databases store the data in table relations that means column and rows format. Every row and column of the table collects the records or data that are related to the table values. The table name and column name is useful to determine the meaning of each row from the table. In relational models, we can arrange data logically as per the user requirement.
Syntax:
Basically, there are multiple syntaxes for relational operation, here we see insert into syntax as follows:
insert into specific table name (colm_name_1 , colm_name_2,….. colm_name_N) values
(statement 1, statement 2,…..statement N),
(statement 1, statement 2,…..statement N),………;Explanation:
Different parameters used in the above syntax are as follows:
- Insert into: The insert into command is used to insert records into the specified table.
- Table name: Table name means an actual table that we need to insert new records.
- Column name: It is the specified column name from the table to insert the values.
- Statement: Statement is used to assign the values to the column in the table, so column name 1 is assigned values of statement 1; similarly, we consider all statements.
How Relational Model Works in DBMS?
Now let’s see how the relational model works in DBMS:
1. Basic Concept in Relational Model
- Attribute: Attributes means each column name from the table. By using attributes, we can define the relation.
- Tables: All data and records we store into the tabular format in a relational model that we call table. Every table contains rows and columns that we also call properties of the table.
- Tuple: Tuple means a single row from the specified table that contains the single value.
- Relational Schema: Relational schema means the name of the relation with its attribute.
- Degree: How many attributes present in the relation that we called the degree of the relation.
- Column: It is a value of a specified attribute.
- Relation Instance: A relation instance means a set of finite tuples, and it never has a duplicate value.
- Relation Key: Each row has more than one attribute, which we called relation key.
- Attribute Domain: Attribute domain means predefined value and scope of an attribute.
2. Relational Integrity Constraints
Relation integrity constraint is used in DBMS for condition, and that condition must be present for the valid relation. These Relational constraints in DBMS are obtained from the standards in the small world that the information represents. Thus, there are numerous sorts of Integrity Constraints in DBMS.
Basically, relation constraints are classified into the three types as follows:
- Domain Constraints: Domain constraint can be abused if specified attribute value not corresponding to the domain, or we can say that not in a specified data type. Domain constraint indicates that inside each tuple, and the estimation of each quality should be one of a kind. This is determined as information types which incorporate standard information type’s numbers, real numbers, characters, booleans, variable-length strings.
- Key Constraints: The key constraint is the most important constraint in the relation model. By using key constraint, we can uniquely identify the rows in the table.
- Referential Integrity Constraints: It is based on the foreign key concept; the foreign key is an essential attribute in relation models because it relates between two different tables. For referential integrity, we must need key attributes in the table.
3. Operations in Relational Model
We can perform the different operations on relational database models as follows:
- Insert: By using the insert operation, we can insert records into the table or say relation.
- Delete: By using the delete operation, we can remove the records from the table.
- Update: By using the update operation, we can modify the existing tuples from the specified table.
- Select: It is used to select the specified rows from the table.
4. Basic Requirement of Relational Model
- We just need to specify the relation clearly.
- Tuples should be related to relation.
- Columns should contain data about the attributes.
- Each cell contains a single value.
- Each column name must be unique.
Example of DBMS Relational Model
Given below is the example of the DBMS Relational Model:
First, we need to create by using a create table statement as follows.
Code:
create table company (Comp_Id int(20), comp_name varchar(30),
comp_address varchar(30));Now perform insert operation by using insert into a statement as follows.
Code:
insert into company (Comp_Id, comp_name,comp_address) values(1, "HP", "mumbai"), (2, "Dell", "Pune");
select * from company;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use to insert into statement. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
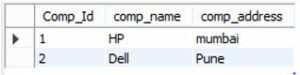
Now perform the update operation.
Code:
update company set comp_address= "Mumbai" where Comp_Id=2;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use update into a statement. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
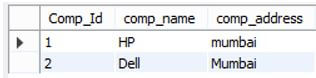
Now perform delete operation.
Code:
delete from company where Comp_Id=2;Explanation:
- In the above example, we use delete into a statement. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
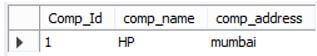
Advantages and Disadvantages of DBMS Relational Model
Given below are the advantages and disadvantages mentioned:
Advantages:
- Simplicity: The relational model is very simple than the other model in DBMS.
- Structural Independence: Because of structural independence, we can improve the performance of the model.
- Easy to Use: Relational models are very simple to understand because they contain columns and rows.
- Query Capability: Query capability means it avoids the complexity of the query, and it provides the high-level query language that is SQL.
- Data Independence: We can easily make the changes in the database without any changes in the application.
- Scalable: We can easily scale the database as per the requirement, which means we can easily add columns and rows to the database.
Disadvantages:
- Field length cannot exceed this is the limitation of relational databases.
- Sometimes relational models are complex because data grows.
- In relational models, we cannot share the data from one system to another system.
Conclusion
From the above article, we have seen the basic syntax of the Relational Model, and we also saw different examples of the Relational Model. We also saw the rules of Relational Models. From this article, we saw how and when we use the DBMS Relational Model.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “DBMS Relational Model” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

