Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to BETWEEN in PostgreSQL
Between in PostgreSQL used to retrieve records from a table with a specified range, it is used in select, delete, update and insert statement. We can use between conditions to retrieve records of numeric and date data type columns, numeric and date data type is most beneficial to retrieve the record from a table using between the condition in PostgreSQL. Between conditions is most important in PostgreSQL to retrieve a record of a specified range. Between conditions in PostgreSQL used with where clause fetch the data from tables with the help of two specified conditions.
Syntax
Below is the syntax between conditions in PostgreSQL as follows.
Select column1, …., columnN from table_name
Where,
Column_name (search condition) BETWEEN (Condition) value1 AND Value2Expression (Expression used to define query)
BETWEEN (condition) value1 AND Value2Select *(select all column from selected table) from table_name
Where
Column_name (search condition) BETWEEN (Condition) value1 AND Value2Select *(select all column from selected table) from table_name
Where
Column_name (search condition) NOT BETWEEN (Condition) value1 AND Value2Below is the parameter description of the above syntax as follows.
Parameter:
- Select: Select statement is used to select the column from the table to retrieve data using between conditions.
- Column 1 to column N: Number of columns selected from the table using the select statement to retrieve a record by using between conditions.
- From: Keyword used to define which table name was used to retrieve the data.
- Table name: Name of the table from which we have fetched data by using between conditions.
- Asterisk (*): Asterisk defines we have selected all columns from the table to retrieve data using between conditions in PostgreSQL.
- Between: Between is a condition in PostgreSQL used to retrieve records from tables with a specified range.
- And: And operator is used between conditions to select a range to records.
- Value1 and value2: It defines the range of records used to fetch the data between conditions from the table.
- Expression: Expression is nothing but a number of the column selected from a table using the select statement to retrieve a record by using between conditions.
- Not between: Not operator used with between operator to fetch record from table.
How BETWEEN Condition Works in PostgreSQL?
- Below is the working between conditions in PostgreSQL as follows.
- PostgreSQL between conditions is used to match the values of table rows against a range value that we have specified in a query.
- We can use the operator in PostgreSQL to match the values with the range of other values.
- We can use a low and high value in a select statement with between conditions to retrieve or fetch data from a table. Suppose the expression first value is less than the expression’s second value. In that case, the expression will return a true value, or if the expression first value is greater than the second value, the word will return false.
- We can write the between operator or condition by using the less than or equal to (<=) or greater than or equal to (>=) operator in the SQL statement.
- We can also use a not-operator using between conditions to check the value of the expression is out of range in the same situation we combine between operator with not operator in PostgreSQL.
- Use between the operator in the where clause of the following statement in PostgreSQL.
- Select
- Update
- Insert
- Delete
- We can specify the range of two values by using the AND operator in between conditions. We use the AND operator to mediate between two values to fetch data from tables.
- PostgreSQL uses the BETWEEN operator with the date and numeric values. Using a between operator, we can match date and numeric values against a range of values in PostgreSQL.
- When we use a numeric value, it will help us retrieve values from tables that lie within a specified range.
- Utilising a date value will enable us to access data from tables that fall inside a specific range.
- When we have used with no operator, the PostgreSQL operator will return the values that didn’t lie within that specified range.
- In PostgreSQL, we can utilize the BETWEEN operator with date values. It means that we specify a range of date values.
- We can use or combine not operator with between operators in PostgreSQL. In such a scenario, the table values that were not in a specified range will be returned.
- We used between the operator in PostgreSQL to select values that were in range. The range is between low to high.
- If values range between low to high in such a scenario expression will return the true condition.
- If values range between high to low in such a scenario expression will return a false condition.
Examples
- We have used the employee table to describe the example.
Example #1
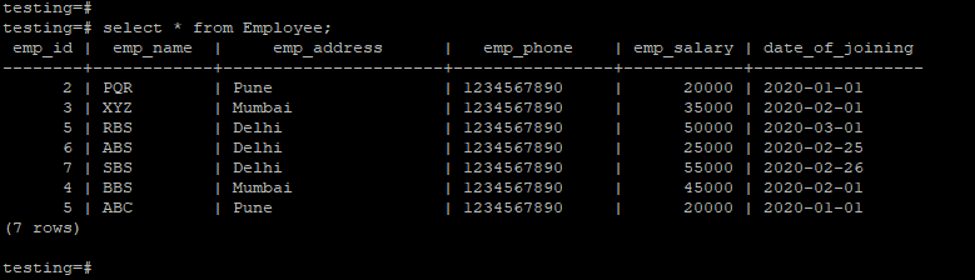
Example of employee table.
testing=# select * from Employee;Output:
Example #2 – Between Operator Using Numeric Values
- Below is an example of between operators using numeric values as follows.
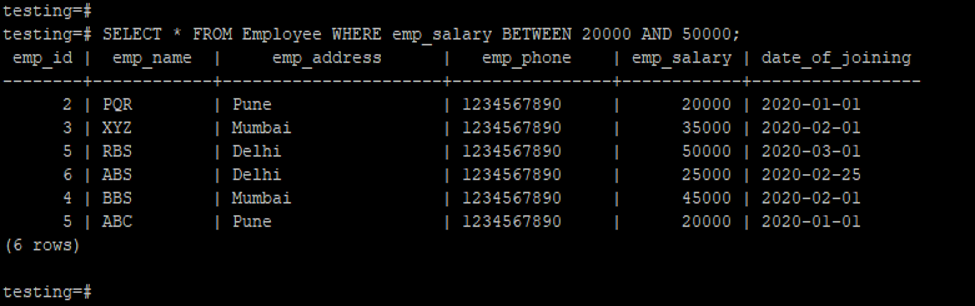
- In the below example, we have retrieved records from the employee table, which have employee salary Between 20000 to 50000.
testing=# SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE emp_salary BETWEEN 20000 AND 50000;Output:
Example #3 – Between Operator Using Date Values
- Below is the example between operators using date values as follows.
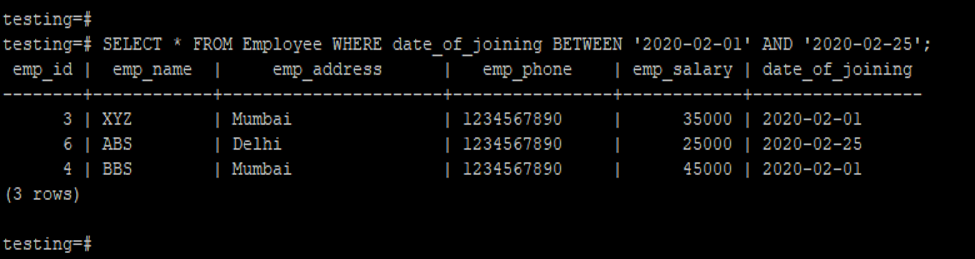
- In the below example, we have to retrieve a record from the employee table with a date of an employee joining Between 2020-02-01 to 2020-02-25.
testing=# SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE date_of_joining BETWEEN '2020-02-01' AND '2020-02-25';Output:
Example #4 – Between Operator Using Not Operator
- Below is the example of between operators by using not operator as follows.
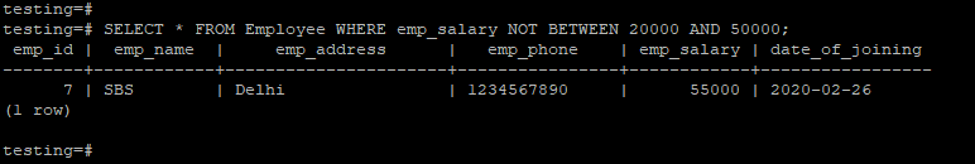
- In the example below, we must retrieve a record from the employee table with the employee salary, not Between 20000 to 50000.
testing=# SELECT * FROM Employee WHERE emp_salary NOT BETWEEN 20000 AND 50000;Output:
Conclusion
Between operators is most important in PostgreSQL to retrieve a record from a table with a specified range. We can use between condition to retrieve records of numeric and date type columns, numeric and date data types is mostly useful to retrieve a record from the table using between the condition in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “BETWEEN in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.