Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to TOP in SQL
TOP is a keyword in SQL SERVER. It is used along with the SELECT clause to limit the number of records to be returned. It comes handy during data analysis. Especially when we just want to see only the first few records to understand the dataset or when we want to find the highest or lowest records from an ordered set of records.
Syntax:
Moving ahead, let’s discuss the SQL TOP keyword in greater detail. The standard syntax for writing it along with the SELECT clause is as follows:
SELECT TOP (NUMBER) | (PERCENT)
expressions, column_name
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
[ORDER BY expression [ ASC | DESC ]];Parameters
The different parameters used in the syntax are:
- TOP (NUMBER): Returns the top number of rows from the resulting recordset. For example, TOP 5 would return the top 5 rows from the resulting set.
- TOP PERCENT: Returns the top number of rows from the resulting recordset. For example, TOP 50 PERCENT would return the top 50% rows from the resulting set.
- Expressions: Mention the aggregate functions or other functions like Distinct etc. For example, SELECT TOP 1 SUM(column_name) would return the first row from the resulting set after performing the sum on column_name.
- Column_name: Mention the column names, which have to be returned in the resultant recordset.
- FROM tables: Mention the table names, from which the records have to be fetched.
- WHERE conditions: It is used to filter records. WHERE condition will return only those records that fulfill the mentioned condition.
- ORDER BY expression [ ASC | DESC ]: This keyword is used to sort the resulting record set in ascending or descending order. If you do not mention anything from ASC|DESC then ORDER BY will sort the records in ascending order by default.
From the above-mentioned parameters, TOP NUMBER OR PERCENT, Column_names and FROM tables are compulsory. Other keywords/parameters can be used based on the requirement. We can also use other SQL keywords, such as JOIN, having, etc. in the given syntax.
Examples of TOP in SQL
In order to demonstrate and explain the TOP keyword effectively, we will be using the following table. It is a sample “customers” table that contains 15 records with each customer’s id, name, city, and the country he/she belongs to.
Schema of “customers” table:
Number of records: 15
| Customers |
| ID(primary key) |
| Customer |
| City |
| Country |
Records in the table:
| ID | Customer | City | Country |
| 1 | Peter King | Manchester | England |
| 2 | Priya Krishna | New Delhi | India |
| 3 | Jim Halpert | Manchester | England |
| 4 | Michael Scott | New York | USA |
| 5 | Harvey Spector | Birmingham | England |
| 6 | Deepa Kamat | Mumbai | India |
| 7 | Anita Desai | London | England |
| 8 | Rachel Zane | Michigan | USA |
| 9 | Pretoria John | Canberra | Australia |
| 10 | John L | Budapest | Hungry |
| 11 | Justin Green | Ottawa City | Canada |
| 12 | Babita Ghosh | Kolkata | India |
| 13 | Krish Pratt | London | England |
| 14 | Elizabeth Blunt | London | England |
| 15 | Nina Debrov | Amsterdam | Netherlands |
Example #1
SQL syntax to demonstrate the basic function of the TOP keyword
Code:
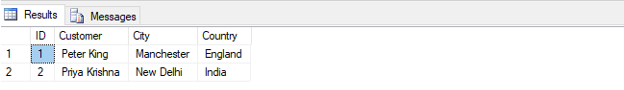
SELECT TOP 2 * FROM customers;Output:
Number of records: 2
In the above example, we can see that the TOP keyword with the SELECT clause returned just the top 2 records from the customer’s data table.
Example #2
SQL syntax to demonstrate the function of the TOP keyword when selecting specific columns only
Code:
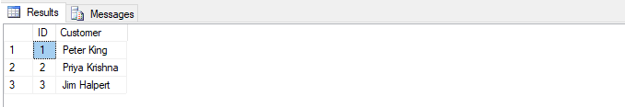
SELECT TOP 3 ID, Customer FROM customers;Output:
Number of records: 3
Example #3
SQL syntax to demonstrate the function of the TOP keyword along with WHERE clause
Code:
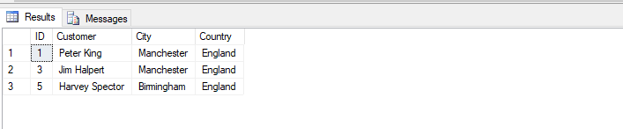
SELECT TOP 3 * FROM customers WHERE Country= 'England';Output:
Number of records: 3
In the above example, the query returned the first 3 records where the country was England.
Example #4
SQL syntax to demonstrate the function of the TOP keyword along with WHERE and ORDER BY clause.
Code:
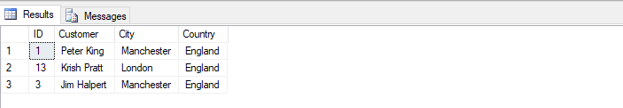
SELECT TOP 3 * FROM customers WHERE Country= 'England' ORDER BY Customer DESC;Output:
Number of records: 3
In the above example, the query returned the first 3 records after sorting the resultant set in decreasing order by customer names.
Example #5
SQL syntax to demonstrate the function of the TOP keyword along with the PERCENT and ORDER BY clause.
Code:
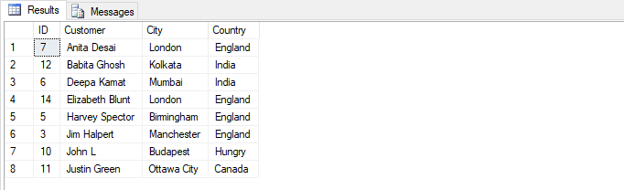
SELECT TOP 50 PERCENT * FROM Customers ORDER BY Customer ASC;Output:
Number of records: 8
The query in the above example returned the top 50% of the total resultant recordset after sorting them in ascending order by customer name.
Conclusion
TOP is a very useful keyword when it comes to getting the few records from an ordered set. For example, we want the first 3 records or the last 3 records, etc. for an ascending or descending result set respectively.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TOP in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.