Updated July 29, 2023

Difference Between Audit vs Assurance
Auditing involves closely examining the accounting information in the organization’s financial statements. One of the primary responsibilities of auditing is to ensure accurate maintenance, fair presentation, and deliberate preparation of financial reports. The reports are created in accordance with accounting principles and standards, and all reporting compliances are followed. Assurance is a set of processes of analyzing and assessing the process, operations, procedures, etc. Nevertheless, assurance is also to assess accounting information and financial records. The major concern of assurance is to check the accuracy of the accounting information and financial records, provide regular updates to stakeholders on financial reports, and ensure that there are no red flags, irregularities, or false representations of information.
Audit
All financial practice regulations require auditing, including auditing an individual’s financial record for taxation purposes. Auditing also regulates dishonest business activities, improper fund utilization, misrepresenting financial statements, embezzlement, etc. Moreover,
There are generally two types of Audits:
- Internal Audits: It is usually conducted by the accountants to ensure that all the financial records comply with the organization’s standards. The company may outsource the auditing service to another external company specialized in this type of evaluation so that the firm may obtain an unbiased view of its financial statements.
- Independent Audits: An audit is conducted by a certified public accountant or chartered accountant who scrutinizes a company’s financial books and business transactions with which he is not affiliated. The purpose of an independent audit is to avoid conflicts of interest and maintain the integrity of the audit standard.
Assurance
The motive of assurance is not to correct the issues in accounting records but to measure the appropriateness of accounting standards and principles and follow their compliance. Furthermore, assurance applies to other aspects, such as evaluating the procedures and processes implemented in operations. In this scenario, close observation is carried out on processes and operations to ensure that the specified procedure is followed, resulting in optimal outcomes.
Assurance setting body IAASB has classified separate standards for each of the three subclassified assurance engagements.
Any engagement that can fulfill the below-mentioned assurance engagement criteria as follows:
- Three party relationship
- Subject matter
- Criteria
- Gathering appropriate evidence
- Expression of opinion
An appropriate measure required for an assurance engagement to be an audit engagement should be reasonable.
Head To Head Comparison Between Audit vs Assurance(Infographics)
Below is the top 8 difference between Audit vs Assurance
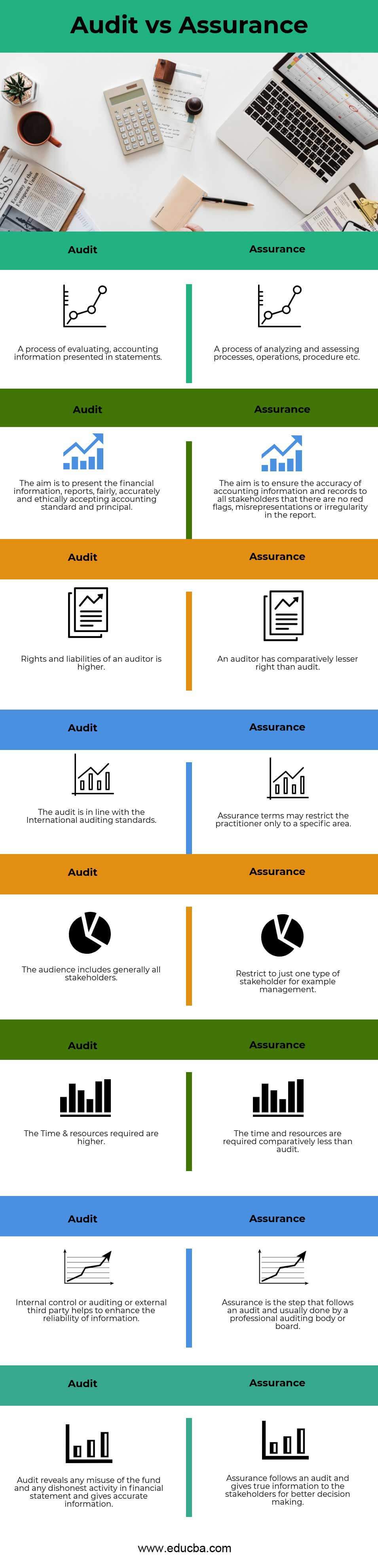
Key Differences Between Audit vs Assurance
Let us discuss some of the major differences between Audit vs Assurance:
- The audit is the process of examination of the accounting information closely, which is presented in the financial statements of the organization. While assurance is a set of processes of analyzing and assessing processes, operations, procedures, etc.
- The aim of the audit is to present the financial information, and reports, fairly, accurately, and ethically accepting accounting standards and principles within compliance. However, Assurance is to evaluate the accuracy of accounting information and records to all stakeholders to avoid any red flags, misrepresentations, or irregularities in the report.
- Auditors have more rights to access any information related to accounting as per International accounting standards, making them more liable. In contrast, an assurance auditor has fewer rights than an auditor because it is limited to a specific region.
- In an Audit, the major concern is towards all the stakeholders who invested in the organization and keeping each individual’s record. Whereas, in assurance, major concern towards a specific type of stakeholder, for example, management.
- To deal with multiple stakeholders, the company needs sufficient resources and time. So they can facilitate them. In against audit, assurance requires limited resources to deal with stakeholders.
- In Audit, internal control or audit or external third party helps to increase the accuracy and reliability of information and avoid any sort of biases. At the same time, assurance is the next step following the audit, done by the professional auditing body or board.
- Audit discloses any misuse of the fund, dishonest business activity, or misrepresentation of financial statements. However, Assurance gives true information to the stakeholders for better decision-making.
Audit vs Assurance Comparison Table
Let’s look at the top 8 Comparison Between Audit vs Assurance
|
S.no |
Audit |
Assurance |
|
1 |
A process of evaluating accounting information presented in statements. | A process of analyzing and assessing processes, operations, procedures, etc. |
|
2 |
The aim is to present the financial information, and reports, fairly, accurately, and ethically accepting accounting standards and principles. | The aim is to ensure the accuracy of accounting information and records to all stakeholders so that the report has no red flags, misrepresentations, or irregularities. |
|
3 |
The rights and liabilities of an auditor are higher | An auditor has comparatively lesser rights than an audit |
|
4 |
The audit is in line with the International auditing standards | Assurance terms may restrict the practitioner only to a specific area. |
|
5 |
The audience generally includes all stakeholders | Restrict to just one type of stakeholder, for example, management. |
|
6 |
The Time & resources required are higher | The time and resources are required comparatively less than an audit. |
|
7 |
Internal control or auditing or external third party helps to enhance the reliability of the information. | Assurance is the step that follows an audit and is usually done by a professional auditing body or board. |
|
8 |
Audit reveals any misuse of the fund or dishonest activity in financial statements and gives accurate information. | The assurance follows an audit and gives true information to the stakeholders for better decision-making. |
Conclusion
Audit vs Assurance is the processes linked to each other and utilized most in evaluating a company’s financial records and performance. Audit vs Assurance are linked to each other both processes are used to verify the information on the company’s accounting standards and principles. Assurance is the next move to the audit, while an audit is processed internally by the company’s account officer or external agency specialized in audits. Even though a professional auditing body or audit board conducts assurance, there should not be any misrepresentation or red flags in the accounting records, and it can supply essential information to stakeholders, which is necessary for better decision-making.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Top difference between Audit vs Assurance. Here we also discuss the Audit vs Assurance key differences with the Infographics and Comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


