Definition of B+ Tree Deletion
B+ Tree is an extension of the B tree that allows more efficient insertion, deletion, and other operations than B tree. Deleting an element in the B+ tree includes three operations Searching, Deleting, and Balancing. First, we will search for the node that is to be deleted and performing a deletion operation on it then we will balance the tree as the final step.
Algorithm of B+ Tree Deletion
Step 1: Take the input in a key-value and search for the leaf node containing the key value.
Step 2: If the key is found, remove that entry from the leaf
• If the leaf meets “Half Full criteria” then it is done
• otherwise, the leaf has some data entries.
Step 3: If the leaf’s right sibling can have an entry. then move the very smallest entry to that right sibling of the leaf.
• Otherwise, if the leaf’s left sibling can take an entry, then move the smallest node to that left sibling of the leaf.
• If it doesn’t meet the above two criteria, merge both leaf and a sibling.
Step 4: While merging, it recursively deletes the entry which is pointing to the leaf or sibling from the parent.
Step 5: Merging could make a change in the height of the tree.
Explanation with an Example
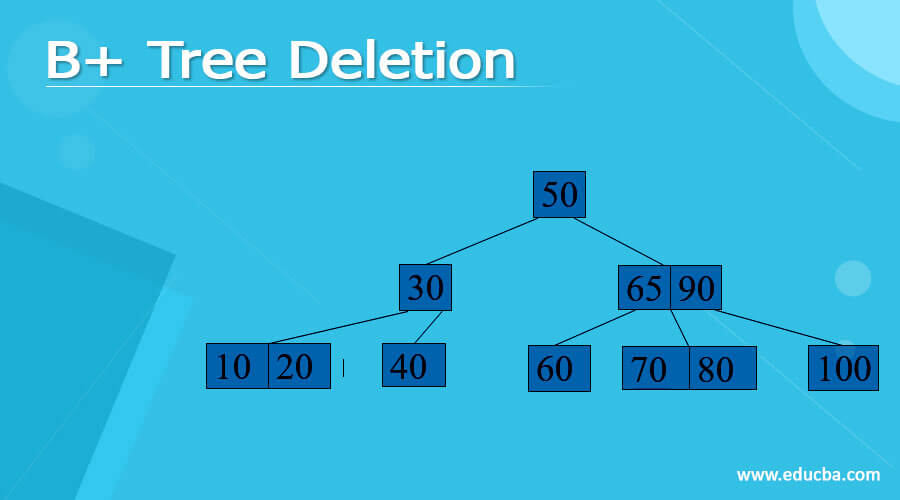
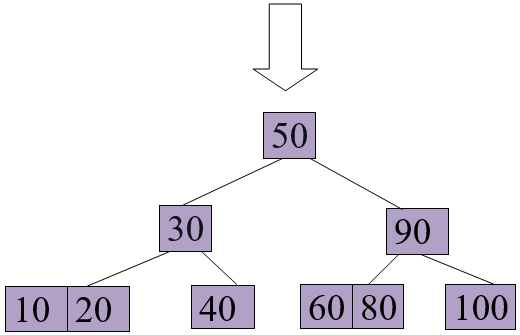
Let us consider a B+ tree as shown below.
