Business Economics Meaning
Business economics is a discipline of applied economics that examines organizations’ issues and paves a path for effective decisions.
For example, Mary owns a winery on the outskirts of a country. Recently, her sales dropped due to the opening of several wineries in the city. To cope, she starts selling her wines online at a low cost. This strategy helped her business grow and generate more revenue. This shows how business economics can boost a business’s revenue.
It assesses factors like budget, availability of resources, and inflation to help companies build effective business strategies. It helps businesses bridge the gap between infinite ambition and limited resources.
Key Highlights
- Business economics uses economic theories to help entrepreneurs make better business decisions.
- It helps analyze businesses’ financial, economic, and market-related challenges.
- Its goal is to improve strategies, make future predictions, form business policies, and increase profitability.
- It also helps in demand and cost analysis, inventory management, and pricing.
Real-Life Examples of Business Economics
Example #1
Uber initially used a business model that helped the riders connect with drivers. Uber permanently connected drivers with the car fleet owners and employed drivers for better reach. Thus, they could fulfill all rider demands without relying on drivers’ availability.
Uber did a cost-benefit analysis and maximized its workforce to meet the rising demand for rides. This change resulted from deep market analysis indicating an increase in supply.
Example #2
SABIC, or Saudi Basic Industries Corporation, is the leading chemical manufacturer in Saudi that is ready to find its feet in China. SABIC invests in technology and innovation development in China as its key strategy.
The company will also invest in renewable energy sources in China, making it an effective foreign investment. Also, in return, the Saudis demand exporting machinery like textiles and machinery.
More Examples
Example #1
Company A has developed a new product that uses aluminum as a raw material. Due to the Covid-19 pandemic, the aluminum supply has been dramatically reduced. The company analyzes different resources used by competitors and finds a replacement.
They do further research and find available materials. They innovate and use that raw material for their products and can thrive.
Example #2
Company B has learned that its products are costlier than its competitors and are losing customers.
They analyze their supply chain, production processes, and raw materials to reduce manufacturing costs. This helps them lower their pricing and regain their lost customers.
Objective
#1 Business Objectives
- Companies can have many different objectives, and the most essential objective is profit maximization.
- Some firms can have goals like customer acquisition, lowering costs, and maximizing efficiency. It helps companies optimize these goals.
#2 Macroeconomic Environment
- A firm is a micro entity that functions in a larger environment where the principles of macroeconomics govern the environment.
- It is essential to have abundant knowledge of the firm’s environment. Therefore, a business must make decisions based on macroeconomic factors like government policies, taxes, demand, supply, etc.
#3 Competitive Advantage
- The principles of business economics help entrepreneurs know the strategies of their competitors.
- They can use this understanding to make appropriate decisions and gain a competitive advantage.
#4 Market Structure
- It is essential to understand the market structure in which a business operates. The market can be a monopoly, an oligopoly, or have perfect competition.
- Different structures have a different influence on the firm’s working and its dependence on other businesses.
#5 Planning and Control
- Business economics helps in planning strategies, quality control, cost control, auditing, etc.
- Better planning and control can help get better yet effective results.
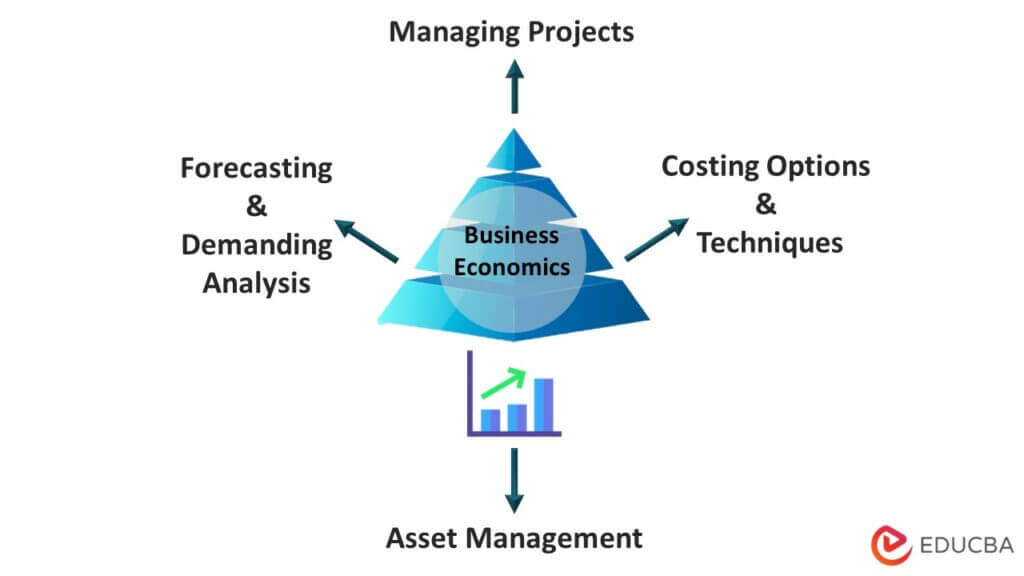
Scope
#1 Forecasting and Demand Analysis
- This assists in guiding the company in setting up production schedules and utilizing resources.
- Identifying numerous elements influencing the demand for the goods also helps to increase revenue and market position.
#2 Costing Options and Techniques
- Since the accuracy of costing decisions is a key component of the company’s success, valuation is the foundation of its profitability.
- In addition, the crucial elements include pricing strategies, price finding in various market contexts, etc.
#3 Managing Profits
- As uncertainty reduction helps the company generate more revenues, the manager must develop an accurate analysis of the company’s potential gains and pricing at various output levels.
- The ideas of profit calculation and profit planning can be quite challenging when understanding the necessity of business economics.
#4 Asset Management
- Due to the significant financial involvement, it implies supervision and drafting of capital costs.
- The company must appropriately manage both current assets and current liabilities.
Types of Business Economics
#1 Managerial Economics
- Managerial economics applies the principles of economics to managerial decisions. It examines the management’s challenges and suggests solutions to further the company’s objectives.
- It focuses on microeconomic factors that arise within an organization. Managerial economics uses these factors to guide corporate strategy and reach the desired business goals.
- Its main goal is to maximize utility and minimize waste.
#2 Business Economics for Non-Profit Organizations
- A non-profit organization (NPO) is a business driven by a cause other than profit.
- Although their goals differ from other organizations, they essentially follow the same economic principles. These organizations also need to improve their output while lowering costs and waste.
- NPOs use economics to improve their strategies and become viable businesses. It also helps them maintain the capital required to run the organization smoothly.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Business Economics
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| The principles of business economics can help businesses strategize and improve their decision-making. | It can sometimes restrict the company’s decision-making, reducing innovation and creativity. |
| It aids the business in gaining a competitive advantage over rival firms. | Competition can be a disadvantage as well. A saturated market will leave no room for new businesses to thrive. |
| It can be used for future predictions. Demand analysis and cost forecasting rely on the rules of economics. | Misreading data or inaccurate forecasting can have disastrous results and lead to financial losses. |
| By learning about it, businesses can improve their profits, maximize efficiency, and minimize waste. | Government regulations and market reforms can lead to an organization’s downfall. For example, the pandemic caused many businesses to shut down. |
| The laws of supply and demand can also drive businesses to innovate and create products that satisfy consumer demand. | The supply and demand situation may not favor the business. It might lead to unwanted decisions like cost cutting. |
| Analyzing economic trends can guide businesses to invest in promising ventures. | Certain trends that worked for the competitors may not produce results for your business. |
Final Thoughts
Business economics establishes a connection between the business and its underlying economic environment. It fills the gap between economic theory and the corporation’s business plan. It can be used in various ways for pricing, controlling, forecasting, and maximizing profit. The integral theory can help a company accomplish its goals and achieve long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is business economics?
Answer: Business economics is the application of the principles of economics to business methodologies. It involves the analysis of micro and macroeconomics to improve business strategies and decision-making. It assesses factors like budget, availability of resources, inflation, etc.
Q2. What is the importance of business economics?
Answer: Business economics is essential for establishing relations amongst economic factors like profit and loss, income, market structures, etc. This assists the executives in making profitable decisions and fueling the organization with effective ideas.
Q3. What are the 2 components of business economics?
Answer: The two main components of business economics are the effect of scarcity and supply & demand. Other factors are consumption, dissemination, and product factors.
Q4. What is the difference between economics and business economics?
Answer: Economics is the study of choice from a personal perspective to the public, whereas business economics is a strategic study where a problem faced by an organization is addressed by effective decision-making.
Recommended Articles
This article explains everything about Business Economics. To know more, visit the following articles: