Updated June 16, 2023

Introduction to C puts() Function
In any programming language, trying the output on the screen is vital. In c, this is achieved with the help of the puts function. Puts is an inbuilt function that writes a line of output to the screen. It returns the number of characters written to the console plus one as it prints a new line along with the output text, thereby moving the cursor to the new line. Its return type is int. If the execution is successful, the non-negative value is returned. If the execution has an error, EOF is returned.
Syntax:
The syntax of the puts function is as follows
int puts(const char *str)The parameter string is the text that should be printed on the console.
Example of puts
Below the given codes and outputs explain the example in puts:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void main () {
char op1[30];
char op2[45];
strcpy(op1, "this is first line of puts example");
strcpy(op2, "this is second line of puts example");
puts(op1);
puts(op2);
}Output:

gets Function in C
The built-in gets function reads characters from the console and stores them in a string. It reads characters until it finds a new line or reaches EOF, whichever occurs first.
Syntax:
char *gets(char *str)str is the pointer in which the character read is stored.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main ()
{
char test[30];
printf("Enter your name");
gets(test);
printf("You entered %s",test);
printf("\n the above is an example of gets function");
}Output:

Example of puts and gets
Below the given codes and outputs explain the example in puts and gets:
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
char name[50];
printf("Enter your name ");
gets(name);
int age[50];
printf("Enter your age ");
gets(age);
char address[50];
printf("Enter your address ");
gets(address);
int pincode[50];
printf("Enter your pincode ");
gets(pincode);
printf("Entered Name is: ");
puts(name);
printf("Entered age is: ");
puts(age);
printf("Entered address is: ");
puts(address);
printf("Entered pincode is: ");
puts(pincode);
getch();
return 0;
}Output:

Functions in puts and gets
The following points explain the function sin puts and gets with examples:
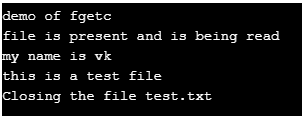
1. Fgetc()
This is an inbuilt file-handling function that reads a file. It reads the file a single character at a time until the end of the file. The function returns a non-negative value for successful execution.
Syntax:
Int fgetc(FILE *fp)The fp is the pointer to the file location.
Code:
# include <stdio.h>
int main( )
{
FILE *testfile ;
char c ;
printf( "demo of fgetc" ) ;
testfile = fopen ( "c:\test.txt", "r" ) ;
if ( testfile == NULL )
{
printf ( "\nCould not open file test.txt" ) ;
return 1;
}
printf( "file is present and is being read" ) ;
while ( 1 )
{
c = fgetc ( testfile ) ;
if ( c == EOF )
break ;
printf ( "%c", c ) ;
}
printf("Closing the file test.txt") ;
fclose ( testfile ) ;
return 0;
}Output:
2. Fputc()
This is an inbuilt file-handling function that writes text to a file. It writes one character at a time. The function returns a non-negative value for successful execution.
Syntax:
int fputc(int char, FILE *fp)Where char is the character to be written, and fp is the location of the file.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ch;
FILE *source;
FILE *destination;
if (source = fopen("c:\source.txt", "r"))
{
ch = getc(source);
destination = fopen("c:\dest.txt", "w+")
while (ch != EOF)
{
fputc(ch, destination);
ch = getc(source);
}
fclose(source);
fclose(destination);
return 0;
}
return 1;
}Output:

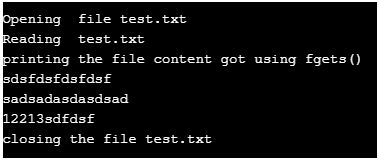
3. Fgets()
This function is similar to fgetc() except that this reads a file line by line.
Syntax:
char *fgets(char *string, int n, FILE *fp)- fp is the location from which the text must be read
- *string is the location in which the read characters are stored
Code:
# include <stdio.h>
int main( )
{
FILE *sourcefile ;
char newdata[50] ;
printf( "Opening file test.txt " ) ;
sourcefile = fopen( "c:\test.c", "r" ) ;
if ( sourcefile== NULL )
{
printf( "Could not open file test.txt" ) ;
return 1;
}
printf( "Reading test.txt" ) ;
while( fgets ( newdata, 50, sourcefile ) != NULL )
printf("\nprinting the file content got using fgets()")
printf( "%s" , newdata ) ;
printf("Closing the file test.txt") ;
fclose(sourcefile) ;
return 0;
}Output:
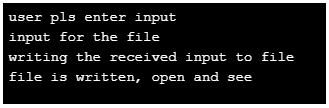
4. Fputs()
This function is similar to fputc() except that this writes to a file line by line.
Syntax:
int fputs(const char *str, FILE *stream)- *stream file to which the string must be written
- Str is the string that is to be written
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main()
{
char input[50];
printf("\n user pls enter input");
scanf("%s",input);
FILE *destfile;
destfile = fopen("D:\test.txt", "w");
if(destfile == NULL)
{
printf("Error opening file\n");
exit(1);
}
printf("\n writing the received input to file");
while( gets(input) != NULL )
{
fputs(input, destfile);
}
printf("\n file is written, open and see");
fclose(destfile);
return 0;
}Output:

Difference Between
- puts() and fputs(): We use puts() to write text to the console, while fputs() serves to write text to a file. Puts() will convert a null character in the input to a new line, whereas fputs() will not handle the null character and stops execution.
- gets() and fgets(): Gets reads the input from the console or stdin, whereas fgets reads the input from a file. Fgets are safe to use in case of overflowing; it will throw an error. Fgets halts when it encounters a new line. Fgets doesn’t check for an out-of-bound exception. It reads until it encounters a new line.
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char author[20];
printf("Enter your favorite author\n");
fgets(author,10,stdin);
printf("My favorite author is %s.\n",author);
FILE *destfile;
destfile = fopen("D:\existing.txt", "w+");
fputs("first line to be entered", destfile);
fputs("second line to be added", destfile);
fputs("thirdine to be added", destfile);
fclose(destfile);
return(0);
}Output:

Conclusion – C puts() Function
Thus, the article covered in detail about puts functions along with their syntax and sample examples. It also covered functions similar to it in detail, such as fputc() and fputs(). We also discuss functions like gets(), fgets(), and fgetc() using suitable examples. We also explain the differences between functions. To learn in-depth about the functions, creating sample programs and having fun working around them is advisable.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C puts() function. Here we discuss puts functions along with their syntax and sample examples and function about fputc() and fputs(). You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


