Updated October 11, 2023

Introduction to Arrays in JavaScript
As we know, objects allow us to store keyed collections of values. But sometimes we need an ordered collection, where we must keep 1st, 2nd, 3rd element and many more. For instance, consider we need to store a list of something: users’ data, goods data, and many more. It is not appropriate to use an object here because it provides no methods to manage the order of elements. Things are not created for such use. There exists a special data structure called Array to store ordered collections. Arrays in JavaScript enable multiple values to be stored in a single variable. It keeps the same kind of element collection sequential fixed-size.
Arrays in JavaScript are used to store an information set, but it is often more helpful for keeping a set of variables of the same type. An array is a single variable in JavaScript that is used to store various elements. It is often used when we want to keep a list of features and access them through a single variable. Unlike many other languages where an array is a variable reference, there is a single variable in the JavaScript array that stores multiple elements. The object Arrays in JavaScript are global object used in array building, which is high-level, list-like objects.
How does the array work in JavaScript?
Arrays in JavaScript are a way to store elements in a single variable in memory. The index starts with 0. Javascript arrays are zero-based, meaning the first element index is 0. This means that an offset of one unit will always exist: the first element will have an index of 0, and the second element will have an index of 1, and so on.
How to Create Arrays in JavaScript? (Example)
The object Array allows you to store various values in one variable. It holds a sequential fixed-size collection of the same type of elements. We use an array to store a collection of elements, but it is often more helpful to consider an array as a set of variables of the same type. The literal notation array makes it simple to create arrays in JavaScript. It comprises two square brackets that wrap optional, comma-separated array elements. Number, string, boolean, null, undefined, object, function, regular expression, and other structures can be any type of array element.
The array can be created in JavaScript, as given below.
var country = [ "India" , "England" , "Srilanka" ];In the above creation, you are initializing an array with the values “India,” “England,” and “Sri Lanka.” The indices for “India,” “England,” and “Sri Lanka” are 0, 1, and 2, respectively. You can add extra elements to the country array; then you can do it as shown below. Angular JS Training Program (9 Courses, 7 Projects)Vue JS Training (1 Course, 3 Projects)
country[3] = "New Zealand" ;
country[4] = "Australia"
var country = new Array ( "India" , "England" , "Srilanka" );OR
var country = new Array ();
country[0] = "India" ;
country[1] = "England" ;
country[2] = "Srilanka" ;Example
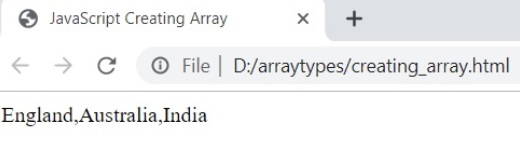
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Creating Array</title>
</head>
<body>
<p id= "myarray" ></p>
<script>
var my_array=[ "England" , "Australia" , "India" ];
document.getElementById ( "myarray" ).innerHTML = my_array;
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Types of arrays in JavaScript (Explain each type with an example)
Below are the different types of arrays in javascript as follows:
Array Literal
The array can be created with an array literal by using the below syntax
var arrayname=[value1, value2.....valuen];Consider the simple example of creating an array in JavaScript by using Array Literal
<html>
<head>
<title>Array Literal</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var country=[ "India" , "Australia" , "England" ];
for ( i=0;i<country.length;i++ ){
document.write( country[i] + "<br/>" );
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

