Updated April 13, 2023
Introduction to C++ namespace
Scope in C++ is a mechanism to create groups of like classes, objects, or functions together out of the global scope. Using this mechanism naming the variables has become easier as a variable with the same name can be declared in 2 different namespaces without giving any compile-time error. Hence namespace refers to different blocks that can be created in a program to group all like objects and all variables, functions, or classes inside a block can be referred to using namespace_name:: function_name. This way many functions can have the same name and all can be accessed from anywhere in the program by referring to its namespace name. In this topic, we are going to learn about C++ namespace.
Syntax
The namespace is a declarative region to define various scopes for various functions and variables, thus when one needs to refer to one such function of the variable we can use namespace name.
Syntax:
namespace myFirstNamespace{
//declare all functions and variables
}Example:
namespace myNamespace{
int var=10;
}Accessing variable in a specific namespace, a scope resolution ( :: )operator is used.
Syntax:
namespace_name :: variable_name
Namespace_name :: function_nameExample:
myFirstNamespace :: varHow does the namespace works C++?
The namespace is a special feature added in C++ but not present in C. It provides a scope to some variables or functions and organizes them into different logical scopes that can be referred to using their names. The namespace is declared in global scopes and can easily be nested in other namespaces. Thus no access specifiers are needed to specify in the namespace.
When a namespace is declared namespace keyword is declared before that. And then all the functions, variables, or classes declared inside that namespace belongs to that block and can be referred to only using the name of that namespace using (:: ) scope resolution operator.
When the compiler encounters a:: operator it sends the control to that namespace block. A namespace can be defined in multiple blocks also.
In case a namespace is unnamed then the variables and functions defined inside them can be accessed directly the same as accessing global variables.
Namespaces can be nested also in other namespaces. To access them we need to use:: operator that number of times.
For eg:
namespace ns1{
namespace ns2{
namespace ns3{
int myvar=10;
}
}
}To access myvar one need to use ns1::ns2::ns3::myvar.
This way namespaces allow us to make different scopes and reuse the same variable names in our application present in different namespaces. Using namespace helps a lot to manage the files present in different libraries.
Examples of C++ namespace
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1
In the below example we will see how to define the same function name in two different namespaces first and second. Also, we will see how to define a class in a namespace and access it.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace first
{
int oper(){
return 10;
}
}
namespace second
{
const double i = 100;
double oper() { return 2*i; }
}
namespace third
{
class example
{
public:
void show()
{
cout << "thrid::example::show()\n";
}
};
}
int main()
{
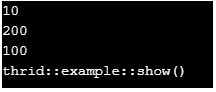
cout << first::oper()<< '\n';
cout << second::oper() << '\n';
cout << second::i << '\n';
third::example myObj;
myObj.show();
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
In the below example we will see how we can define multiple namespaces with the same name. Thus the variables inside all of them in the same scope. Also, we can see how to define unnamed namespaces.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace myNs
{
int var1=10;
}
namespace myNs
{
int var2=20;
}
namespace {
int i=15;
int myVar(){
return i;
}
}
int main()
{
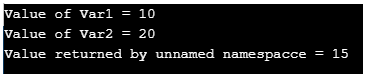
cout << "Value of Var1 = "<<myNs::var1<< '\n';
cout <<"Value of Var2 = "<< myNs::var2<< '\n';
cout <<"Value returned by unnamed namespacce = "<<myVar()<< '\n';
return 0;
}Output:
Example #3
In the below example we will see how nested namespaces can be declared and accessed from outside the namespace. Also how we access a variable in the namespace without:: operator and using “using” directive.
We will also see how we can create an alias for a namespace that helps to directly use it using an alias name.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace first
{
int myvar = 5;
namespace second
{
namespace third
{
int myvar1=myvar;
}
}
}
namespace myalias = first::second::third;
namespace demo
{
int gvar = 300;
}
using namespace demo;
int main()
{
cout << "Value of global variable in demo namespace = "<<gvar << "\n";
cout << "Value of myvar1 in nested namespace third = "<<myalias::myvar1 << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
Advantages
Namespace helps a lot to define various scopes in one program to provide scope to various identifiers declared inside them.
- Using the same variable names – With the help of declaring namespaces, the same variable names can be reused in a single program.
- Use libraries:- Namespaces and named spaces helps a lot to use all libraries together and helps distinguish different which variable we are trying access by specifying the name using:: operator.
- Code Readability- This also enhances the readability of the code by specifying the similar code in different files and different libraries.
Conclusion
Namespace in C+ is referred to as the blocks one case used to group like classes, functions, and variables. It helps to create more than one variable with the same name in different namespaces, each of which can be referred to using scope resolution operator(::).
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ namespace. Here we discuss how does the namespace works C++ along with the advantages and programming examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –