Updated March 31, 2023

Introduction to C++ Identifiers
Identifiers refer to a unique combination of letters and digits, either short or descriptive, that are used to identify a variable, method, class or any other object in a programming language uniquely. The identifiers in C++ can have identifiers with any length of characters. These characters can be alphanumeric i.e can contain letters, digits and underscores and whitespaces and special characters such as @,#,!etc are not allowed. These identifiers must start with a letter or an underscore and are case sensitive thus keywords must not be used as an identifier.
Explain all C++ Identifiers
Identifiers are used to represent various objects such as:-
- 1.Constants
- 2.Variables
- 3.Functions
- 4.Labels
- 5.Defined Data Types
Rules for Declaring an Identifier
Let us understand some rules to declare them otherwise the compiler will throw an error.
- Rule 1: It can be a combination of letters, digits or underscore, no special characters such as #,$,! @ are allowed in identifiers name.
- Rule 2: The first character can be either letter or underscores(_). This means if we use digit as the first character in the name of an identifier such as 1num, it will not be treated as a valid name thus an error will be thrown by the compiler.
- Rule 3: These are case sensitive, which means NUM1 and num1 are not the same identifiers.
- Rule 4: A keyword cannot be used as an identifier. C++ library has a list of keywords used for different purposes such as if, else, long, int, float, goto, etc. These variables cannot be used as an identifier name because there is a reserved meaning for this word defined in the C++ library.
How do C++ Identifiers work?
Let us understand how identifiers can be used in
1. Constants
A constant are the variables whose values cannot be changed in the program execution. These can be declared either using # or const keyword.
Examples of Constants
Valid Identifiers Examples for Constants
- const int _sum
- const float Test1
- const int numberOfVehicles
- #define num 10
Invalid Identifiers Examples
- const float 2data1
- const char name-1
- const int else
Let us understand it through the below example where we have declared constants using #define. Here 1My-Char has been commented because the identifier name cannot contain ‘-‘ and must start with a letter or (_).
Code:
#include <iostream>
#define NUM1 10
#define NUM2 5
#define MyChar1 'E'
#define MyChar2 'N'
#define MyChar3 'D'
//#define 1My-Char
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int mul;
mul = NUM1 * NUM2;
cout<<mul;
cout<< '\n';
cout<< MyChar1;
cout<< MyChar2;
cout<< MyChar3;
return 0;
}Output:

2. Variables
These are names used to hold the value that is meant to be changed during the program execution. The syntax for declaring a variable is
Syntax:
data_typevariable_name1 =value1Validvariable Identifier
- int num1 =30
- float val2 = 40
- char name = ‘A’
Invalid Identifier
- int 1num =30
- char my-Var =’R’
In the below example, we have declared mul, my_Charvariable identifiers that follow the rules for identifiers.
Code
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int mul;
char my_Char='A';
int i=0;
for(i=0;i<3;i++){
cout<<"IN LOOP"<<'\t'<<my_Char<<'\n';
my_Char='T';
}
return 0;
}Output:
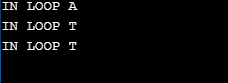
3. Functions
This refers to a group of statements that is meant to perform one independent task and must be given a name with which it can be identified. Here identifier is being used.
Valid function identifiers
int myFun1(){
//group of statments
}Invalid identifier
int my-Fun1(){
// - is not allowed in identifier’s name
}Let us understand the example to see the identifier used as a function name.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int sum4(int a,int b){
return a*b;
}
int main()
{
int res;
res=sum4(5,6);
cout<<res;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
4. Label
These are used to mark one line in the program to be used along with the goto keyword to directly pass the control of program execution to that statement.
Valid identifier names-
- myLabel:
- m2344:
Invalid inentifier names –
- my-Label:
- const:
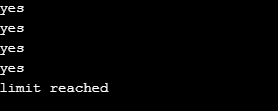
Below is an example of using the label identifier.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<6;i++){
if(i==4){
goto label1;
}
else cout<<"yes"<<'\n';
}
label1: cout<<"limit reached";
}Output:
5. User-defined DataTypes
These are data types defined by the user to store the value of different data types together. There are 3 user-defined data typer allowed in C++:-
- Struct
- Enum
- Union
The names for these data types are given using identifiers.
Valid identifiers
structStudent
{
introll_name;
int marks ;
}Invalid identifier
Struct Student-1{
int 3roll_name;
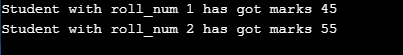
}Below is an example to use the identifier as user data defined data types.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
int roll_num, marks;
};
int main()
{
int i;
struct Student s1 = {1,45};
struct Student s2 = {2,55};
cout<<"Student with roll_num "<<s1.roll_num <<" has got marks "<<s1.marks;
cout<<'\n';
cout<<"Student with roll_num "<<s2.roll_num <<" has got marks "<<s2.marks;
return 0;
}Output:
Let us see one example in case we use an identifier that does not follow the above rules:-
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{
int rollnum, 1marks;
};
int main()
{
int i;
}Output:

Conclusion
The identifier is a combination of digits and letters and underscores(_)such that it starts with a letter or underscore that can be used as variable, constant, function names or user datatype variables. All identifiers must follow some of the rules otherwise will not be recognized by the compiler and error will be thrown and must not be one of the keywords defined keywords in C++ libraries.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Identifiers. Here we discuss how the 5 C++ Identifiers work in detail with rules to use and examples to implement with codes and outputs. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


