Introduction to Asset Securitization
Generally, banks sell these mortgages to investors more than they issue a loan. The bank will sell these mortgages to investors and make an immediate profit. This is one of the ways that banks create money for themselves. JKM Bank issues thousands of loans in New York City, and they get the right to a mortgage over the loan. JKM bank creates a pool of these mortgage loans into marketable securities. Tradable market security is a process of converting a pool of mortgage loans into market security called securitization. This is just a general idea. Let’s get the gist of the concept of asset securitization.
What is Securitization?
Asset Securitization is the process of conversion of receivables and cash flow generated from a collection or pool of financial assets like mortgage loans, auto loans, credit card receivables, etc., into marketable securities. Respective assets back these securities.
Various financial institutions that originate loans, including banks, credit card providers, auto finance companies, and consumer finance companies, turn their loans into marketable securities with the help of SPV (special purpose vehicle)
Asset Securitization
Asset securitization is the process whereby interests in loans and receivables are packaged and sold in the form of ABS asset-backed securities.
Parties Involved in Asset Securitization
Originator
The originator is the original lender and the seller of the receivables.
Typical originators:
- Mortgage financiers
- Banks
- Finance companies
- Credit card companies
- Hoteliers
- Public utilities
- Intellectual property holders
- Insurance companies
- Aviation companies
- Governments
Obligator/borrowers
The borrower is the counterparty to whom the originator makes the loan.
Issuer
Typically, SPV is set up by trust. The trust issues securities with the help of SPV, and then investors subscribe to these securities.
Investors
Investors are the persons who subscribe to the securities. Banks, financial institutions, NBFC, and mutual funds are the main investors in a securitized paper.
Trustee
Trustees usually have reputed banks, financial institutions, or independent trust companies set up to settle trusts. Trustees oversee the performance of the transaction till maturity and are vested with the necessary powers to protest investors’ interests.
Credit Rating Agencies
Independent rating agencies analyze the risks associated with asset securitization transactions and assign a credit rating to the instrument issued. These rating agencies perform a vital role in structured finance. They are evaluating the credit quality of the transactions. They are experts in evaluating various underlying asset types. Ratings are important because investors generally accept ratings by major public rating agencies like moody, standard, and poor.
Special Purpose Vehicle
SPVs are companies or trusts formed for the specific purpose of issuing securities in asset securitization transactions whose ownership and management are independent of the Originator. SPV is mainly formed to raise funds by collateralizing future receivables.
Typical Asset Securitization Structure
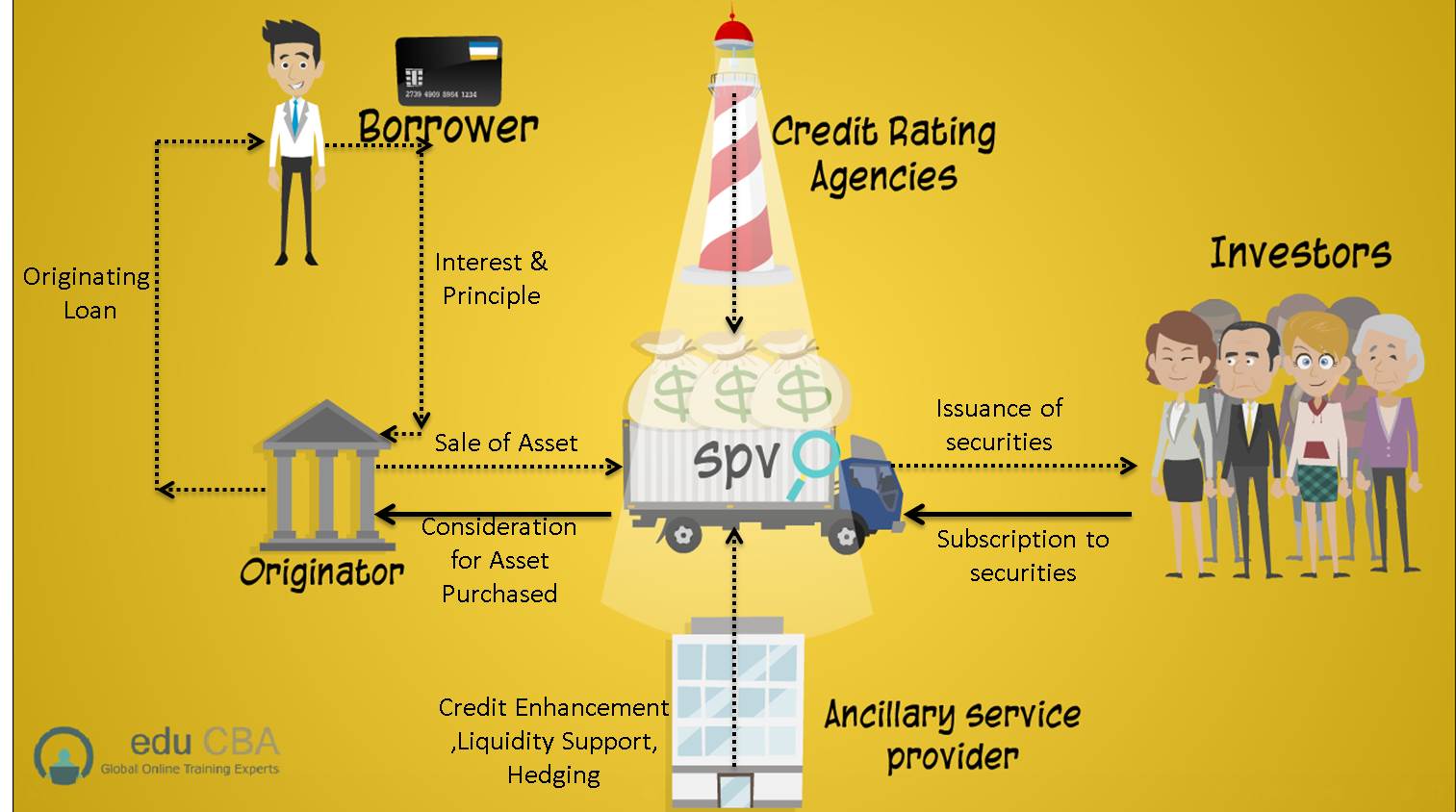
Analyze the picture below to get a general idea of asset securitization structure.
- As you know, John wants to buy a house and approached the loan originator, i.e., JKM Bank.
- Thousands of Johns are getting a loan from the bank by keeping a different type of mortgage.
- The bank issues a loan to them and creates a pool of mortgages.
- The bank then sell this pool of mortgages to the SPV (Special Purpose Vehicle) with the intention to convert this pool of mortgages into marketable securities.
- Then credit rating agencies and investment banks (Ancillary service providers) come into the picture. Credit rating agencies give a rating to the securities, and investment bank provide liquidity support to the security.
- When such structured securities are issued in the market, many Investors subscribe to them.
Concepts in Asset Securitization
Let’s look at a few concepts of asset securitization.
1. Asset Back Securities (ABS)
Asset-backed securities are bonds or notes backed by some financial assets. These assets include mortgage loans, credit card receivables, auto loans, manufactured housing contracts, and home equity loans.
2. Collateralized Debt Obligation
It is an investment-grade security backed by a pool of various other securities.
3. Mortgage-Backed Securities (MBS)
Mortgage-backed securities are bonds that are backed by pools of mortgage loans. For examples, mortgage papers, house papers, land and property papers.
4. Collateralized Mortgage Obligations (CMOs)
The CMO is a multiclass bond backed by a pool of mortgage pass-through or mortgage loans. CMOs may be collateralized by mortgage pass-through securities, mortgage loans, or some combination.
Difference Between MBS and ABS
| No. | MBS | ABS |
| 1 | The Duration for trading is more than 15 years. | The Duration for trading is up to 5 years. |
| 2 | Securities: Mortgage papers, house papers, land and property papers. | Securities: Credit card papers, share certificates, auto or vehicle papers. |
Benefits of Asset Securitization
For Originators
Asset securitization improves ROC (returns on capital). Securitization may also lower borrowing costs, release additional capital for expansion, and improve asset/liability and credit risk management.
For Investors
Asset securitization offers a combination of attractive yields, greater liquidity of security in the market, and protection by way of collateral.
Borrowers
Borrowers benefit from the increasing credit availability on terms that lenders may not have provided had they kept the loans on their balance sheets.
Recommended Articles
Here are some articles that will help you to get more details about asset securitization.