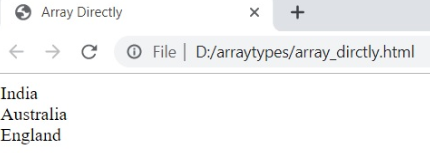
Array Directly
The array can be created with the array directly by using the new keyword, as shown below in the syntax.
var arrayname=new Array ();Below is an example of creating an array in JavaScript by using Array Directly with the help of the new keyword
<html>
<head>
<title>Array Directly</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var num;
var country = new Array ();
country[0] = "India";
country[1] = "Australia";
country[2] = "England";
for ( num=0;num<emp.length;num++ ){
document.write ( emp[num] + "<br>" );
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
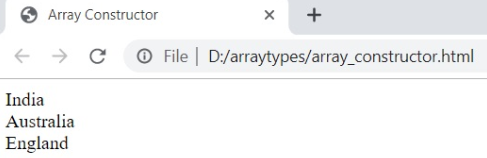
Array Constructor
Passing arguments in a constructor can create the array instance. The following example creates an array in JavaScript by using Array Constructor with the help of the new keyword.
<html>
<head>
<title>Array Constructor</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var num;
var country = new Array ();
country[0] = "India";
country[1] = "Australia";
country[2] = "England";
for ( num=0;num<country.length;num++ ){
document.write ( country[num] + "<br>" );
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
Explain Array in JavaScript (List)
Below, the array in JavaScript is as follows.
1. Concat () method
You can create a new array with a combination of two or more arrays with the help of the Concat () method.
Syntax
array.concat ( val1, val2, ..., valN );Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var chars = [ "A" , "B" , "C" ];
var num = [10 , 20 , 30];
var concat_res = chars.concat ( num );
document.write ( "Concatenated Result : " + concat_res );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

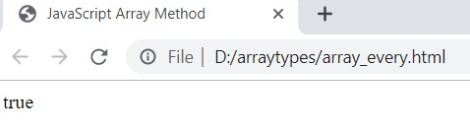
2. every ()
every () method checks whether given elements are true or false in an array as provided in the condition. It returns true if the state matches the given situation; otherwise returns false.
Syntax
Array. every ( callback, thisArg )The callback is a condition to test the function, and thisArg is an optional parameter used when executing the callback.
Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var vals=[150, 400, 450, 375, 200];
function check_num ( value )
{
return value>100;
}
document.writeln ( vals.every ( check_num ));
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
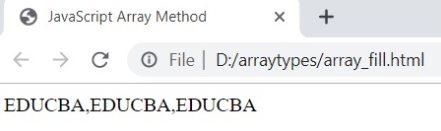
3. fill ()
The fill () method fills the specified static values by modifying the original values in the given array.
Syntax
array.fill ( value )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "England" , "Australia" , "India" ];
var array_result=my_array.fill ( "EDUCBA" );
document.writeln ( my_array );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
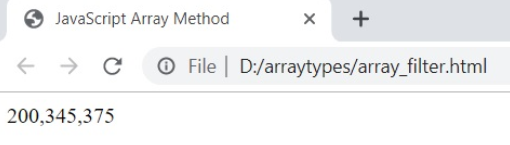
4. filter ()
The filter () method filters the array of elements based on the given condition.
Syntax
array.filter ( callback, thisArg )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var vals=[150 , 200 , 345 , 375 , 125];
function check_num ( value )
{
return value>150;
}document.writeln ( vals.filter ( check_num ));
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
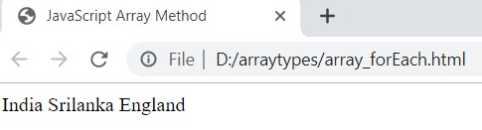
5. forEach ()
The forEach () method is used to invoke the function for each array element.
Syntax
array.forEach ( callback , thisArg )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array = ['India' , 'Srilanka' , 'England'];
my_array.forEach ( function ( fetch ) {
document.writeln ( fetch );
});
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
6. includes ()
The includes () method is used to check whether the given element is included in the array or not. If the element is included in an array, it returns true or false.
Syntax
array.includes ( element) //where "element" is a value that is to be searched in the arrayExample
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "Sachin" , "Dhoni" , "Kohli" , "Rohit" , "Dhawan" ] var array_result=my_array.includes ( "Sachin" );
document.writeln ( array_result );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

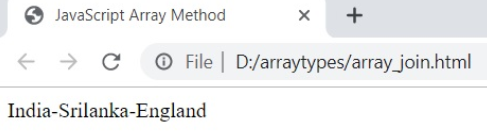
7. join ()
The join () method combines the array elements into the string and provides a new string.
Syntax
array.join ( separator )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=['India' , 'Srilanka' , 'England'] var array_result=my_array.join ( '-' )
document.write ( array_result );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
8. pop()
The pop () method is used to extract the last element of the given array.
Syntax
array.pop ( operator )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "England" , "Australia" , "India" ];
document.writeln ( "Real array elements: "+my_array+"<br>" );
document.writeln ( "Extracted element of array: "+my_array.pop ()+"<br>" );
document.writeln ( "Remaining elements of array: "+ my_array );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

9. push ()
The push() method is used to append an element to the end of an array.
Syntax
array.push ()Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "England" , "Australia" , "India" ];
my_array.push ( "Srilanka" );
document.writeln ( my_array );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

10. reverse ()
The reverse () method is used to reverse the sequence of the given array of elements. The last element will become the first, and the first element will become the last.
Syntax
array.reverse ()Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "England" , "Australia" , "India" ];
var reverse_val=arr.reverse ();
document.writeln ( reverse_val );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

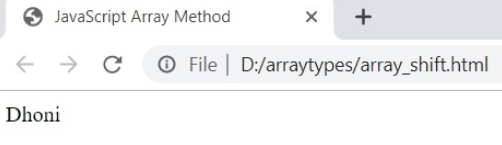
11. shift ()
The shift() method returns the first element of an array.
Syntax
array.shift ()Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "Dhoni" , "Sachin" , "Kohli" , "Rohit" , "Dhawan" ]
var array_result=my_array.shift ();
document.writeln ( array_result );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
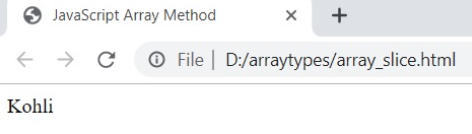
12. slice ()
The slice() method displays a portion of the given array’s elements without modifying the original array.
Syntax
array.slice ( start, end )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "Dhoni" , "Sachin" , "Kohli" , "Rohit" , "Dhawan" ];
var array_result=my_array.slice ( 2, 3 );
document.writeln ( array_result );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:
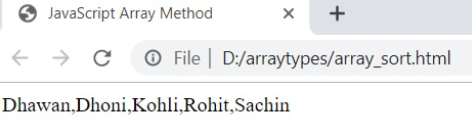
13. sort ()
The sort () method displays the array of elements in ascending order.
Syntax
array.sort ()Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "Dhoni" , "Sachin" , "Kohli" , "Rohit" , "Dhawan" ];
var array_result=my_array.sort ();
document.writeln ( array_result );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output
14. unshift ()
The unshift () method adds elements at the beginning of the array.
Syntax
array.unshift ( "element" )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "Dhoni" , "Sachin" , "Rohit" , "Dhawan" ];
var array_result=my_array.unshift ( "Kohli" );
document.writeln ( my_array );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

15. indexOf ()
The indexOf() method searches for the position of an element in a given array.
Syntax
array.indexOf ( "element" )Example
<html>
<head>
<title>JavaScript Array Method</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
var my_array=[ "Dhoni" , "Sachin" , "Rohit" , "Dhawan" ];
var array_result=my_array.indexOf ( "Rohit" );
document.writeln ( array_result );
</script>
</body>
</html>Output:

Conclusion
As discussed until now, an array is a special kind of object for storing and managing data elements. An array is an object that provides a group of elements and is useful for storing a large amount of data of the same type. The properties and methods of array objects help developers to handle arrays easily. As a global object, the JavaScript Array can be used in the construction of arrays that are high-level.
Recommended Article
This is a guide to Arrays in JavaScript. Here we have discussed the different types and methods of arrays and examples. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more.


