Updated July 11, 2023
Definition of Cost of Goods Sold
It is the total cost of the goods produced or sold or the total cost of services rendered, which includes direct labor costs, overhead costs, direct material costs, payroll taxes, and other related costs; In other words, the production of goods or services incurs the total cost directly in bringing the goods to their point of sale. Calculating the gross profit utilizes this important aspect.
Explanation
The C.O.G. sold is the total cost directly incurred in bringing the goods to their point of sale. In the Profit & Loss account, there are two parts. In the first part, we calculate the gross profit, taking the total income and deducting all the costs directly incurred in producing those goods. and In the second part, we deduct all the indirect costs not directly incurred in producing goods from the gross profit to calculate the net profit. Hence, all the identifiable costs directly incurred in producing goods constitute the C.O.G Sold.
Purpose
The most important purpose of C.O.G is its requirement for the calculation of the gross profit of the company in the company’s profit and loss account. In the Profit and loss account, there are two parts, the first part of which includes the costs which are directly related to the production of the goods sold and the second part which the cost that are not directly related to the production of the goods sold, i.e., indirect costs are included With the help of first part, gross profit calculates and second part helps in the calculation of net profit. Hence, it helps calculate gross profit, which measures the company’s efficiency in managing its labor and supplies in production. The cost of goods sold is inverse to the company’s income.
The Formula
The Formula for calculating the C.O.G sold is:
Example
Let’s consider Company XYZ Ltd., which is a manufacturing company in the field of Coal. It has an opening inventory at the beginning of the year of $15,000. Its Inventory during the end of the year is $7,000. During the entire year, it has made purchases of $9,000. In this case, the C.O.G sold calculate as:
Solution:
C.O.G calculates as:
Cost of Goods Sold = (Opening Inventory + Purchases – Closing Inventory)
- C.O.G sold = ($15,000 + $9,000 – $7,000)
- C.O.G sold = $17,000
What Includes in Cost of Goods Sold?
The following costs include in the C.O.G sold:
- Cost of purchase of a product or its parts.
- Cost of Purchase of the raw material of the product.
- Direct Labor Cost is paid for the production of goods or the rendering of services.
- Storage Costs
- Shipping charges and freight charges
- Machinery Costs or other production equipment cost
- Warehousing cost
- Other Overhead costs.
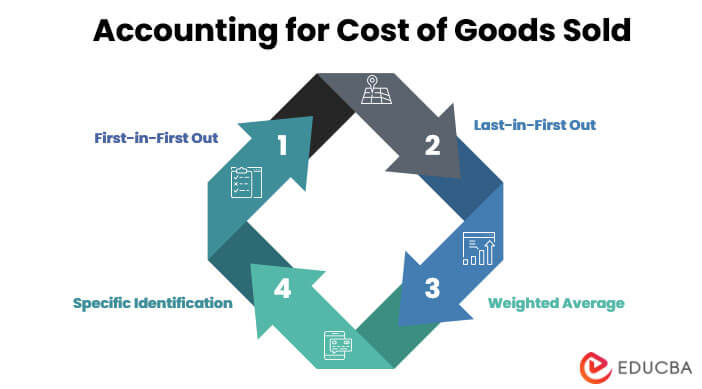
Accounting for Cost of Goods Sold
There are four methods of accounting for the C.O.G sold:
- First-in-First Out (FIFO): The FIFO method of accounting considers the costs incurred first when calculating COGS.
- Last-in-First Out (LIFO): In the LIFO method of accounting, the calculation of the Cost of Goods Sold considers the costs incurred in the later time period.
- Weighted Average: In this method of accounting, we divide the total cost of the goods available for sale by the number of goods sold to calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Specific Identification: In this method of accounting, we consider the specific costs attributable to the unit sold as the cost of goods sold. These are the identifiable costs that are product-specific.
The Journal Entry for recording C.O.G Sold:
| Date | Particulars | Debit | Credit |
| Cost of goods sold A/C Dr | $ | ||
| To Purchases A/c | $ | ||
| To Inventory A/C | $ |
Advantages
The following are the benefits of the C.O.G sold:
- The calculation of the C.O.G. sold gives an accurate and more specific calculation for the inventory valuation. We get a clear picture of the inventory costs and hence can have better inventory classification too.
- As the cost of inventory valuation is clearly defined, it helps the enterprise in the proper future prediction of the costs and also the other costs that it can afford.
- We get to know the time period of the inventory purchase, too, i.e., we can get an idea as to which inventory is the latest and which is the most updated.
- The C.O.G. Sold helps the enterprise in the calculation of gross profit. The gross profit helps measure the enterprise’s efficiency in terms of its labor and other supplies. Hence it helps the enterprise evaluate its labor and other supplies’ cost efficiency.
Disadvantages
The following are the disadvantages of the C.O.G Sold:
- Generally, the C.O.G. sold reflects the purchase cost of the materials. i.e., the historical cost of the materials. Hence, it does not take the current market value of the material.
- The costs of the materials and other things used in the production process keep fluctuating due to the market effect. Hence, we do not get the estimation of the real cost that is updated. Hence, the true picture of the cost sheet is not reflected properly, considering updation as per the market conditions.
Conclusion
The C.O.G. sold helps in the inventory valuation, and inventories are converted into profits. The C.O.G. sold helps to track the overall costs, which are essential for calculating tax purposes and profit margins. Hence, this helps the enterprise properly plan for future projects or predictions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Cost of Goods Sold. Here we discuss the definition and purpose of the cost of goods sold and its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –