Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to DB2 replace
DB2 replace is a function provided by IBM in the DB2 database management system which helps us to replace a particular string present inside the original string with any other required string. By using this function, all the occurrences of the mentioned string in the supplied string are being replaced. We can use this function in DB2 with string values, string literals, and even the fields of the columns that store the string values in them.
In this article, we will study the syntax of the replace() function in DB2, its usage, and implementation with the help of certain examples that will include replace() function used with string literals and some field values. The replace() function can be used in select as well as update query statements.
Syntax
The syntax of the replace function is as shown below
REPLACE (main supplied string, string to be replaced, replace string value)
In the above syntax, the main supplied string is the original string that is passed to the function that consists of one or more occurrences of the string to replace. The string to be replaced is the unwanted string in the original string, in place of which we want to put some other value of the string. The replace string is the string with which the string to be replaced should be replaced. It is necessary to specify the main supplied string and string to be replaced. Replace string value is optional for the specification which when not specified the REPLACE() function evaluates to the same value as supplied as the main string. If any of the arguments to the REPLACE() function is passed as NULL then it will return the output value as NULL. In DB2, we mostly use the REPLCAE() function for cleaning up the data.
Examples
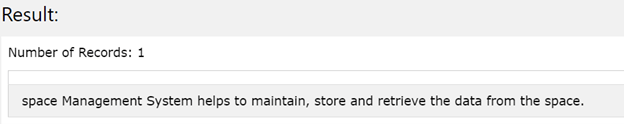
Let us have a look at how we can implement the REPLACE() function when using it with string literals. Consider one sample string say “Database Management System helps to maintain, store and retrieve the data from the database.”. In this original source string which will act as the main supplied string to our REPLACE() function, we have to replace all the occurrences of the database to space. Hence, our string to replaced is the “database” and the replace string with which we want to replace the “database” string is “space”. Hence, in order to retrieve the resultant replaced string, our query statement will become as shown below –
SELECT REPLACE('Database Management System helps to maintain, store and retrieve the data from the database.', 'database', 'space');
The output of the above-mentioned query statement is as shown below with all the occurrences of the “database” string being replaced by the “space” string in the original string –
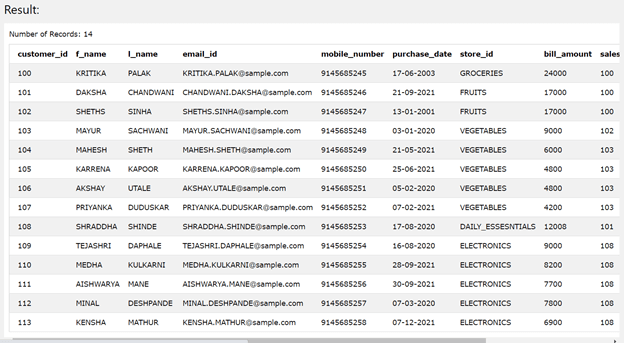
Let us now consider an example of REPLACE() function with field values of the table. Suppose we have a table named Sales_Customers which stores all the data related to the sales done for each of the stores. The data related to each sale transaction along with the details of the customer is being recorded in this table.
Let us retrieve the records of that table by using the following select query –
SELECT * FROM [Sales_Customers];
The output of the above query statement is as shown below –
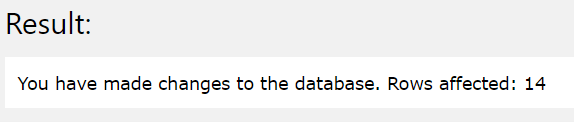
Now, consider that we have to replace all the occurrences of the “sample” word in the “email_id” column with the “demo” word. This can be done by using the replace function with the source string value mentioned as the name of the field whose internal strings are to be replaced. In this case, the source string can be mentioned as email_id as the name of the column. Further the string value to be replaced will be “sample” and the string with which the value should be replaced is “demo”. Hence, our query statement will now become as shown below with and UPDATE query statement used instead of a SELECT query statement as we have to update all the row’s column values for email_id.
UPDATE
Sales_Customers
SET
email_id = REPLACE(email_id,'sample','demo');
The execution of the above query statements gives the following output on the screen affecting all the 14 rows present in it.
Let us check whether the change has been updated or not in the Sales_Customers table by executing the following select query –
SELECT * FROM [Sales_Customers];
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output as a resultant –

We can observe that the values in the column of email_id have been properly updated and the sample in the email id values has been replaced with a demo string.
Let us take one more example of a SELECT query statement, but this time we will consider a string field value and try to retrieve all the occurrences of a particular string in that string column with replaced values only for display purpose. However, internally the contents of the table should not get modified. Consider the same table Sales_Customers in which we will try to retrieve the values of the mobile number column but instead of 9145685 at the beginning of the number value we will replace it with ******* while retrieving. However, the stored values won’t be modified.
Our query statement for retrieving such kind of result will be as shown below –
SELECT customer_id, REPLACE(mobile_number, "9145685","*******") as "Encoded Mobile Number" FROM Sales_Customers;
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output with all the initial 7 characters of that mobile number modified to the * character in those places and displaying the last three characters numbers in it. We can recognize the customer from its customer_id field.
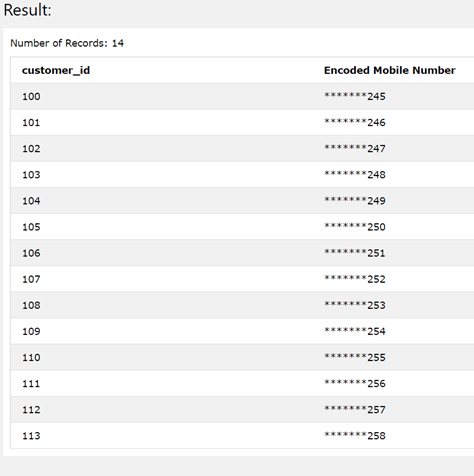
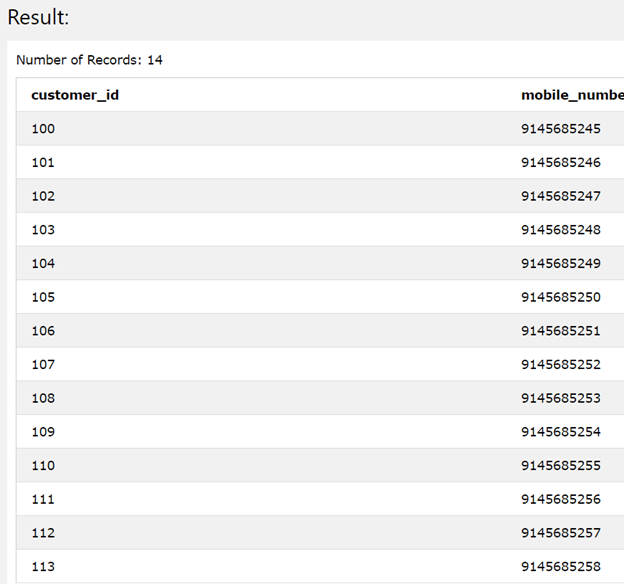
Let us once again confirm the values of the mobile_number and customer_id column in the Sales_Customers table to verify if the mobile numbers are still intact as they were original and are not being replaced by using the following query statement –
SELECT customer_id, mobile_number FROM Sales_Customers;
The execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
Conclusion – DB2 replace
We can use the REPLACE() function in DB2 provided by IBM to replace the string literal values. We can even replace the field values of the column and retrieve the replaced values keeping the content intact as well as if required update the replaced value permanently stored in that column with the help of the UPDATE statement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 replace. Here we discuss the syntax of the replace() function in DB2, its usage, and implementation with the help of certain examples. You may also look at the following article to learn more –

