Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to DB2 LIKE
DB2 LIKE statement is used to get the Boolean value after the mentioned expression contains a characteristic or a particular part of the string inside the original expression mentioned. The pattern string can contain many characters in it. Some of which can be regular characters, while other ones can be special characters which are also referred to as wildcards. This is the same pattern that we are trying to search and retrieve from the main original string. Here, we will see how we can use the LIKE operator to recognize any particular string inside the main or the original string inside. We are trying to search the pattern, its syntax and the implementation, and certain examples.
Syntax of DB2 LIKE
The syntax of the LIKE operator is as shown below:
Name of the column/ expression LIKE required pattern [ESCAPE character which needs to be escaped]
The LIKE operator returns the Boolean value as it is a logical operator. It returns the true value when it finds the specified pattern followed by the main string or expression which we have specified. Note that we can specify the regular characters containing alphabets and numbers as well as special characters like other symbols such as #, %,$, {,}, etc.. inside the pattern string that we will specify. In the above syntax, the name of the column can be any column whose value will be in varchar datatype or can be implicitly converted to varchar datatype.
We can use the LIKE operator inside the SELECT, UPDATE or even the DELETE operator. It is not necessary that we use the LIKE operator for columns only. It can also be used for expressions that evaluate to a string value. Further, we have to specify the pattern, which is the string that we are trying to search for in our column of expression, which can be a combination of regular and special characters. The special characters having the symbols _ and % are called as wildcard characters. They have special meaning when specified in a pattern. When % is used we mean that zero or more number of occurrences of any characters can be present over there. While the use of _ in the pattern means that we can have any single occurrence of character at that particular space.
For example, when we specify “%as” the pattern then what we mean is that the expression or column can have any number of the characters at the beginning of the string. However, it should end with as in the end. Suppose that now we specify the pattern containing _ in it. Our pattern is “s_r”, which means that the column value or expression should evaluate to a value that should be beginning with s and ending with r, containing any one character between them such as sir, sar, etc.
If the column value or the expression contains any special characters which are wild card characters like _ of %, then they can be escaped by specifying it as the escape character, when they are escaped using the escape character they are considered as the regular characters inside the main column or expression.
Examples of DB2 LIKE
Given below are the examples of DB2 LIKE:
Let us now consider certain examples that will help us understand how we can use the LIKE operator to make the efficient detection of a particular pattern inside the string.
Firstly, we will search for a pattern inside the column values of a particular table.
Consider a table named employee_details that contains all the information related to each of the employees in it. When we try to retrieve the data of that table we can make the use of the following query statement.
Code:
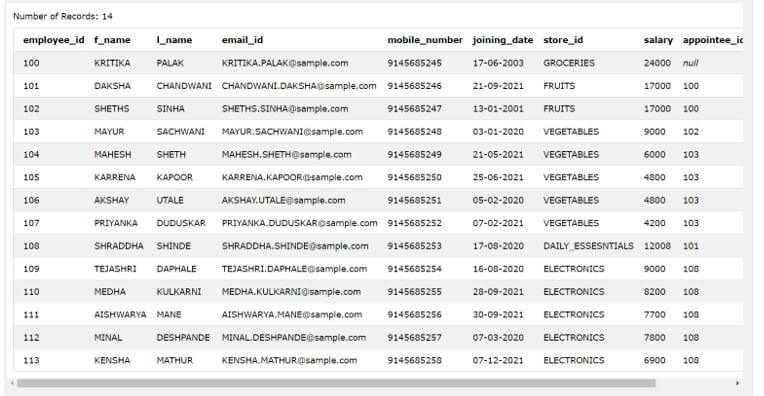
SELECT * FROM [employee_details]
The execution of above query statement gives the following output with all the details in it.
Output:
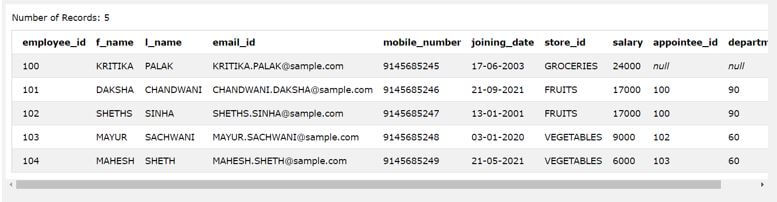
Now, let us take the example that we want to retrieve all the records of the employees whose mobile number has the value 914568524 at the beginning of 9 characters of it and can have any character at the ending last 10th place. Hence, we can make the use of the LIKE statement in this case, which will have the pattern “914568524_” where _ will help us to specify that the 10th place can have any character at that position.
Code:
SELECT * FROM [employee_details] WHERE mobile_number LIKE "914568524_";
The execution of above query statement gives the following output with all the details of an employee whose number has 914568524 as the first 9 digits of it.
Output:
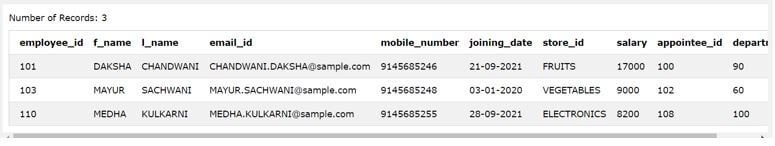
Let us consider one more example on the column name l_name of the employee_details table and try to retrieve all the employees whose last name ends with “NI”. In order to do that, our search pattern will be “%NI” which means that the column value of the string can precede with any number of the characters in the beginning, but it should end with NI characters only.
Code:
SELECT * FROM [employee_details] where l_name LIKE "%NI" ;
The execution of above query statement gives the following output with all the details of an employee having NI in the ending of their last name, as shown below.
Output:
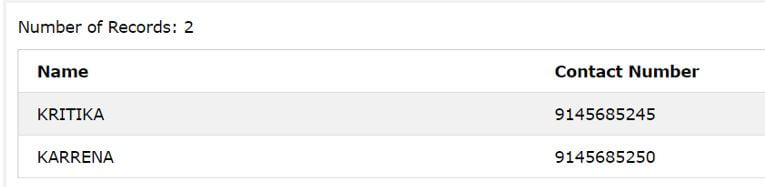
Now, suppose that we have to get the details of employee name and mobile number of the employees that have joined in either 6th month of 6th date or 6th year. Then we can say that the joining date should include 06 in it. This can be done using the pattern “%06%” specifying that the string can contain any characters in the beginning and even at the ending but should contain 06 in it.
Code:
SELECT f_name as Name , mobile_number as "Contact Number" FROM [employee_details] where joining_date LIKE "%06%" ;
The execution of above query statement gives the following output with all the details of an employee having 06 in the joining date column.
Output:
Conclusion
We can make the use of the LIKE operator in DB2 to get a Boolean value which helps to determine whether a particular column or string value follows the specified pattern.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 LIKE. Here we discuss the introduction and the examples of the DB2 LIKE for a better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –