Updated March 14, 2023

Introduction to dbms entity
In dbms, we show our tables in the form of entities that contain attributes of the table. These entities are used to show the relationship among different tables in the database. The ER diagram represents this entity relationship; this helps us understand the relationship between the two tables. We can represent them using the ER diagram for this; this ER diagram consists of the attribute, their relation with another table attribute, etc. We have different types of representation for each of the attributes of the table. For example, we have different types of entity in dbms, which are mainly categorised as weak entities. In short, if we have any database, then all the different tables for that database will represent the entity, and the relationship among them will be represented by using the ER diagram as discussed. In the coming section of the article, we will discuss their implementation in detail.
Types of dbms entity
In this section, we will discuss the different types of entities in dbms; in the database, we mainly have two types of entity which are categories as below; let’s discussed each of them in detail;
1. Weak entity: This type of entity does not contain any primary key, which means a table that cannot contain any primary key is termed as a weak entity in dbms. It basically depends on the other entity, or we can say the parent entity. If we have any weak entity, then it can be represented by the ‘ double backed ‘ in ER diagram in dbms; see below example for better clarity;
Weak entity representation ;

2. Strong entity: This type of entity has its own existence, which means the entity that contains a primary key can b termed a String entity because it does not depend on the other entity for its existence and does not depend on the other entity or tables. We can represent a string entity by using a ‘ single rectangle’ box.
Strong entity representation ;

entity Attributes
In dbms, every entity is represented or created using the attribute; these attributes are the entity’s property. Like we have different types of columns in tables. For example, we have an employee table and columns of the table as age, city, salary, so these are the attribute of the entity. All these attributes contain a value. We can apply any range of the value or specific domain to the attribute to restrict users from saving invalid data for a particular attribute. For example, we have employee salary, which will only contain a numeric value, not alphabets, so we can apply value range or domino here to restrict this attribute. Now let discuss the different type of attribute in entity for better understanding see below;
1. Simple attribute: A simple attribute is consists of one value, and it cannot be divided into further parts. It means it is an atomic value attribute; let’s take an example; employee salary cannot be divided into two parts or values. So this type of attribute is termed as ‘Single Attributes’.
2. Key attribute: This attribute helps us uniquely identify the entity; by using this, we can easily identify a unique record from the list of records we have. Let’s understand by one example we have student roll number which can easily use to identify a particular student from the list of students we have. Also, this type of attribute is represented by using the ‘oval’ shape in the representation.
Key attribute representation :
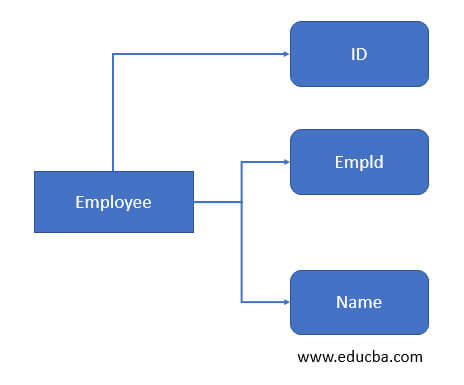
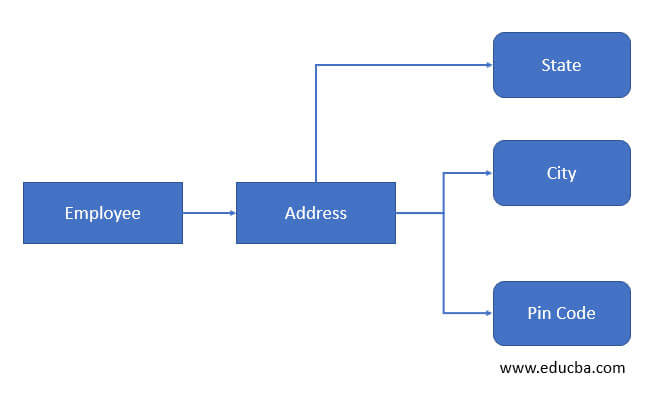
3. Composite attribute: As the name suggests, if the attribute is used to represent by combining another attributthenan it is termed as ‘ composite attribute ‘. That means we can combine two or more attributes on an entity to create this type of attribute in dbms. Let’s understand by the example, in the employee table; we have employee address which can be created by using the different attributes of the employee table like city, state, pin code, house no, etc.
Composite attribute representation :
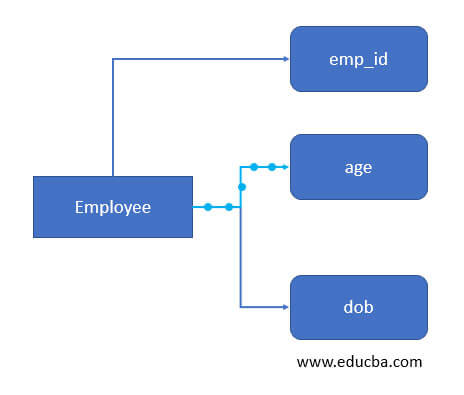
4. Derived attribute: As the name suggests, those attributes whose value is derived from the other attribute are termed a derived attributes. Also, it is dynamic in nature. to represent this is ER diagram, we use a dashed oval shape. An example of this is the ‘age’ of an employee can be derived from the ‘dob’ attribute.
Derived attribute representation:
5. Multivalued attribute: Attributes represent or create by using multiple attributes termed as ‘Multivalued attribute’ in the entity. The use of ‘oval shape can represent this type of attribute’. For example, an employee can have more than one phone number.
ER Diagram in DBMS entity
ER diagram stands for Entity Relationship diagram, and it is used to represent the relationship between different entities in the database. We have different types of relationships which can be used to define between entities. Also, these entities can be created by using a different type of attribute and so on that we have already discussed in the article. ER diagram in dbms helps us represent the logical structure of our database. This ER diagram can be created using the attribute, relationship among them, and entities of the database. In this section, we will see a different type of relation available in it; let’s get started;
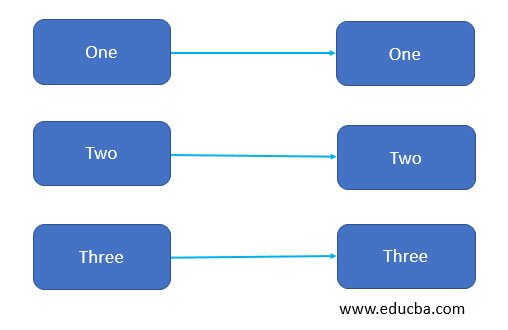
1. one-to-one: In this type of relationship, one entity’s attribute can be associated with almost one attribute of the different entity. Let’s suppose A entity can be associate with at most one entity of the other entity.
example:
2. one too many: In this type of relationship, one instance of the entity can be associated with the multiple instances of the other entity. which means a single record from one table can have multiple records in the other table.
example:
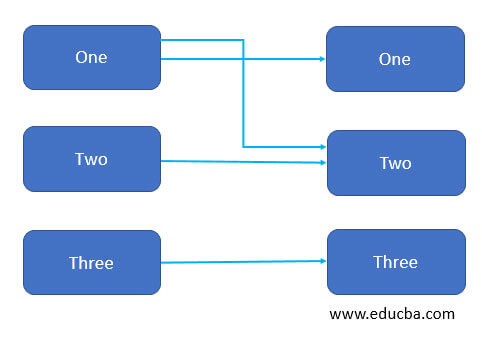
3. Many to one: In this type of relationship, multiple instances of an entity can be associated with the single instance of another entity, then the relation is termed as ‘Many to one ‘.
example:

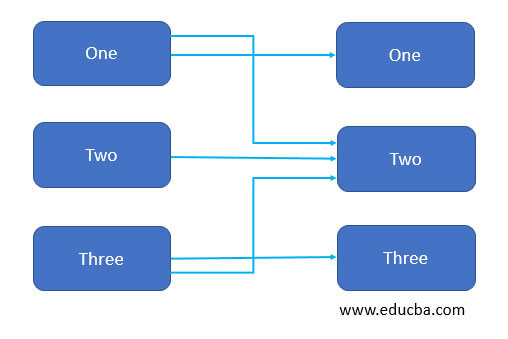
4. Many to Many: In this type of relationship, we can have multiple instances of the one entity that can be associate with the multiple instances of the other entity.
example:
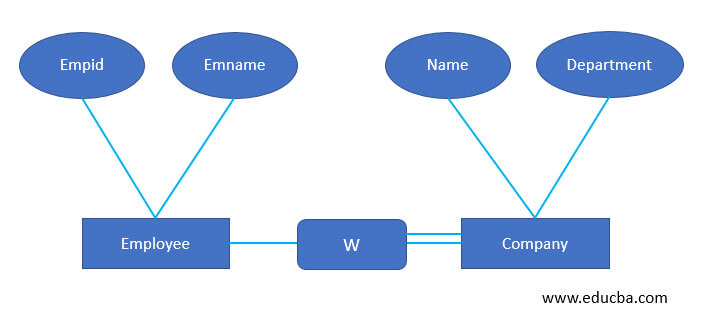
Complete ER diagram:
Conclusion
By the use of Er diagram, we can easily represent our entity in dbms. This helps us give a high overview of our database and help us understand the mapping among them. It is easy to use create and the main table.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to dbms entity. Here we discuss the different types of entities in dbms; In the database, we mainly have two types of entity which are categories. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