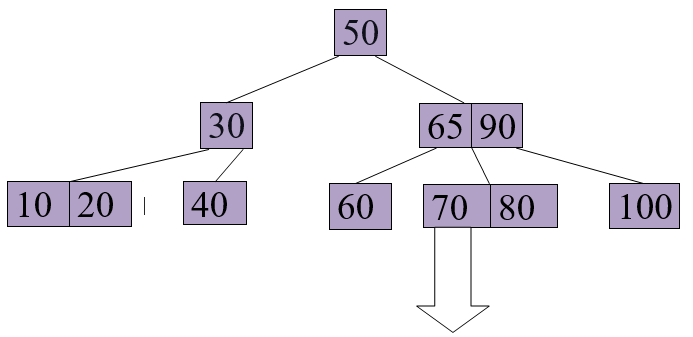
Delete 65 from the above B+ tree
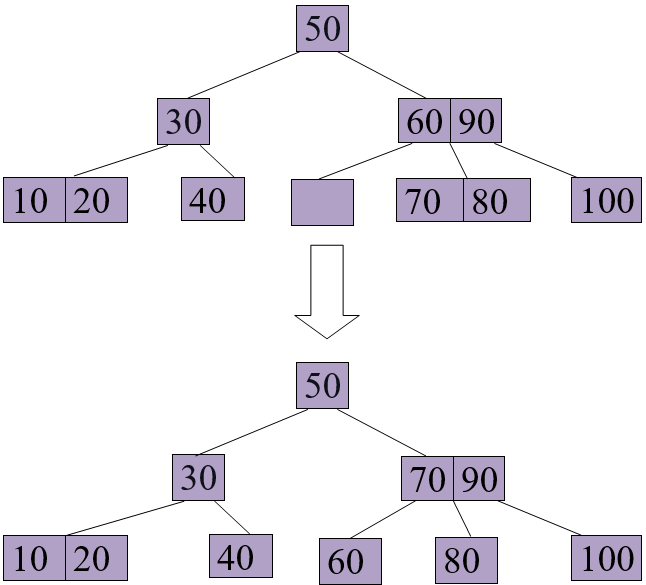
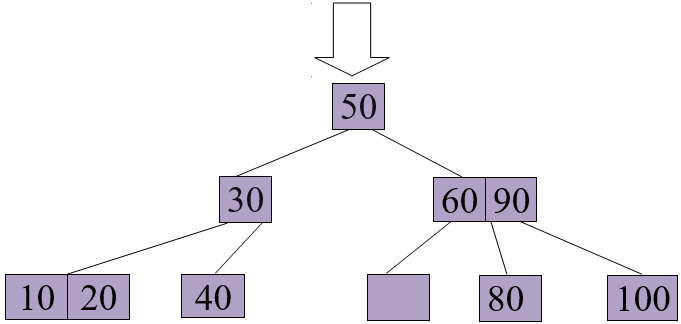
Delete 70 from the above B+ tree
Source Code
import math
# Node creation
class Node:
def __init__(self, order):
self.order = order
self.values = []
self.keys = []
self.nextKey = None
self.parent = None
self.check_leaf = False
# Insert at the leaf
def insert_at_leaf(self, leaf, value, key):
if (self.values):
temp1 = self.values
for i in range(len(temp1)):
if (value == temp1[i]):
self.keys[i].append(key)
break
elif (value < temp1[i]):
self.values = self.values[:i] + [value] + self.values[i:]
self.keys = self.keys[:i] + [[key]] + self.keys[i:]
break
elif (i + 1 == len(temp1)):
self.values.append(value)
self.keys.append([key])
break
else:
self.values = [value]
self.keys = [[key]]
# B plus tree
class BplusTree:
def __init__(self, order):
self.root = Node(order)
self.root.check_leaf = True
# Insert operation
def insert(self, value, key):
value = str(value)
old_node = self.search(value)
old_node.insert_at_leaf(old_node, value, key)
if (len(old_node.values) == old_node.order):
node1 = Node(old_node.order)
node1.check_leaf = True
node1.parent = old_node.parent
mid = int(math.ceil(old_node.order / 2)) - 1
node1.values = old_node.values[mid + 1:]
node1.keys = old_node.keys[mid + 1:]
node1.nextKey = old_node.nextKey
old_node.values = old_node.values[:mid + 1]
old_node.keys = old_node.keys[:mid + 1]
old_node.nextKey = node1
self.insert_in_parent(old_node, node1.values[0], node1)
# Search operation for different operations
def search(self, value):
current_node = self.root
while(current_node.check_leaf == False):
temp2 = current_node.values
for i in range(len(temp2)):
if (value == temp2[i]):
current_node = current_node.keys[i + 1]
break
elif (value < temp2[i]):
current_node = current_node.keys[i]
break
elif (i + 1 == len(current_node.values)):
current_node = current_node.keys[i + 1]
break
return current_node
# Find the node
def find(self, value, key):
l = self.search(value)
for i, item in enumerate(l.values):
if item == value:
if key in l.keys[i]:
return True
else:
return False
return False
# Inserting at the parent
def insert_in_parent(self, n, value, ndash):
if (self.root == n):
rootNode = Node(n.order)
rootNode.values = [value]
rootNode.keys = [n, ndash]
self.root = rootNode
n.parent = rootNode
ndash.parent = rootNode
return
parentNode = n.parent
temp3 = parentNode.keys
for i in range(len(temp3)):
if (temp3[i] == n):
parentNode.values = parentNode.values[:i] + \
[value] + parentNode.values[i:]
parentNode.keys = parentNode.keys[:i +
1] + [ndash] + parentNode.keys[i + 1:]
if (len(parentNode.keys) > parentNode.order):
parentdash = Node(parentNode.order)
parentdash.parent = parentNode.parent
mid = int(math.ceil(parentNode.order / 2)) - 1
parentdash.values = parentNode.values[mid + 1:]
parentdash.keys = parentNode.keys[mid + 1:]
value_ = parentNode.values[mid]
if (mid == 0):
parentNode.values = parentNode.values[:mid + 1]
else:
parentNode.values = parentNode.values[:mid]
parentNode.keys = parentNode.keys[:mid + 1]
for j in parentNode.keys:
j.parent = parentNode
for j in parentdash.keys:
j.parent = parentdash
self.insert_in_parent(parentNode, value_, parentdash)
# Delete a node
def delete(self, value, key):
node_ = self.search(value)
temp = 0
for i, item in enumerate(node_.values):
if item == value:
temp = 1
if key in node_.keys[i]:
if len(node_.keys[i]) > 1:
node_.keys[i].pop(node_.keys[i].index(key))
elif node_ == self.root:
node_.values.pop(i)
node_.keys.pop(i)
else:
node_.keys[i].pop(node_.keys[i].index(key))
del node_.keys[i]
node_.values.pop(node_.values.index(value))
self.deleteEntry(node_, value, key)
else:
print("Value not in Key")
return
if temp == 0:
print("Value not in Tree")
return
# Delete an entry
def deleteEntry(self, node_, value, key):
if not node_.check_leaf:
for i, item in enumerate(node_.keys):
if item == key:
node_.keys.pop(i)
break
for i, item in enumerate(node_.values):
if item == value:
node_.values.pop(i)
break
if self.root == node_ and len(node_.keys) == 1:
self.root = node_.keys[0]
node_.keys[0].parent = None
del node_
return
elif (len(node_.keys) < int(math.ceil(node_.order / 2)) and node_.check_leaf == False) or (len(node_.values) < int(math.ceil((node_.order - 1) / 2)) and node_.check_leaf == True):
is_predecessor = 0
parentNode = node_.parent
PrevNode = -1
NextNode = -1
PrevK = -1
PostK = -1
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.keys):
if item == node_:
if i > 0:
PrevNode = parentNode.keys[i - 1]
PrevK = parentNode.values[i - 1]
if i < len(parentNode.keys) - 1:
NextNode = parentNode.keys[i + 1]
PostK = parentNode.values[i]
if PrevNode == -1:
ndash = NextNode
value_ = PostK
elif NextNode == -1:
is_predecessor = 1
ndash = PrevNode
value_ = PrevK
else:
if len(node_.values) + len(NextNode.values) < node_.order:
ndash = NextNode
value_ = PostK
else:
is_predecessor = 1
ndash = PrevNode
value_ = PrevK
if len(node_.values) + len(ndash.values) < node_.order:
if is_predecessor == 0:
node_, ndash = ndash, node_
ndash.keys += node_.keys
if not node_.check_leaf:
ndash.values.append(value_)
else:
ndash.nextKey = node_.nextKey
ndash.values += node_.values
if not ndash.check_leaf:
for j in ndash.keys:
j.parent = ndash
self.deleteEntry(node_.parent, value_, node_)
del node_
else:
if is_predecessor == 1:
if not node_.check_leaf:
ndashpm = ndash.keys.pop(-1)
ndashkm_1 = ndash.values.pop(-1)
node_.keys = [ndashpm] + node_.keys
node_.values = [value_] + node_.values
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.values):
if item == value_:
p.values[i] = ndashkm_1
break
else:
ndashpm = ndash.keys.pop(-1)
ndashkm = ndash.values.pop(-1)
node_.keys = [ndashpm] + node_.keys
node_.values = [ndashkm] + node_.values
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(p.values):
if item == value_:
parentNode.values[i] = ndashkm
break
else:
if not node_.check_leaf:
ndashp0 = ndash.keys.pop(0)
ndashk0 = ndash.values.pop(0)
node_.keys = node_.keys + [ndashp0]
node_.values = node_.values + [value_]
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.values):
if item == value_:
parentNode.values[i] = ndashk0
break
else:
ndashp0 = ndash.keys.pop(0)
ndashk0 = ndash.values.pop(0)
node_.keys = node_.keys + [ndashp0]
node_.values = node_.values + [ndashk0]
parentNode = node_.parent
for i, item in enumerate(parentNode.values):
if item == value_:
parentNode.values[i] = ndash.values[0]
break
if not ndash.check_leaf:
for j in ndash.keys:
j.parent = ndash
if not node_.check_leaf:
for j in node_.keys:
j.parent = node_
if not parentNode.check_leaf:
for j in parentNode.keys:
j.parent = parentNode
# Print the tree
def printTree(tree):
lst = [tree.root]
level = [0]
leaf = None
flag = 0
lev_leaf = 0
node1 = Node(str(level[0]) + str(tree.root.values))
while (len(lst) != 0):
x = lst.pop(0)
lev = level.pop(0)
if (x.check_leaf == False):
for i, item in enumerate(x.keys):
print(item.values)
else:
for i, item in enumerate(x.keys):
print(item.values)
if (flag == 0):
lev_leaf = lev
leaf = x
flag = 1
record_len = 3
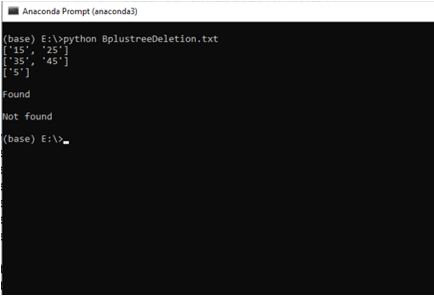
bplustree = BplusTree(record_len)
bplustree.insert('5', '33')
bplustree.insert('15', '21')
bplustree.insert('25', '31')
bplustree.insert('35', '41')
bplustree.insert('45', '10')
printTree(bplustree)
print()
if(bplustree.find('5', '33')):
print("Found")
else:
print("Not found")
print()
if(bplustree.find('5', '34')):
print("Found")
else:
print("Not found")
Output:
Time Complexity of B+ tree
- Best Case Time Complexity
The Best case time complexity of the deletion operation of a B+ tree is the same as the searching operation in a B+ tree. So, The best case time complexity of B+ tree deletion is Θ(logn)
- Average Case Time Complexity
The average case time complexity of B+ tree is Θ(logn). The deletion algorithm of B+ tree also takes the same time as performing search operation. So the time complexity of both search and Deletion will be equal.
- Worst Case Time Complexity
The worst-case time complexity of B+ tree is Θ(logn).
- Space Complexity of B+ tree
The average case space complexity and worst-case space complexity are equal in B+ tree.
The average case space complexity is Θ(n)
The best-case space complexity is Θ(n)
Application of B+ tree
- In the B+ tree we store all the data in leaf nodes which makes the tree shorter and have more branching in these trees which reduces disk I/O. So we can implement these in Secondary storage devices.
- By using the B+ tree, one can retrieve partial retrieval or range retrieval. Traversing through the B+ tree makes this easier
Advantages of B+ tree
- By using disc accesses, any records can be searched and accessed very easily.
- When compared to other trees, the height of B+ tree remains short and balanced.
- The data in B+ tree can be accessed sequentially or directly.
- As the data is stored in leaf nodes, it can be accessed fastly.
Conclusion
- B+ Tree is an extension of the B tree that allows the more efficient insertion, deletion, and other operations than Btree
- Deleting an element in the B+ tree includes three operations Searching, Deleting, and Balancing
- If the height of the B+ tree gets shrunk it gets very complicated to continue further processes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to B+ Tree Deletion. Here we discuss the definition, Algorithm of B+ Tree Deletion, explanation with example with code implementation and advantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –