Updated April 6, 2023

Introduction to C ftell()
The C ftell() function is used to return the current position of the specified file stream. The ftell() function is a built-in function in c. Some times in program while we reading or writing the data from or to the file we need to get the current position of the file to read data from a specific location or to write the data to a specific location, so to get the current location of the file pointer we can use ftell() function and the later to change or move the pointer location we can use the fseek() function(), which is also a built-in function. The ftell() function accepts file pointer which points to the specific file, so this function returns the current position of that specific file and this function also can be used to return the size of the file by moving the pointer to the end of the file with the help of SEEK_END constant value.
The Syntax of the ftell() function in C
Following is the syntax to call the ftell() function in c –
long int ftell(FILE *fstream);Parameters –
*fstream – *fstream parameter specifies the FILE type pointer which points to specific FILE object.
Return value –
The return value of the function as is int, it returns the current location of the file pointer pointing, otherwise returns -1L if any error occurs.
Working and Examples of ftell() function in C
Next, we write the C code to understand the ftell() function working more clearly with the following example where we use ftell() function to get the current location of the file pointed by the pointer, as below –
Example #1
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char fdata[50];
// Open f1.txt file in read mode
// fstream is the FILE type pointer which will point to the FILE object or data.txt
FILE *fstream = fopen("data.txt","r");
// get the location of pointer
printf("The current location of th pointer before reading from the file is : %ld\n", ftell(fstream));
// store the read from the file to fdata array
fscanf(fstream,"%s",fdata);
printf("The current data read from the file is : %s\n", fdata);
printf("The current location of th pointer after reading from the file is : %ld\n", ftell(fstream));
}Output:
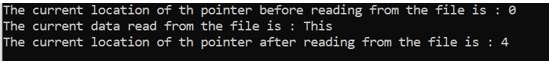
As in the above code, the file “data.txt” is opened and the fstream is a FILE type pointer which is pointing to this file, if any operation needs to perform-like read, write, append, etc, we can perform with the help of this FILE pointer(fstream). When the new file is open the file pointer always points to the starting position of the file that is 0 in the file. Farther in the code the ftell() function is used before and after reading some data from the file. So before reading the data the ftell() return the pointer location is 0, after reading data “This” which is of four lengths the ftell() return the pointer location is 4, which are correct.
Next, we write the C code to understand the ftell() function working where we use ftell() function to get the total length of the file by using the file pointer, as below –
Example #2
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
char fdata[50];
int length;
// Open f1.txt file in read mode
// fstream is the FILE type pointer which will point to the FILE object or data.txt
// data.txt file contain "This is the file data." in file.
FILE *fstream = fopen("data.txt","r");
// get the location of pointer
printf("The current location of th pointer before seek is : %ld\n", ftell(fstream));
// fseek() function move the file pointer
fseek(fstream, 0, SEEK_END);
length = ftell(fstream);
printf("The total length the file is : %ld\n", length);
printf("The current location of th pointer after seek is : %ld\n", ftell(fstream));
}Output:
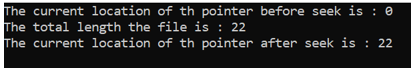
As in the above code, the file “data.txt” is open which stores the data “This is the file data.” of length 22 and the fstream is a FILE type pointer which is pointing to this file. Farther in the code the fseek() function is used to move the pointer to the end of the file with the help of SEEK_END constant value and then after moved with the help of ftell() function return the pointer location which is 22 that is the last location or index pointing by the point and that is what the length of the file.
Next, we write the C code to understand the ftell() function working where we use ftell() function to get the location of the file which does not exist or cannot open by using the file pointer, as below –
Example #3
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int i;
// Open f1.txt file in read mode
// data1.txt file does not exits.
FILE *fstream = fopen( "data1.txt","r" );
i = ftell(fstream);
if(i == -1L)
{
printf( "A file error has occurred!!\n" );
}
// get the location of pointer
printf( "The current location of the pointer is : %ld\n", ftell(fstream) );
}Output:
![]()
As in the above code, the file “data1.txt” is trying to open but that file does not exist. The fstream FILE type pointer is trying to point to this file as the file does not exist the fopen() function return 0 and so the ftell(fstream) function return -1L, as because the error occurs to open the file.
Conclusion
The ftell() function is a built-in function in C, which is used to return the current position of the file stream. The ftell() function accepts one parameter of File type pointer which points to the file.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C ftell(). Here we discuss an introduction to ftell() with the working of this function and respective examples for better understanding. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


