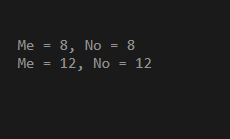Updated June 15, 2023
Introduction to C++ Union
Union is a datatype defined by the user, and all the different members of the union have the same memory location. The member of the union, which occupies the largest memory, decides the union’s size. Users mostly use the union when they want to utilize a single memory location for multiple members. Unions are very much similar to the structures. It is defined in the same way as the structures are done. We need to use the word “union” in C++ to define Unions. This article explains the concept of Union in C++. The examples below will help you understand and use the concept according to the requirements.
Syntax:
The syntax of using Union in C++ language is written below:
union <Name of the union> {
Define the members;
} variable names ;Explanation:
- Name of the union – One can use any name as the union’s name. After writing the union, name the union according to the requirement.
- Define the members − Here, the coder has to define the member variables.
- Union objects − Here, the coder can write the objects of the union.
Working of Union in C++
Coders use unions to utilize the same memory for multiple members. For example, if we have to create a binary tree data structure where every leaf node will have a double data value and every internal node will have two pointers, there are no data along with them. If we create structures to implement this, every node will need 16 bytes, where half will be wasted for each node. If we declare all nodes using Union, we can save a lot of space. This is how we can use Union to save space instead of structure. This is the main reason that although Unions are very similar to Structures, Union has a good advantage.
Examples of C++ Union
Lets us discuss examples of C++ Union:
1. Defining a Union in C++
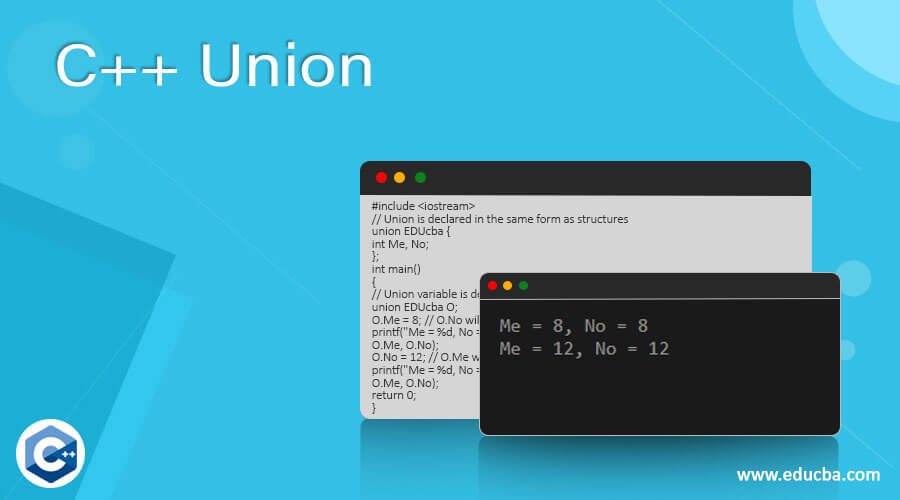
This is a basic example of defining a union in C++. Here we have defined the union with the union name “EDUcba,” which has two members, “Me” and “No,” respectively. It shows how we can set the value of “O.Me” and “O.No”, and it changes the value of “Me” and “No,” respectively.
Code:
#include <iostream>
// Union is declared in the same form as structures
union EDUcba {
int Me, No;
};
int main()
{
// Union variable is defined as O
union EDUcba O;
O.Me = 8; // O.No will also get value as 8
printf("Me = %d, No = %d\n",
O.Me, O.No);
O.No = 12; // O.Me will also be updated to 12
printf("Me = %d, No = %d\n",
O.Me, O.No);
return 0;
}Output:
2. Size of Union
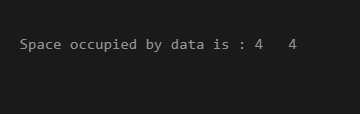
This is an example that outputs the size of the Union. Here a Union is defined with the Union name as “ EDUcba” with members as “M” & “N” and the objects as “Course1” & “Course2”. This program prints the size of the objects.
Code:
#include <iostream>
union EDUcba {
int M;
float N;
} Course1, Course2;
int main( ) {
printf( "Space occupied by data is : %d\t%d", sizeof(Course1), sizeof(Course2));
return 0;
}Output:
3. Deciding on the Size of the Union by the Compiler
This example explains how the compiler assigns the memory spaces to different unions. In a Union, space is decided by the largest member. Here we have defined three unions that have different members respectively. Ultimately, this program prints the spaces allocated to the different unions.
Code:
#include <iostream>
union educba {
int M;
int N;
} EDUCBA;
union training {
int M;
char N;
} TRAINING;
union technology {
int ray[10];
char N;
} TECHNOLOGY;
int main()
{
printf("EDUCBA = \n%lu\n"
"TRAINING = \n%lu\n"
"TECHNOLOGY = \n%lu\n",
sizeof(EDUCBA) ,
sizeof(TRAINING), sizeof(TECHNOLOGY));
return 0;
}Output:
4. Pointers to Unions
This example shows us the way to assign a pointer to a union. Here we have created a union named “ EDUCBA”. There is a pointer created to the union “EDUCBA”.
Code:
#include <iostream>
union EDUCBA {
int M;
char N;
};
int main()
{
union EDUCBA A;
A.M = 89;
// B is a pointer to union A
union EDUCBA* B = &A;
// With the help of pointer union members are accessed
printf("%d %c", B->M, B->N);
return 0;
}Output:
5. Declaration of the Union
This example explains how to define a Union where the members are defined using the scope resolution operator.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdint>
union EDUCBA
{
std::int32_t X; // it will occupy 4 bytes
std::uint16_t M[2]; // it will occupy 4 bytes
std::uint8_t A; // it will occupy 1 byte
}; // & whole union will occpy 4 bytes
int main()
{
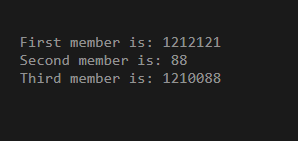
EDUCBA M = {0x1212121}; // first member is intitalized
std::cout << std::hex << "First member is: " << M.X << '\n';
M.M[0] = 0x0088; // M.M is initialised
std::cout << "Second member is: " << +M.A << '\n' // 88
<< "Third member is: " << M.X << '\n'; // 12340088
}Output:
6. Union Members with Classes as User-Defined Constructors & Destructors
This example explains to us how Unions are defined with classes where the unions are also used as constructors and destructors.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
union EDUCBA
{
std::string ABC;
std::vector<int> XYZ;
~EDUCBA() {}
};
int main()
{
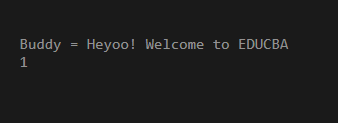
EDUCBA M = {"Heyoo! Welcome to EDUCBA"};
std::cout << "Buddy = " << M.ABC << '\n';
M.ABC.~basic_string();
new (&M.XYZ) std::vector<int>;
M.XYZ.push_back(20);
std::cout << M.XYZ.size() << '\n';
M.XYZ.~vector();
}Output:
7. Union like Classes
This example explains the concept of Union in classes.
Code:
#include <iostream>
struct EDUCBA
{
enum{DS, DA, DE} tag;
union
{
char M;
int N;
double O;
};
};
void display(const EDUCBA& P)
{
switch(P.tag)
{
case EDUCBA::DS: std::cout << P.M << '\n'; break;
case EDUCBA::DA: std::cout << P.N << '\n'; break;
case EDUCBA::DE: std::cout << P.O << '\n'; break;
}
}
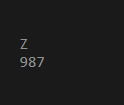
int main()
{
EDUCBA P = {EDUCBA::DS, 'Z'};
display(P);
P.tag = EDUCBA::DA;
P.N = 987;
display(P);
}Output:
Conclusion
Based on this article, we understood the concept of Union in the language C++. This article explains the advantage of using Union in C++ and the ways to use Union according to the different requirements of the program. This article will simplify the concept of Union for all the coders.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Union. Here we discuss the introduction, working of Union in C++, and examples along with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –