Introduction
Preventive maintenance is critical in the lifespan and minimization of unexpected downtime of the equipment. However, in the case of maintenance programs that rely heavily on manual scheduling and reporting, the benefits can be compromised by errors and inefficiencies. The automation regulations have revolutionized this process by enabling maintenance teams to maintain consistency, anticipate potential problems, and simplify task management. By incorporating automation into the workflow of preventive maintenance, organizations can achieve a closer approach to predictive accuracy, enhanced asset reliability, and improved cost efficiency.
Automation is not a substitute for the human factor in maintenance management, but is an addition to it. With the successful implementation of automation rules, teams would be in a position to make more strategic choices and spend less on repetitive tasks. Such a balance between human control / automated implementation enables maintenance procedures to operate at a higher level of performance without compromising quality and compliance. It is therefore necessary to understand how to design and implement these rules in an organization that intends to modernize its preventive maintenance systems.
Understanding Automation in Preventive Maintenance
Automation of preventive maintenance involves the application of automated rules and triggers to perform maintenance procedures without necessarily involving human operators. Such rules may schedule inspections, assign technicians to perform tasks, reorder spare parts, or initiate work orders when specific conditions occur. It aims to establish a predictive, rather than a reactive, maintenance cycle. For example, automation ensures that maintenance teams perform lubrication, calibration, and safety checks at fixed intervals, either time-based or use-based, minimizing the chances of overlooking them.
Automation is applied strategically to provide every asset with care before it fails. It connects with digital systems that monitor performance information, equipment welfare, and atmospheric conditions. The system is also able to automatically create a notification or task once the maintenance team has been notified that a threshold is met. This automatically prevents delays and ensures that maintenance teams perform preventive activities within the correct timeframe, saving costs and prolonging equipment life.
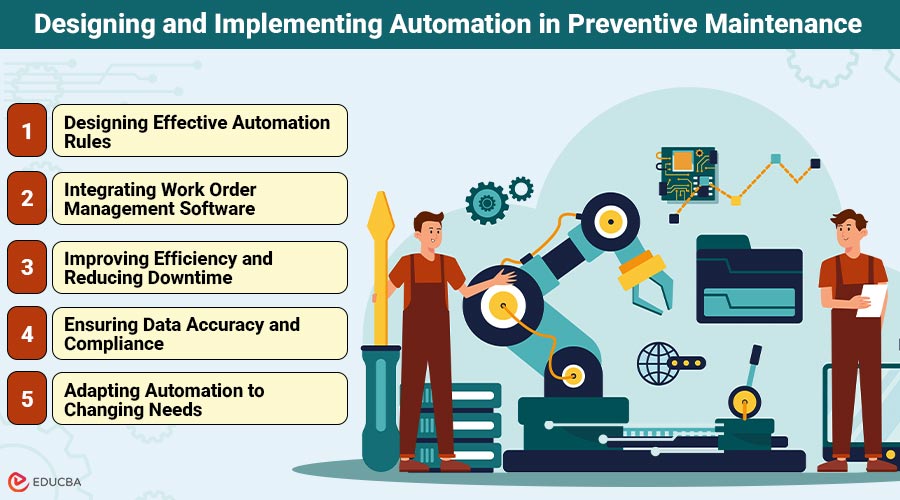
Designing and Implementing Automation in Preventive Maintenance
Automation in preventive maintenance involves establishing intelligent rules, integrating work order systems, enhancing efficiency, ensuring data accuracy, and adapting to evolving operational requirements. Each of these components works together to streamline maintenance processes, reduce downtime, and enhance asset reliability.
1. Designing Effective Automation Rules
The process of creating automation rules starts by identifying repetitive and predictable maintenance activities, such as inspections, part replacements, and lubrication, which can be easily automated. Maintenance software can manage scheduling by linking these tasks to system triggers, such as machine hours or sensor readings. Rules should also include escalation policies, issuing alerts when tasks are delayed or exceed thresholds to ensure timely completion and accountability.
Automation can also streamline team communication. For example, the system can automatically update asset records, close completed work orders, and notify supervisors. Properly designed rules should map dependencies so that one automated action flows seamlessly into the next, ensuring the entire maintenance system operates efficiently and in a coordinated manner.
2. Integrating Work Order Management Software
Automated preventive maintenance systems are based on work order management software. It enables organizations to consolidate all maintenance requests in a centralized platform, allowing them to delegate duties and track progress. Maintenance teams can automate work orders using sensor data or predetermined intervals, allowing the software to generate work orders automatically when it applies automation rules. This makes every action trackable, increasing transparency and accountability across the maintenance team.
Furthermore, the software offers predictive capabilities and enables the gathering of information related to connected devices and Internet of Things (IoT) sensors. It analyzes performance patterns and automatically adjusts maintenance schedules based on real conditions rather than fixed intervals. This flexibility optimizes resource use, reduces downtime, and ensures that maintenance teams complete all tasks on multiple assets while keeping priorities aligned with production needs.
3. Improving Efficiency and Reducing Downtime
Automation in preventive maintenance significantly improves operational efficiency by enabling maintenance teams to eliminate manual input errors and perform tasks at the optimal time. This leads to higher equipment reliability, fewer unplanned stoppages, and better resource planning, as future tasks and parts needs are visible in advance—reducing disruptions and boosting productivity.
Faster response times and improved team communication further minimize downtime. Automation can trigger immediate alerts, generate work orders, and assign technicians without manual approval, resolving issues before they escalate. This proactive approach cuts costs and boosts the organization’s reputation for stable operations.
4. Ensuring Data Accuracy and Compliance
Automation enhances the accuracy of maintenance data, which is crucial for ensuring compliance and effective performance monitoring. Automated rules ensure tasks are completed and documented consistently, creating detailed records and audit trails that simplify regulatory compliance and support trend analysis, identification of weak areas, and informed decision-making.
Accurate data also enhances managerial decision-making by reducing human error in reporting and data entry. Reliable information improves forecasting, inventory control, and performance evaluation, while increasing accountability and ensuring preventive maintenance activities align with organizational objectives.
5. Adapting Automation to Changing Needs
The maintenance environment is dynamic, so automation rules must adapt to changes in equipment, production loads, or new technologies. Regularly checking and updating automation settings, with feedback from technicians and performance data, keeps preventive maintenance effective, relevant, and efficient.
Scalability is also key—automation frameworks must be easily adaptable to accommodate company growth or new facilities. Configurable software lets you easily integrate new equipment or processes, keeping the preventive maintenance system ready for the future and strong against changing industrial needs.
Final Thoughts
The use of automation in preventive maintenance enables organizations to combine predictive insights with operational discipline, ensuring maintenance activities are precise, consistent, and carried out in a timely manner. The implementation of tools like work order management software improves visibility, reliability of data, and communication within maintenance teams. The improvements not only decrease the downtime but also contribute to the long-term asset reliability and cost control.
The aspect of automating preventive maintenance is not to remove human judgment, but to empower it. Maintenance professionals would be able to focus on areas such as problem-solving, innovation, and continuous improvement, thanks to the ability of systems to automate repetitive scheduling and monitoring functions. With proper use, automation can turn preventive maintenance into a key advantage that boosts efficiency and long-term performance.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on Automation in Preventive Maintenance helped you understand its benefits. For more insights, explore these related articles below:
