Updated March 10, 2023

Introduction to DB2 current timestamp
Database management systems provide a different kind of function to the user; the current timestamp function is one of the functions that is provided by the DB2 to users. In which we can return the current time and date when the SQL statement will be executed on the current server. Basically, CURRENT TIMESTAMP is a special purpose register, which depends on the system’s clock. The CURRENT TIMESTAMP that we call a special register and is used for more than one time within a specified SQL statement, or we can say that CURRENT DATE or CURRENT TIME for a single SQL statement. One more important point is that all values of CURRENT TIMESTAMP depend on the single clock reading.
Syntax
select current_timestamp output from the system table or specified table;
Explanation
In the above syntax, we can use a select statement with different parameters as follows.
current_timestamp: It is a special-purpose register, and it is used to return the current date and time for every SQL statement.
output: It is used for results.
system table or specified table: System table means system generated table, and specified table means user-generated table.
How current timestamp function work in DB2?
Now let’s see how the current timestamp works in DB 2 as follows.
Basically, we can use different parameters for the current timestamp as follows:
Year: It is used to return the current year.
Month: It is used to return the current month.
Day: It is used to return to the current day.
Hour: It is used to return the hour.
Minute: It is used to return the current minute.
Second: It is used to return the current second.
Microsecond: It is used to return the current microsecond.
The CURRENT TIMESTAMP exceptional register determines a timestamp that depends on reading the hour-of-day clock when the SQL statement will be executed on the current server.
On the off chance that this unique register is utilized more than one time inside a solitary SQL statement or utilized with CURRENT DATE or CURRENT TIME inside a solitary proclamation, all qualities depend on a solitary clock reading.
The estimation of CURRENT TIMESTAMP in a client characterized work or put away strategy is acquired by using the standards.
Indicating CURRENT_TIMESTAMP is identical to determining CURRENT TIMESTAMP. On the off chance that you need a timestamp with a predetermined accuracy, the extraordinary register can be referred to as CURRENT TIMESTAMP(integer), where the whole number can go 0 – 12. The default accuracy is 6. SYSDATE can likewise be determined as an equivalent word for CURRENT TIMESTAMP (0).
On the off chance that you need a timestamp with a time region, the uncommon register can be referred to as CURRENT TIMESTAMP (number) WITH TIME ZONE, or CURRENT TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE? SYSTIMESTAMP can be indicated as an option in contrast to CURRENT TIMESTAMP (12) WITH TIME ZONE. The time region is resolved from the CURRENT TIME ZONE unique register.
On the off chance that the CURRENT TIMESTAMP extraordinary register is referred to in timestamp with time region setting (for instance, when contrasted and a timestamp with time region segment), the understood time region for the CURRENT TIMESTAMP exceptional register will be founded on the implied time region framework boundary, which could be an alternate worth from the CURRENT TIME ZONE uncommon register. To keep away from confusion of the time region for this situation, CURRENT TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE ought to be utilized.
Examples of DB2 current timestamp
Now let’s see the different examples of the current time to understand better as follows:
First, we need to create a database and table by using the following statement as follows.
create databases demo;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a create database statement to create a new database name as a demo. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
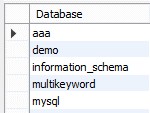
Now create a new table by using the create table statement as follows.
create table company (Comp_Id int(20), comp_name varchar(30),
comp_address varchar(30));
Explanation
In the above example, we use a create table statement to create a new table name as a company with different attributes such as Comp_id, comp_name, and comp_address with different data types and different sizes as shown in the above statement.
For confirmation, insert some records by using the following insert into the statement as follows.
insert into company (Comp_Id, comp_name,comp_address) values(1, "HP", "mumbai"), (2, "Dell", "Pune");
select * from company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use to insert into statement. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
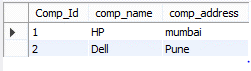
Now use the CURRENT TIMESTAMP function () as follows.
SELECT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP output FROM demo.company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement with the current_timestamp function, here the demo is a database name, and the company is a table name that is created by the user. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
![]()
Without underscore (_), we cannot use the current timestamp function, so instead of a select statement, we can use the values keyword.
Now let’s see how we can extract the microsecond, second, minute, hour, day, month, and year by using the current timestamp function as follows.
SELECT
YEAR (current timestamp) present_year,
MONTH (current timestamp) present_month,
DAY (current timestamp) present _day,
HOUR (current timestamp) present_hour,
MINUTE (current timestamp) present_minute,
SECOND (current timestamp) present_second,
MICROSECOND (current timestamp) present_microsecond
FROM
demo.company;
Explanation
In the above example, we use a select statement with the current timestamp function (), here we use different parameters as follows.
Year: it is used to fetch the current year.
Month: it is used to return the current month.
Day: It returns the current date.
Hour: It is used to show the current hour.
Minute: It is used to show the current minute.
Second: It is used to show the current second.
Microsecond: It is used to show current microseconds.
Here demo is the database name, and the company is the table name. The end out we illustrate by using the following screenshot as follows.
![]()
In this way, we can use the CURRENT TIMESTAMP function, and as per user requirement, we utilize this function.
Conclusion
We hope from this article you have understood about the DB 2 current timestamp functions. From the above article, we have learned the basic syntax of the current timestamp function, and we also see different examples of the current timestamp function. From this article, we learned how and when we use the DB 2 current timestamp function.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to DB2 current timestamp. Here we discuss the basic syntax of the current timestamp function, and we also see different examples of the current timestamp function. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


