What is Asset Protection?
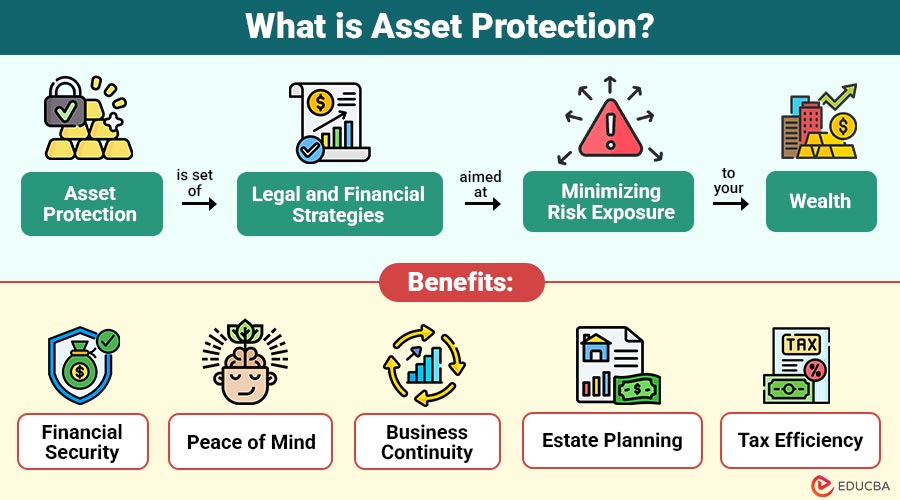
Asset protection is set of legal and financial strategies aimed at minimizing risk exposure to your wealth. The goal is to legally safeguard assets from potential claims or liabilities while ensuring they remain accessible for personal or business use.
In essence, asset protection balances risk management with wealth preservation. It is not about evading taxes or hiding assets but creating structured defenses that comply with legal standards.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Key Principles
- Strategies
- Benefits
- Limitations
- Real-World Examples
- Steps to Implement Asset Protection
Key Takeaways:
- Proactively protecting assets ensures long-term financial stability by effectively reducing vulnerability to lawsuits, creditors, and unexpected economic challenges.
- Combining legal structures, insurance, and strategic planning provides a comprehensive shield for personal, business, and family wealth.
- Early asset protection planning strengthens peace of mind, enabling confident decision-making without fear of financial loss or liability.
- Tailored strategies considering jurisdiction, risk exposure, and estate goals maximize protection while maintaining legal compliance and accessibility.
Key Principles of Asset Protection
Here are the essential principles to safeguard your assets effectively:
1. Risk Identification
Before protecting assets, you need to identify potential risks. These could include lawsuits, creditor claims, business liabilities, professional malpractice, or family disputes. A risk assessment helps tailor asset protection strategies to your specific situation.
2. Separation of Assets
Dividing personal and business assets reduces exposure. Using business structures like corporations or LLCs can protect personal wealth from business-related liabilities.
3. Legal Structures
Implementing legal frameworks such as trusts, limited partnerships, and offshore accounts can offer additional layers of protection.
4. Insurance Coverage
Insurance is a critical element in asset protection. Proper coverage for health, life, property, and business liability mitigates risks.
5. Proactive Planning
The best way to protect assets is to take action before an issue occurs. Legal alternatives may be limited if you wait until after a lawsuit or financial catastrophe.
Common Asset Protection Strategies
Here are some commonly used strategies to safeguard your wealth from risks and liabilities:
1. Business Structures
Forming a Limited Liability Company or corporation separates personal and business liabilities. In case of lawsuits or debts, creditors can only claim business assets, not personal wealth.
2. Trusts
Trusts are legal arrangements where a trustee holds assets for beneficiaries. They are effective in shielding assets from lawsuits, creditors, or estate taxes.
3. Homestead Exemptions
Certain states offer homestead exemptions, protecting the primary residence from creditors up to a specified value. This ensures that essential housing is preserved even in financial distress.
4. Retirement Accounts
In many countries, laws protect retirement accounts like 401(k)s, IRAs, or pension funds from creditors. Properly funding these accounts not only ensures future financial security but also provides a legal shield for assets.
5. Offshore Asset Protection
Holding assets in foreign jurisdictions with strong privacy laws can offer additional protection from domestic creditors. Countries like the Cayman Islands, Switzerland, and Singapore are popular for offshore trusts and accounts.
