Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to Comparison Operators in SQL
Comparison operators in SQL are relational operators used to compare expressions’ values. These expressions can be a variable or column name, a constant value, a scalar function, a SQL query snippet, or a combination of these. These operators are used to test for inequality or equality of values. In SQL or any other query language (like Hive), large data chunks can be filtered out using these operators in the WHERE clause. This facilitates focusing on data that satisfy certain conditions, as per the result of the comparison operators. Also, these operators are used in CASE WHEN.. or IF-ELSE statements to form a grouping of records basis some specified conditions.
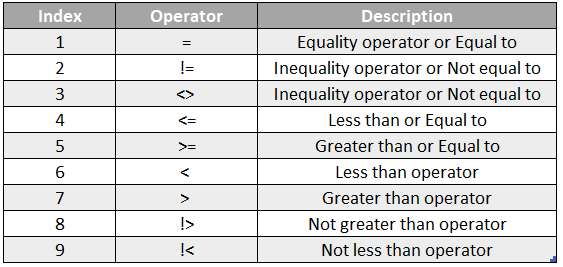
The list of commonly used relational or comparison operators is below:
The above operators include both the relational and advanced operators, which are frequently used in SQL coding. This favor is deriving useful insights from large chunks of data.
Various Comparison Operators in SQL
Let us now understand each of these in detail, accompanied by relevant examples.
1. Equality or Equal Operator
The equality or equal operator is used to check if values are equal or not an expression.
Syntax:
expression = variable/another expression/constant ;2. Inequality or Not Equal to Operator
The inequality or not equal to an operator is used to check if values are not equal in an expression or query. The two ways of doing this are using != or <>. Exclamation mark! signifies “not.” <> this signifies “neither less than nor greater than,” thus implying not equal to operation.
Syntax:
Expression != variable/another expression/constant ;
Expression <> variable/another expression/constant ;3. Less than or Equal to Operator
The less than or equal to operator checks for an expression “less than or equal to” to right-hand side values.
Syntax:
Expression <= variable/another expression/constant ;4. Greater than or Equal to Operator
The greater than or equal to operator checks for an expression to be “greater than or equal to” to right-hand side values.
Syntax:
Expression >= variable/another expression/constant ;5. Less than Operator
The less than operator checks for an expression to be “less than” to right-hand side values.
Syntax:
Expression < variable/another expression/constant ;6. Greater than Operator
The greater than operator checks for an expression “greater than” to right-hand side values.
Syntax:
Expression > variable/another expression/constant ;7. Not Greater than Operator
The not greater than operator checks for an expression to be “not greater than” to right-hand side values. This means the value can be less than or equal to the right-hand expression.
Syntax:
Expression !> variable/another expression/constant ;8. Not Less than Operator
The not less than operator checks for an expression to be “not less than” to right-hand side values. This means the value can be greater than or equal to the right-hand expression.
Syntax:
Expression !< variable/another expression/constant ;Let us consider an example of “Employees” data. This employee data has the Employee Id, first name, last name, and date of birth of these employees. There can be different data tables where key performance metrics (KPIs) must be evaluated. We shall perform a comparison operation on them as below to derive essential insights from them.
Examples of Comparison Operators in SQL
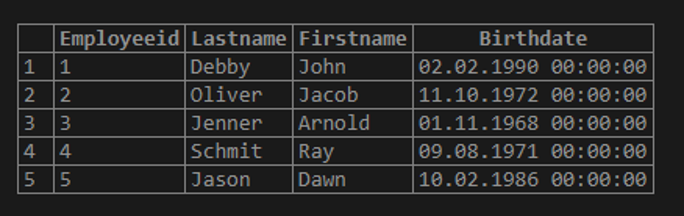
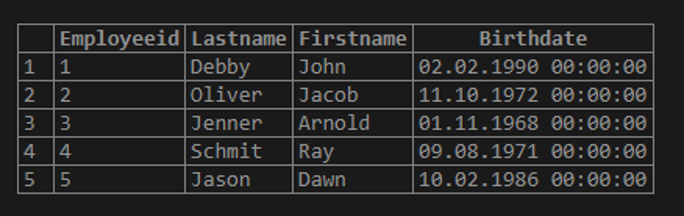
To create an employee table and insert five records into it:
Query:
Create table employee
(
Employeeid Int,
Lastname varchar(50),
Firstname varchar(50),
Birthdate date
);
Insert into employee
(Employeeid, lastname, firstname, birthdate)
Values
(1, 'Debby', 'John', '1990-02-02'),
(2, 'Oliver', 'Jacob', '1972-10-11'),
(3, 'Jenner', 'Arnold', '1968-11-01'),
(4, 'Schmit', 'Ray', '1971-08-09'),
(5, 'Jason', 'Dawn', '1986-02-10'<)
);Query:
Select * from employee;Output:
To get the employees born before Jan 1971, the query is:
Query:
SELECT employeeid, lastname, firstname, birthdate FROM employee where birthdate <= '1971-01-01';Output:
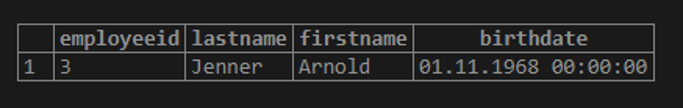
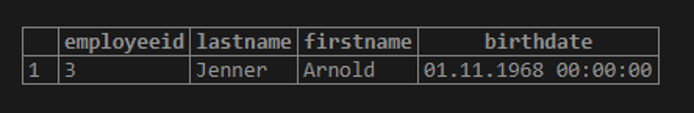
The query below can be used to get the employees whose date of birth is not beyond 8th Dec 1968.
Query:
SELECT employeeid, lastname, firstname, birthdate FROM employee where
birthdate !> '1968-12-08';Output:
To return employees whose birthdate is filled in, the query is to remove cases with no date of birth present,
Query:
SELECT employeeid, lastname, firstname, birthdate FROM employee where birthdate <> '';Output:
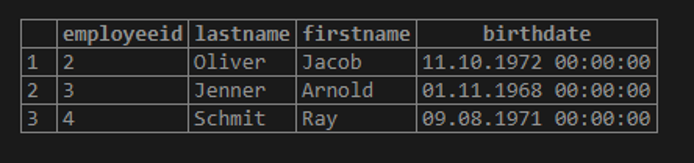
To return employees who are born between 1960 and 1970, the query uses both greater than and less than operator:
Query:
SELECT employeeid, lastname, firstname, birthdate FROM employee where birthdate >= '1960-01-01' and birthdate <='1980-12-31';Output:
Importance of Comparison Operator
- These operators enable the development of precise queries with limited use of other logical operators (like OR or AND) in INSERT, UPDATE, and SELECT statements.
- These help easily compare numerical, non-numerical, or date field data values.
- These operators are compatible with various versions of SQL databases like Parallel Data Warehouse, Azure SQL database, Azure SQL data warehouse, SQL Server 2008, and later versions.
- Handling missing values is an important task in database management. Comparison operator like equality and inequality operators helps filter out records that satisfy this condition.
- Aggregation performed on large data sets using sum(), min(), max(), avg(), and so on can also be compared or filtered using comparison operators.
Conclusion
Comparison Operators reserved words facilitate comparing values of expressions comprising various values from tables. These operators make data analysis and summarization easy to execute and understand. Developers have been using these in SQL and other DML queries also. This article highlights the usage and syntax of comparison operators, widely used in data analytics using SQL as a language. However, these operators are language agnostic and almost identical in all languages.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Comparison Operators in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.