Updated March 23, 2023

Introduction to Assignment Operators in C++
Here, let us begin on knowing about assignment operators in C++. As the name already suggests, these operators help in assigning values to variables. We discuss these with respect to operators and operands. These operators help us in allocating a particular value to the operands.
The main simple assignment operator is ‘=’. We have to be sure that both the left and right sides of the operator must have the same data type. We have different levels of operators. Let us learn about each of those in C++. Assignment operators are a part of binary operators. Examples for these are: =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=. Let us learn about each of these with examples.
Assignment Operators
There are three levels of operators.
- Unary Operators
- Binary Operators
- Ternary Operators
Assignment operators are a part of binary operators.
Examples for these are: =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=. Let us learn about each of these with examples.
Examples #1
Let us start with the first example with the ‘=’ operator as given below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b;
char c;
float d;
a=10;
b=10.5;
c='R';
d=5.85;
cout<<" Value of a is: "<<a<<endl;
cout<<" Value of b is: "<<b<<endl;
cout<<" Value of c is: "<<c<<endl;
cout<<" Value of d is: "<<d<<endl;
}Output:
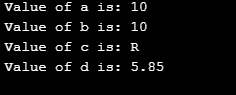
So, as an example, we can understand that the assignment operator ‘=’ is just going to assign values based on the data type using the operands and variables. Above, we can see that for the value b which is given data type of int, gives only the value till the decimal point. Only if we give the data type float like the variable d, the complete value gets displayed. So, we can say that data type also plays an important role in setting and displaying the values of different operands based on their values.
Examples #2
In this example let us learn how ‘+=’ this operand works.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
a=10;
b=5;
c=5;
a+=6;
b+=20;
c=c+20;
cout<<" Value of a is: "<<a<<endl;
cout<<" Value of b is: "<<b<<endl;
cout<<" Value of c is: "<<c<<endl;
}Output:
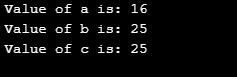
As observed above, the example of how we got the value for variable c, is the process of how the operator ‘+=’ works. As per the operand, first, the left side operand is added to the left side operand and then the final value is being assigned to the left side operand. This is how ‘+=’ is used.
Examples #3
Now, let us learn on the operand ‘-=’. This is almost similar to that of ‘+=’. The above operand adds the value, but here it gets subtracted. Let us see an example below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
a=10;
b=5;
c=5;
a-=6;
b-=20;
c=c-4;
cout<<" Value of a is: "<<a<<endl;
cout<<" Value of b is: "<<b<<endl;
cout<<" Value of c is: "<<c<<endl;
}Output:

Here also we have given example for variable ‘c’ on how actually the assignment of value is done. First, the left side operand value subtracts the right-hand value from it. In this process, there might be a negative value obtained.
Examples #4
Here let us have an example for the assignment operator *=, /= and %= together.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
a=10;
b=20;
c=25;
a*=2;
b/=5;
c%=10;
cout<<" Value of a is: "<<a<<endl;
cout<<" Value of b is: "<<b<<endl;
cout<<" Value of c is: "<<c<<endl;
}Output:
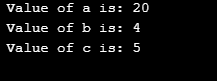
Now coming to the interpretation of the above example.
- The value for variable ‘a’ is just by multiplying the right with left operands and value respectively.
- The value of variable ‘b’ is obtained by dividing the left operand with the right side value. The output is the quotient obtained from that division.
- The value for variable ‘c’ is obtained by division only. But here the output value is the remainder of the division. As already known the left operand is divided with the right side value/operand.
Examples #5
Now let us look at how operators &=, ^= and |= as shown below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
a=5;
b=6;
c=7;
a&=3;
b^=3;
c|=3;
cout<<" Value of a is: "<<a<<endl;
cout<<" Value of b is: "<<b<<endl;
cout<<" Value of c is: "<<c<<endl;
}Output:
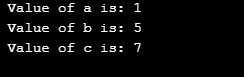
Did we expect this output? Let us now see how it is being calculated. We would start with ‘&=’ operation. Below is the table for the bitwise operator values.
| P | Q | P^Q | P&Q | P|Q |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
We already know, ‘&’ is a bitwise and operator. So, for the output of variable, ‘a’ our calculation would be as follows. Initial value of ‘a’: 5 – 101 in Binary The right value is 3 – 011 in Binary. Now calculating the ‘&’ value between those two gives 001. This is number one (1) in normal decimals. That is how we get the output.
Examples #6
Here, let us learn about the operators <<= and >>= as given below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a,b;
a=5;
b=5;
a>>=1;
b<<=1;
cout<<" Value of a is: "<<a<<endl;
cout<<" Value of b is: "<<b<<endl;
}Output:
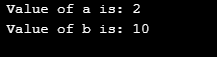
So, let us now see how these operators are actually performing its operations. For the operator, >>=; which is called the right shift operator. First, the left operand values are converted to their binary representation. Here a: 5 – 101 in binary and the right-side value is 1 (001). Now from the binary values shift one digit to right and the empty place at the left is replaced by zero.
101 → _10 1→ 010 1 → 010 → 2 (in Decimal conversion)
For the same let me explain to you with example 5>>=2.
101 → _ _ 1 01 → 001 01→ 001→1 (in Decimal conversion)
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Assignment Operators in C++. Here we discuss the basic concept and various examples of assignment operators in C++ respectively. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


