Updated March 6, 2023

Introduction to DB2 load
DB2 provides the LOAD online utility to the user, in which we can load more than one table into the tablespace. By LOAD online utility, we can load different records into the table and create, or we can, say, build any index defined on them. Sometimes tables contain some records. At that time, we have two options. First, we can add new records to the table, and the second option is that we can replace the existing records at the time of the LOAD utility. After Load operation, we are able to perform the different kinds of operation such as edit or validation etc.
Syntax
load from specified file name with file extension del insert into specific table name;
Explanation
In the above example, we use the load command to load the content of the specified file into the specified table by using the insert into the statement.
How does load command work in DB2?
Now let’s see how the load command works in DB2 as follows. How the LOAD utility Load DB2 tables as follows:
Utilize the LOAD utility to load more than one table into the tablespace, or at least one partition of table space. The LOAD utility works on table space, so you should have the authority of all tables’ access in the tablespace when we need to run the LOAD command.
The LOAD utility loads record into the tables and constructs or broaden any lists characterized on them. If the tablespace as of now contains information, you can pick up any option that is whether you need to add the new records into the current records or choose a replacement option; both options depend on the user.
Moreover, you can utilize the LOAD utility to perform the following task as follows.
- We can compress the data and build the directory as per the requirement.
- By using the LOAD command, we can convert the records into the compatible data format and between the encoding schemas.
- By using the LOAD command, we can load multiple tables into a solitary table space.
a) Delimited input and output files
The LOAD and UNLOAD utilities can acknowledge or create a delimited record or files, which is a consecutive BSAM document with row delimiters and column delimiters. You can dump information from different frameworks into at least one document that utilizes a delimited record arrangement and afterwards utilize these delimited records as for contributions for the LOAD utility. Likewise, you can dump DB2 information into delimited documents by utilizing the UNLOAD utility and afterwards utilising these records to contribute to another DB2 data set.
b) INCURSOR choice
The INCURSOR choice of the LOAD utility indicates a cursor for the info informational collection. Utilize the EXEC SQL utility control proclamation to proclaim the cursor prior to running the LOAD utility. You characterize the cursor with the goal that it chooses information from another DB2 table. The segment names in the SELECT proclamation should be indistinguishable from the segment names of the table that is being stacked. The INCURSOR alternative uses the DB2 cross-loader work.
c) CCSID alternative option
You can load input information into ASCII, EBCDIC, or Unicode tables. The ASCII, EBCDIC, and UNICODE alternatives on the LOAD utility proclamation let you indicate whether the configuration of the information in the info record is ASCII, EBCDIC, or Unicode. The CCSID choice of the LOAD utility articulation allows you to indicate the CCSIDs of the information in the info record. On the off chance that the CCSID of the information doesn’t coordinate with the CCSID of the tablespace, the information fields are changed over to the CCSID of the tablespace before they are stacked.
d) Accessibility during load
For non-parcelled tablespaces, information for different tables in the tablespace that isn’t important for the table that is being loaded is inaccessible to other application programs during the heap activity except for LOAD SHRLEVEL CHANGE. For divided tablespaces, information that is in the tablespace that is being loaded is likewise inaccessible to other application programs during the heap activity except for LOAD SHRLEVEL CHANGE. Furthermore, some SQL proclamations, like CREATE, DROP, and ALTER, may encounter disputes when they run against another tablespace in a similar DB2 information base while the table is being loaded.
e) Default esteems for a column.
At the point when you load a table and don’t supply an incentive for at least one of the sections, the move DB2 makes relies upon the conditions.
On the off chance that the section isn’t a ROWID or personality segment, DB2 loads the default estimation of the segment, which is determined by the DEFAULT proviso of the CREATE or ALTER TABLE proclamation.
On the off chance that the segment is a ROWID section that utilizes the GENERATED BY DEFAULT alternative, DB2 creates an extraordinary worth.
On the off chance that the segment is a personality section that utilizes the GENERATED BY DEFAULT alternative, DB2 offers a predetermined benefit.
With XML sections, if there is a certainly made DOCID segment in the table, it is made with the GENERATED ALWAYS trait.
You can’t supply worth for ROWID or character segments that utilize the GENERATED ALWAYS choice since this alternative implies that DB2 consistently offers a benefit.
Examples
Now let’s see the different examples of load command as follows.
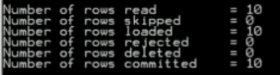
db2 –tvf demoload.txt
Explanation
The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
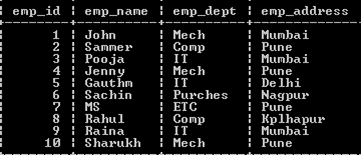
load from emp.ixf of ixf replace into emp_copy
After that, run a select statement to see the result as follows.
select * from emp_copy;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement to see the load command result. The end output of the above statement we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the DB2 Load command. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of the load command, and we also see different examples of Load command. We also learned the rules of the load command. From this article, we learned how and when we use the DB2 Load command.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 load. Here we discuss the basic syntax of the load command, and we also see different examples of Load command. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

