Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to C++ Literals
The value which is assigned to the constant variable is called literals. The constant value can be named differently as literal. For example, “const int value= 15” assigns a constant integer value 15 to a value, which is an integer literal. In this article, we will explain each of the different types of literals in C++ along with its example.
Types of C++ Literals
Five different types of literals can be used in C++, as mentioned below:
- Integer Literal: It is used to represent an integer constant.
- Float Literal: It is used to represent float constant.
- Character Literal: It is used to represent a single character.
- String Literal: It represents the character sequence(string).
- Boolean Literal: It represents Boolean(true or false).
Each of the above-mentioned different types of literals is explained below, along with its example code:
1. Integer Literals
Integer literals in C++ represent integer constant values. You can represent integer literals in two primary ways: by adding a prefix or a suffix.
Prefix
The prefix in an integer literal indicates the base used to represent the integer value.
1. Decimal-literal in base 10: This represents value in decimal (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9) digits. The value must start with a non-zero decimal digit.
Code:
// For representing decimal integer literal in base 10
const int value= 95;
const int value= 76;
const int value= 7;2. Binary-literal in base 2: This represents value in binary (0,1) digits. The value must start with a prefix of 0b or 0B.
Code:
// For representing binary integer literal in base 2
const int value= 0b101;
const int value= 0B001;
const int value= 0B1111;3. Octal literal in base 8: This represents value in octal (0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7) digits. The value must start with a prefix of 0.
Code:
// For representing octal integer literal in base 8
const int value= 0356;
const int value= 0732;
const int value= 0137;4. Hex-literal in base 16: This represents value in hex (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, a, A, b, B, c, C, d, D, e, E, f, F) digits. The value must start with a prefix of 0x or 0X.
Code:
// For representing hex integer literal in base 16
const int value= 0xA3;
const int value= 0X38C;
const int value= 0XFFFF;Suffix
The suffix represents the type in which the integer literal is stored.
| Suffix | Type |
| u or U | unsigned int |
| l or L | long int |
| ul or UL | unsigned long int |
| ll or LL | long long int |
| ull or ULL | unsigned long long int |
| No suffix | int |
Code:
// include required header files
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// Body of main()
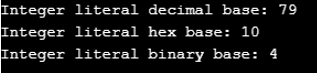
const int val_decimal = 79; // assigning decimal integer
const int val_hex = 0xA; // assigning hex integer literal
const int val_binary = 0b100; // assigning binary integer literal
std::cout << "Integer literal decimal base: "<< val_decimal << "\n";
std::cout << "Integer literal hex base: "<< val_hex << "\n";
std::cout << "Integer literal binary base: "<< val_binary << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
2. Float Literals
Float literals are used to represent real numbers. There are mainly two ways to represent float literals. You can store the data in either decimal or exponential format.
- You use decimal points and exponent parts in decimal format to represent float literals.
- Both integer and fractional parts represent float literals in exponential format.
Syntax:
// For representing float literals using decimal format and exponential format
const float float_leteral1 = 34.876
const float float_leteral1 = 34876E-3Code:
// include required header files
#include <iostream>
int main()
{ // Body of main()
// float literal
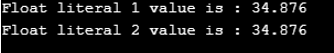
const float float_leteral1 = 34.876;
const float float_leteral2 = 34876E-3;
// both float_leteral1 and float_leteral2 are same only representation is different
std::cout << "Float literal 1 value is : "<< float_leteral1 << "\n";
std::cout << "Float literal 2 value is : "<< float_leteral2 << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
3. Character Literals
You can store single characters using character literals. Use single quotes to represent a single character. wchar_t represents a wide-character literal, as mentioned in the example below. Use the letter L to assign a wide-character value to a single character.
Syntax:
// For representing character literal
const char character_literal = 'A';
//For representing wide character literal
const wchar_t character_literal = L'A';Code:
// include required header files
#include "iostream"
int main()
{
// Body of main()
// character literal
const char char_literal = 'H'; //’H’ is assigned to char_literal
std::cout << "Character literal value is : "<< char_literal << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
4. String Literals
String literals are used to represent string (sequence of characters). To represent a string, use double quotes.
Syntax:
// For representing string literal
const char string_literal[] = "mystring";Code:
// include required header files
#include "iostream"
int main()
{
// Body of main()
// string literal
const char string_literal[] = "mystring"; //”mystring” is assigned to string_literal
std::cout << "String literal value is : "<< string_literal << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
5. Boolean Literals
Boolean literal represents Boolean constant value. This literal type can take only two Boolean values(true/false).
Syntax:
// For representing boolean literal
const bool bool_literal1 = true;
Const bool bool_literal2 = false;Code:
// include required header files
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// Body of main()
// assigning Boolean values to Boolean literals bool_literal1 and bool_literal2
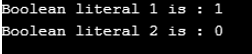
const bool bool_literal1 = true; // assigning true to Boolean literal bool_literal1
const bool bool_literal2 = false; // assigning fasle to Boolean literal bool_literal2
cout << "Boolean literal 1 is : "<< bool_literal1 << "\n";
cout << "Boolean literal 2 is : "<< bool_literal2 << "\n";
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
This tutorial will explain various types of C++ literals with example code. This tutorial will be helpful while working with literals in C++.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Literals. Here we discuss five different types of literals in C++, along with examples and appropriate syntax. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


