What is Autonomous AI?
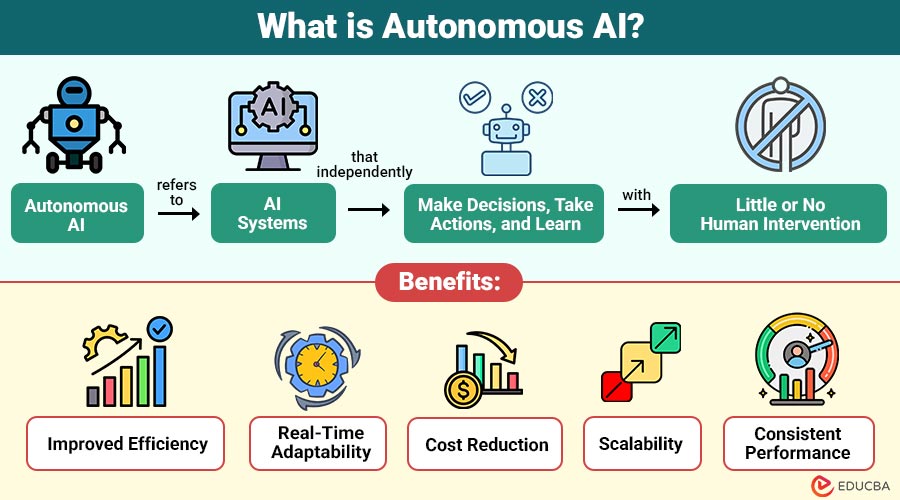
Autonomous AI refers to AI systems that independently make decisions, take actions, and learn with little or no human intervention.
Unlike conventional AI, which typically responds to predefined inputs or instructions, autonomous AI systems:
- Continuously perceive their environment
- Evaluate multiple decision paths
- Execute actions
- Learn and improve over time
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Autonomous AI systems operate independently, making decisions, executing actions, and learning continuously with minimal human involvement.
- They integrate perception, reasoning, action, and learning into a closed-loop system capable of real-time adaptation.
- Core technologies such as reinforcement learning, large language models, and computer vision enable autonomy, intelligence, and contextual awareness.
- Autonomous AI delivers significant efficiency, scalability, and consistency benefits across industries such as transportation, finance, manufacturing, and cybersecurity.
Key Characteristics of Autonomous AI
Here are the main characteristics that define autonomous AI:
1. Self-Decision Making
Autonomous AI evaluates multiple options and selects the best course of action based on objectives, constraints, and real-time data.
2. Continuous Learning
Using feedback loops, these systems improve over time through techniques like reinforcement learning and online training.
3. Goal-Oriented Behavior
Operates toward specific goals, optimizing outcomes such as efficiency, accuracy, safety, or profitability.
4. Environmental Awareness
Can recognize and respond to changes in its environment through sensors, APIs, and data streams.
5. Minimal Human Intervention
Once deployed, these systems require limited human oversight, reducing operational dependency.
Autonomous AI Architecture
Autonomous AI systems typically follow a layered architecture:
1. Perception Layer
Gathers and interprets multimodal data from sensors, logs, user inputs, images, and streams to enable environmental awareness.
2. Decision Layer
Analyzes perceived data to select optimal actions using models, policies, reinforcement learning, and reasoning mechanisms.
3. Action Layer
Executes chosen decisions by triggering physical movements, digital operations, API calls, or system-level configurations.
4. Learning Layer
Continuously improves system performance through feedback, online learning, reward optimization, and periodic model retraining.
Core Technologies Powering Autonomous AI
Here are the core technologies that enable Autonomous AI:
1. Reinforcement Learning
Allows AI agents to learn optimal actions through continuous interaction with rewards, penalties, and environmental feedback.
2. Large Language Models
Enable reasoning, planning, natural language understanding, and communication capabilities within autonomous AI agents.
3. Computer Vision
Helps systems analyze visual inputs to recognize objects, navigate environments, and understand spatial context.
4. Multi-Agent Systems
Enable multiple autonomous agents to collaborate, coordinate, or compete while solving complex distributed problems.
5. MLOps and Automation Pipelines
Ensure efficient continuous deployment, monitoring, version control, scalability, and retraining for autonomous AI systems.
Use Cases of Autonomous AI
Here are some practical use cases:
1. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars use autonomous AI to navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make real-time driving decisions.
2. Smart Manufacturing
AI-driven robots optimize production lines, predict equipment failures, and self-adjust operations.
3. Financial Trading Systems
Autonomous trading agents analyze markets, execute trades, and manage risks automatically.
4. Cybersecurity
AI agents autonomously detect threats, respond to attacks, and patch vulnerabilities in real time.
5. Supply Chain Optimization
Predicts demand, manages inventory, and optimizes logistics routes.
Benefits of Autonomous AI
Here are the key benefits offered by Autonomous AI:
1. Improved Efficiency
Automation reduces manual effort and accelerates decision-making across processes, workflows, and operations, organization-wide and globally, continuously and efficiently.
2. Real-Time Adaptability
Autonomous systems respond instantly to changing conditions in dynamic environments without human-intervention delays, effectively and continuously.
3. Cost Reduction
Reduces work costs and stoppages by using automation and making the best use of resources in businesses worldwide.
4. Scalability
Autonomous systems efficiently scale to manage large-scale operations without requiring proportional increases in human resources.
5. Consistent Performance
Delivers reliable outcomes by reducing human error, fatigue, and variability across repetitive tasks consistently over time.
Challenges of Autonomous AI
Here are the main challenges and risks associated with autonomous AI:
1. Ethical Concerns
2. Lack of Explainability
Complex models act as black boxes, making autonomous decisions difficult to interpret, justify, audit, or debug.
3. Safety Risks
Errors in autonomous systems can cause severe harm, especially in healthcare, transportation, and critical infrastructure.
4. Data Dependency
Relies heavily on high-quality, unbiased data to ensure reliable, fair, and accurate behavior outcomes.
5. Security Vulnerabilities
Differences Between Autonomous AI and Traditional AI
Here is a comparison highlighting the key differences between traditional AI and autonomous AI:
| Feature | Autonomous AI | Traditional AI |
| Decision Control | Self-driven | Human-driven |
| Learning | Continuous | Periodic |
| Adaptability | High | Limited |
| Environmental Response | Proactive | Reactive |
| Human Intervention | Minimal | High |
Final Thoughts
Autonomous AI represents a major shift from assistive automation to self-governing intelligence. By sensing, deciding, acting, and learning on their own, systems can work at large scale with little human help. However, clear rules, ethics, transparency, and strong safety measures are needed for responsible use.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is Autonomous AI the same as AGI?
Answer: No. Autonomous AI is task-specific, while artificial general intelligence aims for human-like intelligence across all domains.
Q2. Does Autonomous AI eliminate human roles?
Answer: It reduces manual tasks but increases demand for oversight, strategy, and ethical governance roles.
Q3. How is Autonomous AI trained?
Answer: Using a combination of supervised learning, reinforcement learning, simulations, and real-world feedback.
Q4. Is Autonomous AI safe?
Answer: With proper monitoring, validation, and governance, it can be safe and reliable.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Autonomous AI” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

