Updated March 4, 2023

Introduction to DB2 LISTAGG
DB2 LISTAGG is the function available in DB2 which helps to create a joined and concatenated single string result from more than one string expressions. This resultant can contain multiple string values separated by any of the configurable and required separator which can be mentioned in the function argument while aggregating multiple strings. The LISTAGG function is most often used for generating a comma-separated string value from the multiple row data of a particular table in relational database which is similar to denormalization. However, the concatenated result set is also retrieved by specifying any other separator for efficient readable format of data.
Syntax of DB2 LISTAGG
The syntax of the LISTAGG() function in DB2 is as shown below:
LISTAGG (DISTINCT| ALL expression(s), customized_separator)
WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY expression used for sorting DESC | ASC)
In the above syntax, the different elements that need to be specified in LISTAGG() function are given one by one:
- DISTINCT | ALL: We can specify if we have to consider all the string expression values that are mentioned along with the duplicate values or only the unique string expression values while concatenating or aggregating them in LISTAGG() function with the help of specifying DISTINCT or ALL before specifying any other string expression.
- Expression(s): This can be any literal or constant value or even the name of the column of the table which ultimately retrieves a value which is in the VARCHAR datatype. If the value is not in VARCHAR datatype, it is firstly converted to VARCHAR datatype and then considered for aggregation. This are the actual values that we have to concatenate.
- Customized_Separator: We can specify a particular character by using which all the string expression values should be separated in the concatenated string value which we want to retrieve as the final resultant by specifying it in place of customized_separator.
- WITHIN GROUP: We have to specify the group of data from which we have to consider all the string expressions are to be aggregated. This should be done by writing the group inside the WITHIN GROUP statement.
- ORDER BY: We can optionally specify the order of the string expressions in which they should be concatenated by using the ORDER BY statement.
- Expression Used for Sorting: We can specify the expression or expressions on the basis of which we want to order the string expressions while aggregating using this expression used for sorting.
- ASC | DESC: The sorting of the string expressions should be done on the basis of expression used for sorting in ascending or descending manner can be specified by using ASC or DESC. By default when we don’t specify, it considers the ascending order for string expressions in order by statement.
Example of DB2 LISTAGG
Given below is the example of DB2 LISTAGG:
Let us now consider an example of LISTAGG() function with field values of the table.
Suppose we have a table named Sales_Customers created by using the below query statement which stores all the data related to the sales done for each of the store. The data related to each sale transaction along with the details of the customer is being recorded in this table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE customers
( customer_id NUMBER(6)
, f_name VARCHAR2(20)
, l_name VARCHAR2(25)
, email_id VARCHAR2(40)
, mobile_number VARCHAR2(20)
, purchase_date DATE
, store_id VARCHAR2(20)
, bill_amount NUMBER(8,2)
, salesman_id NUMBER(6)
, department_id NUMBER(4)
) ;
Let us retrieve the records of that table by using the following select query:
Code:
SELECT * FROM [Sales_Customers];
Output:

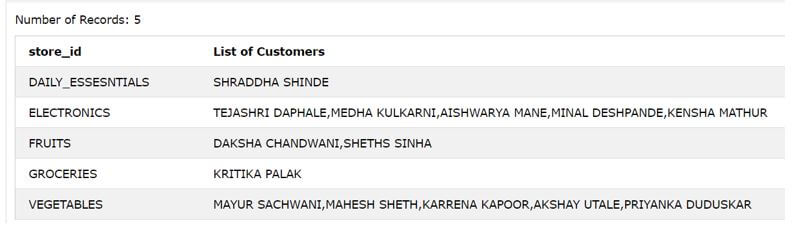
Now, consider that we have to get all the customers full name that should be grouped according to the store_id where that customer has done the purchasing and the names of the customers need to be separated with a comma. This can be done by using the LISTAGG function with the string expressions containing the concatenation of f_name and l_name column as they store the first name and the last name of each customer. The separator that we will use will be comma as multiple customer names needs to be comma separated and the GROUP by clause will contain the store_id column on the basis of which we will be grouping all the customers.
Code:
SELECT
store_id,
LISTAGG(f_name || ' ' || l_name,',') "List of customers"
FROM
Sales_Customers
GROUP BY
title;
The execution of above query statements gives the following output on the retrieving all the stores and the list of customers separated with comma for each of the customer who has done the purchasing from that particular store.
Output:
Suppose that we have a table named products and it contains the data of all the product names, the supplier id from where we purchase those products the category id in which the products fall in, the unit of the product and the price of the product as shown in the below image when retrieved by using the following select query.
Code:
SELECT * FROM Products;
Output:

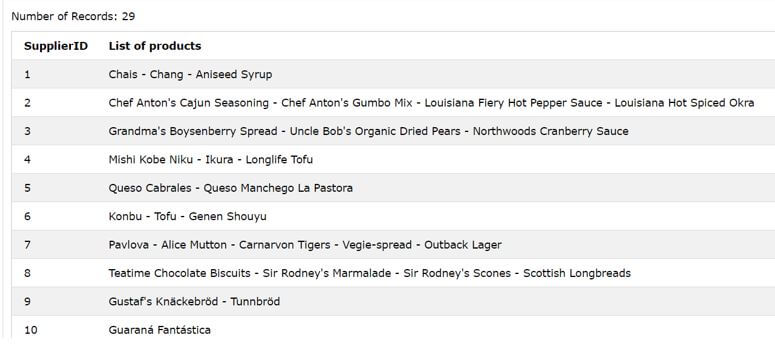
Now, suppose we have to retrieve the grouped list of the names of the products based on each of the supplier id. This can be done by using the LISTAGG() function with string expression specified using the column name productname and the grouping clause with contain supplier id in it. The separator will be a dash and spaces.
Code:
SELECT
SupplierID,
GROUP_CONCAT(productName, " - ") "List of products"
FROM
Products
GROUP BY
SupplierID;
The execution of above query statements gives the following output on the retrieving all the supplier ids and the list of product names separated with a dash for each of the product.
Output:
Conclusion
We can make the use of LISTAGG() function to aggregate multiple string values and to retrieve a single string value out of all of them which can be separated from each other with a separator as specified by us.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 LISTAGG. Here we discuss the introduction and the example of DB2 LISTAGG for a better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


