Updated June 8, 2023

Definition of C++ Lambda Expressions
Lambda Expressions in C++ is mostly supported by C11 and above versions whose primary goal is to provide users with the ability to implement inline functions that may not be require for any reusability purpose later. Lambda expressions are special types of expression that may not require any external specification and explanation and the return type for that specific inline function is not required for complex cases of conditional statements. Any requirement which is very complex does not require Lambda expression but still is considered an added advantage in terms of easy computational statements required at compilation time.
Syntax:
[ inline_define_clause/empty_clause ] (arguments/parameters) ->return_type
{
method_defination
}The syntax flow is in a way where the inline_define_clause will take care of the clause followed by the argument or parameter that will provide the values to the defined clause followed by return type for the defined method with a set of arguments. Sometimes the return type can be ignored, whereas the arguments or parameters gets evaluated at the time of compilation.
How do Lambda Expressions work in C++?
Lambda Expressions are special expressions in C++ that got introduced in the versions of the compiler after C11 and its above series. There are certain good and attractive features related to lambda Expressions working, which is like:
- It is a very convenient way to make some functions as global and can be used in terms of small functions instead of complex functions.
- It makes use of the inline function, which gives the user the ability to customize its parameter directly at the time of compilation and then it helps in making the functionality to use simple and easy to use.
- The arguments defined will act as local, which means that the scope will act as local to the entire global members, and then it will capture those variables which will be used later point in time for some evaluations.
Let’s check the working flow of Lambda Expressions in C++, which are as follows :
- Lambda expression will start itself by defining the inline_define_clause where the condition or the constraint will be provided, followed by the list of parameters or arguments.
- This set of lambda expressions comprises of arguments that will capture all the values and then it will get evaluated by the compiler for all the values followed by return type.
- The return type is optional in terms of Lambda Expression in C++ as it will not make much adverse effect on the inline method declaration with the set of the code snippet.
- Whenever there will be some complex definition with a lot of expression evaluation and external declaration of the method, then it will have the values.
- The inline function defined with the method once declared cannot be changed or used for any re-usability purpose.
- The scope of the requirement for making usage of C++ lambda expression must be local and small with less complex modules.
- Any lambda expression has a lot of power, and it can be transformed in any way as compared to any ordinary function by accessing the variables accordingly.
- There are three ways of capturing the parameters or the arguments within the function, which are:
-
- Capturing the values by reference
- Capturing the values by the actual value
- Capturing the values by mixing both reference and actual value.
- For each of the ways of capturing the parameters and arguments for manipulation involves following symbols for representation:
-
- [&] – a symbol used for capturing the value by reference
- [=] – symbol used for capturing the value by the actual value
- [a, &b] – symbol used for capturing the value by mixing both reference and actual value.
- There can also be a case where the inline_define_clause section might be empty, then, in that case, the clause section[] will be able to access only those variables or values which comes out to be local.
Thus If a proper insight is taken towards the C++ lambda Expression, then a proper fact can be considered, as the scope for entire global and local functions get used in the proper sense, which gives flexibility to the user in terms of implementation and these inline functions can be called with ease anytime.
Examples of C++ Lambda Expressions
Following are the examples of c++ lambda expressions are given below:
Example #1
This program demonstrates the inline lambda expression where the method defined within the function is used for performing the operation and getting the value as shown in the output.
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
intmain() {
vector<int>m_vect;
m_vect.push_back(2);
m_vect.push_back(3);
m_vect.push_back(4);
for_each(m_vect.begin(), m_vect.end(), [](int o) {
cout<<o+o*o*o <<endl;
});
}Output:
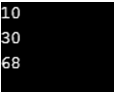
Example #2
This program demonstrates the empty clause [vct_1]() as function which is used as a lambda expression for manipulating the values and then performing the lambda expression operation with various conditions as shown in the output.
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
intmain()
{
vector<int> vct_1 = {2, 8, 3, 6};
vector<int> vct_2 = {15, 12, 8, 10, 7};
auto pushinto = [&] (intjl)
{
vct_1.push_back(jl);
vct_2.push_back(jl);
};
pushinto(20);
[vct_1]()
{
for (auto jl = vct_1.begin(); jl != vct_1.end(); jl++)
{
cout<< *jl<< " ";
}
};
int no = 8;
vector<int>:: iterator jl = find_if(vct_1.begin(), vct_1.end(), [no](int o)
{
return o> no;
});
cout<< "No_larger_from_6 : " << *jl<<endl;
intcount_no = count_if(vct_1.begin(), vct_1.end(), [=](int o)
{
return (o >= no);
});
cout<< "number_larger_than_six_and_equal_as_well : "
<<count_no<<endl;
}Output:
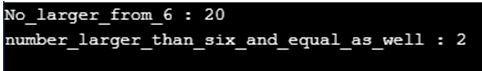
Advantages
- The most added advantage of using lambda expression is that it provides the flexibility and ease to users for making function calls frequent and easy.
- The re-usability function doesn’t make use because of which the complexity and other feature gets enhanced.
Conclusion
Lambda expressions are the special type of expressions that are being introduced for compilers of version c11 and above. It has provided a lot of versatility and simplicity to the programmers in terms of implementation as It gives the user to define any function within the scope easily.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Lambda Expressions. Here we also discuss how do lambda expressions work in c++ along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