6. Insurance
Insurance is often the first line of defense. Liability insurance, umbrella policies, and professional malpractice insurance can prevent lawsuits from reaching your core assets.
7. Gifting and Family Transfers
You can decrease your vulnerability to lawsuits by strategically and legally transferring assets to family members or nonprofits to avoid accusations of fraudulent conveyance.
Benefits of Asset Protection
Implementing asset protection strategies provides multiple benefits for individuals and businesses alike:
1. Financial Security
Asset protection minimizes the risk of losing personal or business wealth by legally safeguarding assets from lawsuits, creditors, or unexpected financial claims.
2. Peace of Mind
It reduces stress and uncertainty by proactively planning for potential risks, ensuring that personal and business assets remain secure under all circumstances.
3. Business Continuity
Asset protection allows businesses to continue operations uninterrupted during legal disputes or financial setbacks, preserving revenue streams and organizational stability for stakeholders.
4. Estate Planning
Implementing legal frameworks such as trusts, limited partnerships, and offshore accounts, when structured in line with estate planning guidelines, can offer additional layers of protection.
5. Tax Efficiency
Certain asset protection strategies offer tax planning advantages, helping optimize wealth management legally while reducing liabilities and maximizing long-term financial benefits.
Limitations of Asset Protection
While asset protection is effective, it has limitations:
1. Fraudulent Transfer Laws
Implementing asset protection after a lawsuit or debt arises can be deemed fraudulent, potentially resulting in legal reversal and financial penalties.
2. Costs
Creating legal structures like trusts, LLCs, or corporations involves significant setup, maintenance, and professional fees, which can be expensive for individuals.
3. Complexity
Effective asset protection requires careful planning, understanding of laws, and expert guidance to ensure compliance and avoid legal or financial complications.
4. State-Specific Rules
Asset protection effectiveness varies by jurisdiction, meaning strategies must comply with local laws and regulations, which can limit options and flexibilit_y.
Real-World Examples
Here are some practical scenarios illustrating how asset protection strategies are applied:
1. Professional Liability Protection
A surgeon facing potential malpractice claims may use a combination of liability insurance and irrevocable trusts to protect personal wealth.
2. Business Protection
A tech startup operating as an LLC ensures that if a lawsuit arises due to product defects, the founders’ personal homes and savings remain safe.
3. Estate Planning
Families with high-value estates often create irrevocable trusts to protect assets from potential creditor claims while ensuring inheritance goals are met.
Steps to Implement Asset Protection
Implementing asset protection requires a systematic approach to safeguard your wealth effectively. Here are the key steps:
1. Conduct a Comprehensive Asset Audit
Review all personal, business, and investment assets thoroughly to understand current value, ownership, and vulnerability to potential risks or claims.
2. Identify Potential Risks
Analyze threats to personal, business, and family assets, including lawsuits, creditors, divorce, or financial instability, to design targeted protection strategies.
3. Choose Appropriate Legal Structures
Select suitable entities such as LLCs, corporations, or trusts to separate, protect, and manage assets while limiting liability exposure.
4. Obtain Adequate Insurance Coverage
Secure liability, property, health, and professional insurance policies to mitigate potential claims and provide an additional protective layer for assets.
5. Consider Retirement Accounts and Exemptions
Maximize contributions to protected retirement accounts and use exemptions to legally shield essential assets like your primary residence or personal property.
6. Plan Transfers or Gifting Strategies
Legally transfer or gift assets within regulatory limits to reduce exposure, protect wealth, and facilitate strategic estate planning.
Final Thoughts
Asset protection is a fundamental component of financial planning. By proactively implementing strategies such as business structures, trusts, insurance, and retirement planning, individuals and businesses can safeguard their wealth from unexpected challenges. The key is early planning, legal compliance, and a comprehensive approach tailored to individual risks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Can I protect my assets after a lawsuit has been filed?
Answer: Asset protection is most effective before legal issues arise. Post-lawsuit protection may be considered a fraudulent conveyance and invalidated.
Q2. Does asset protection eliminate all risks?
Answer: No strategy can offer 100% protection, but legal and financial measures significantly reduce exposure.
Q3. Is asset protection the same as tax avoidance?
Answer: No. Asset protection focuses on safeguarding wealth legally, while tax avoidance relates to minimizing taxes within legal limits.
Q4. Can offshore accounts protect my assets?
Answer: Offshore accounts can provide additional privacy and protection, but must comply with reporting laws and tax regulations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Asset Protection” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

