Updated April 18, 2023

Introduction to Copy Command in Linux
Cp command is an abbreviated form of “Copy”.As the name suggests, we can replication either the file or the directory in a particular ecosystem like Unix, Linux, Windows, or even Mac Operating system.
Copy Command(cp) is based on a command-line terminal used for copying files/directories. This command creates an exact image of a file/directory with the same/different file name on the disk.cp command takes at least two arguments as input.
Nowadays it’s very common to use cp for replicating the files and rsync command for copying the directories. Copying of a file is different from moving a file from source to destination.
Prerequisite
To copy a file using the cp command is that the user must have permission for source and target files or directories.
Syntax
1.cp source destination
2.cp source Target_Directory
3.cp source1 source2 source3 sourceN Target_Directory
4.cp [options] source destinations
5.cp [option] source directory
where the first & second syntax we will copy the source file to destination files or directories
Moreover, in the third syntax we can copy multiple source files to target directory and the fourth and fifth syntax is with options that we can use for different purposes.
Options
1. cp -a: This option is used to archive the existing files in the directory for retention purpose.
2. cp -f: This option forcefully copy the files even it may remove the target file if needed. It is applicable if the file is already in use.
3. cp -i: This option stands for interactive mode, which means that it will ask the user to overwrite the file by prompt.
4. cp -l: This option is used to link files with other existing ones instead of copying them.
5. cp -L: It is will create a symbolic link for the file.
6. cp -n: This Option is used not to overwrite any existing file.
7. cp -R: This option means recursive copy means that it will copy all files with a cascading directory including hidden file.
8. cp -u: This means update, and copy when the source file is new than the destination file.
9. cp -v: This option stands for verbose which means that will it print all the process which happens on a file while copying.
Examples of Copy Command in Linux
Now let us discuss each option with an example for a better understanding of the concept.
1. Copying file to a target directory
Suppose we want to copy the /application/Praveen/file.txt file to /application/Praveen/Backup directory, so need to run below:
Command :
cp /application/Praveen/file.txt /application/Praveen/BackupOutput :
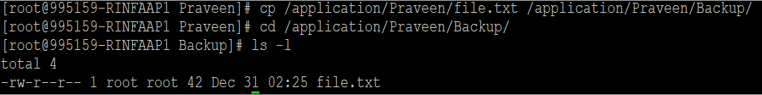
The above output shows that the file has been copied at the target directory.
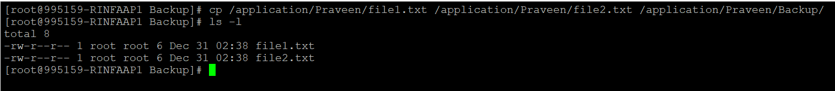
2. Multiple file copy at the same time
Command :
cp /application/Praveen/file1.txt /application/Praveen/file2.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Output :
3. Copying the file in interactive mode (-i)
If we want to copy the file in interactive mode, then we will use the option “-i”.Interactive Mode work if the same file already exists in the target directory already.
Command :
cp -i /application/Praveen/file1.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Output :

4. Copying File with Verbose mode enabled
We will use “-v” option for this.
Command :
cp -v /application/Praveen/file1.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Output :

If we want to use both verbose and interactive mode then use option “-iv”
Command :
cp -iv /application/Praveen/file1.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Output :

5. Copying a folder or directory (-R or -r)
In order to copy a directory from one to another place, we will use -R or -r options
Command :
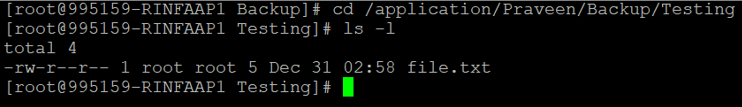
cp -r /application/Praveen/Testing /application/Praveen/Backup/Output :
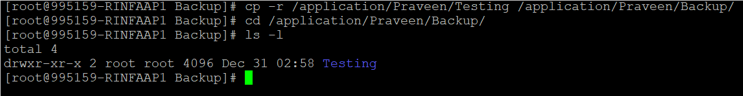
The above output shows the files and directory will be recursive.
Let us verify the contents :
Source :
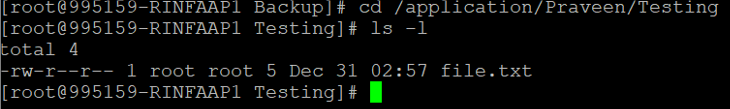
Target:
6. Archiving of files and directory
We will use the option “-a” instead of “-r” or “-R” options
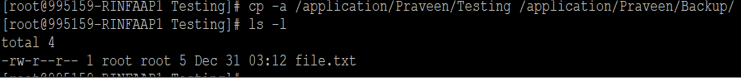
Command :
cp -a /application/Praveen/Testing /application/Praveen/Backup/Output :
7. Copying of file only when new source arrives
There are cases where we want to copy files only when the source file is newer than the target by using the option “-u”. We have added file2.txt at the source.
Command :
cp -v -u /application/Praveen/Testing/file*.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/Output :

Only file2.txt has been updated in the target directory.
8. If not to overwrite the existing file
There may be the case where we do not want to overwrite the existing file in the target.
In this case use “-n” option
Command:
cp /application/Praveen/Testing/file*.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/Output: Without using -n option

Command :
cp -n /application/Praveen/Testing/file*.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/Output :

9. Creation of symbolic link of a file
In case we need to create a symbolic link instead of copying then we will use “-s” option.
Command :
cp -s /application/Praveen/Testing/file2.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/Output :
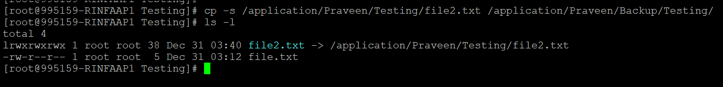
In the above output, we can see that file2.txt colored and pointing to the link.
Also, the permission is “lrwxrwxrwx”, where l stands for a symbolic link.
10. Creation of Hard link of a file
There are cases where we need to have a hard link instead of the symbolic link and copying of file, so we will achieve this by the option “-l”.
In Hard link inode, no. of source and link file will be the same.
Command :
cp -l /application/Praveen/Testing/file.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/Target file inode :
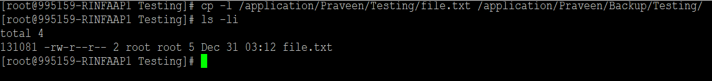
Source file inode :
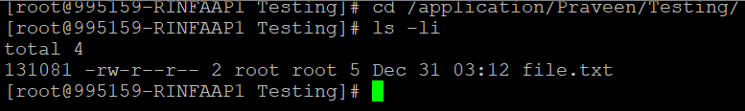
We can see that the inode is “131081” for both source and target files.
11. Creation of backup file of existing destination
As we know the by default cp command overwrites the file if exists. If we need to take the backup then we have to use “–backup” option, where we have to give the path at which backup to be taken.
Command :
cp --backup=simple -v /application/Praveen/Testing/file.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/file.txtOutput: It is created the same file with the extension(~) on the target path.
12. Copying files/directory forcefully(-f)
There are cases where the existing destination file cannot be opened and removed and if we want to copy the file in place of the existing destination file, then the “-f” option can be used.
Command :
cp -f /application/Praveen/Testing/file.txt /application/Praveen/Backup/Testing/Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Copy Command in Linux” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


