Updated July 6, 2023

Introduction to Data Definition Language
Data Definition Language is a programming language through which data structures are defined. Acronymed as DDL, it can be considered a standard specifying commands that define data structures.
There are four kinds of data languages:
- Data Definition Language (DDL): Code the data structures.
- Data Manipulation Language (DML): Store and play with the data in those structures.
- Data Control Language (DCL): Decide who can play with the structure and the data.
- Data Query Language (DQL): Query the database for results and data mining.
Thus, in the simplest terms, DDL is a computer language used to code data structures.
Why Data Definition Language?
Data Definition Language dates back to the CODASYL database model. The schema of the database was written in a syntactical language. It thoroughly described the records, sets, fields, and the model as a whole. This was gradually adopted as a standard for declaring tables, columns, constraints, etc., in Structured Query Language (SQL). Thus, over time, DDL became a subset of SQL.
How Does Data Definition Language Work?
DDL is a set of guidelines to which all Structured Query Languages adhere. As in the computer programming languages, we have the OOPS guidelines that all the programming languages adhere to. Similarly, we have Data Definition Language standards that all the database languages adhere to – MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, etc.
Data Definition Language deals with the database structure where the data will be stored. It does not deal with the data itself. Thus, in any structured query language, a command that can modify the structure, tables, or relations of the database is a DDL command. A command that modifies the data stored is a DML command. A command that modifies the authorization rules is a DCL command. A command that queries the database to fetch results is a DQL command.
Data Definition Language Commands
One thing needs to be thoroughly kept in mind – DDL deals with the structure of the database and not the data itself.
1. CREATE
So, the first command under DDL is the Create command. The Create command is used to create a new database or a new component in the database, like tables, stored procedures, indexes, etc.
Let’s see all the commands one by one in action.
CREATE DATABASE
The Create Database command creates a new database.
Syntax:
CREATE DATABASE <DatabaseName>Example:
CREATE DATABASE ExampleDB;
CREATE TABLENow that we have a new database created, we need to create tables in our database.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE <TableName> (
<Column1> <DataType>,
<Column2> <DataType>,
<Column3> <DataType>,
.
.
.
<ColumnN> <DataType>,
)Example:
CREATE TABLE Employees (
Id INT,
Name VARCHAR(50),
Phone BIGINT,
IsContractor BIT
);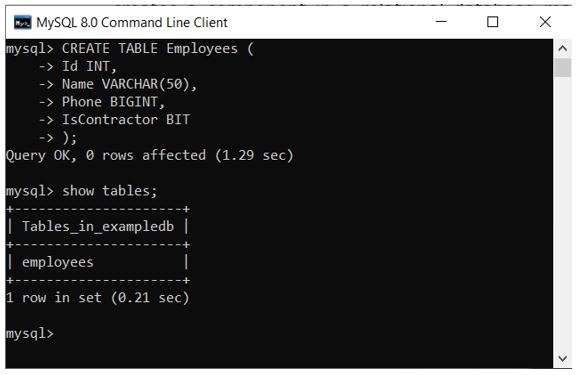
Our table is created. Now we can add data and query the results as and when needed.
2. ALTER
Now let’s look at the Alter commands in DDL. You can modify tables by adding, renaming, editing, or deleting a column. Alter command can also rename the table itself.
Alter Table
Let’s see the various Alter DDL commands:
- Add a column
- The Alter Table command allows us to add a column to an existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE <TableName> ADD <ColumnName> <DataType>Modify a column
The Alter Table command allows us to modify an existing column in an existing table. This is useful when modifying the type or the size of the column.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE <TableName> MODIFY <ColumnName> <DataType>An important thing to keep in mind is that we cannot rename a column with the modified sub-command. To rename, there is a separate sub-command.
Rename a table
The Alter Table command allows us to rename a table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE <TableName> RENAME TO <NewTableName>Rename a column
The Alter Table command allows us to rename a column in an existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE <TableName> RENAME COLUMN <ColumnName> TO <NewColumnName>Delete a column
The Alter Table command lets us delete a column and its entire data from an existing table.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE <TableName> DROP COLUMN <ColumnName>Example:
Run the below lines of command in sequence to add a new column to the table, modify the column type, rename the column, drop the column, and finally rename the table itself.
ALTER TABLE Employees ADD Department VARCHAR(20);
ALTER TABLE Employees MODIFY Department INT;
ALTER TABLE Employees RENAME COLUMN Department TO DepartmentId;
ALTER TABLE Employees DROP COLUMN DepartmentId;
ALTER TABLE Employees RENAME TO Employee;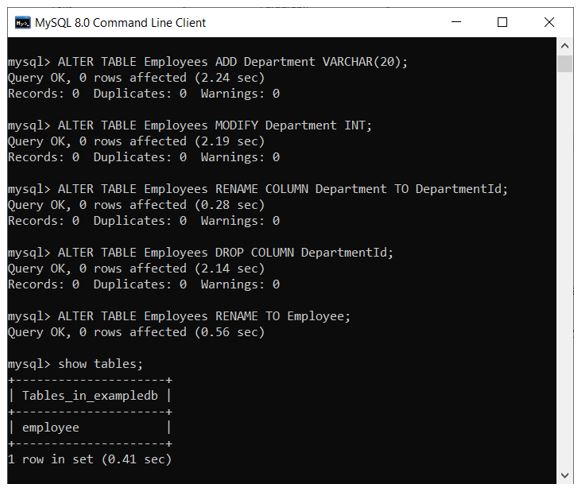
3. DROP
The DROP commands delete objects from the database or the schema. It can delete a table, view, stored procedure, index, or database.
DROP TABLE
The drop Table command deletes the whole table along with all the data.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE <TableName>Example:
DROP TABLE Employee;DROP DATABASE
The Drop Database command deletes the database and all the objects in it.
Syntax:
DROP DATABASE <DatabaseName>Example:
DROP DATABASE ExampleDB;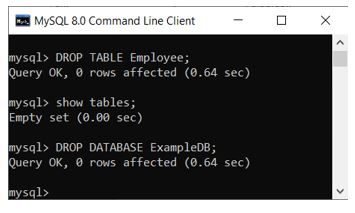
Advantages
Below are some of the advantages explained.
- The single largest advantage of Data Definition Language is uniformity.
- A set of standards to which all Structured Query Languages conform.
- You can store database schemas easily by writing them in command form using DDL.
- This also becomes easy to understand and write new commands over time.
- Thus, DDL, DML, DCL, and DQL bring uniformity at the elementary level of all the structured query languages.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the Data Definition Language, its concept, its purpose, and a few examples in MySQL. Since it is a common assessment subject, grasping the concept of DDL is essential for excelling in the Information Technology field.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Data Definition Language” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

