Updated June 21, 2023

Introduction to Armstrong Number in C++
A number that is equal to the sum of the cube of its digit is an Armstrong Number. A number is called an Armstrong number if the sum of the cube of all its digit equals that number. This article will discuss how to check the Armstrong number using the C++ programming language. Some Armstrong numbers are – 0, 1, 153, 407. Let’s check it using mathematical computation.
0 = 0 * 0 * 0 = 0
1 = 1 * 1 * 1= 1
153 = (1 * 1 * 1) + (5 * 5 * 5) + (3 * 3 * 3) = 1 + 125 + 27 = 153
407 = (4 * 4 * 4) + (0 * 0 * 0) + (7 * 7 * 7) = 64 + 0 + 343 = 407
Algorithm to Check Armstrong Number
The algorithm to check the Armstrong number in C++ is given below:
Step 1: Enter the Number
Step 2: Find the cube of each digit of entered number
Step 3: Add the cube of all the digits
Step 4: If the output of Step 3 is equal to the entered number, i.e., Step 1. Then the print entered number is Armstrong number.
Step 5: If the output of Step 3 is equal to the entered number, i.e., Step 1. Then print entered number is not an Armstrong number.
Examples of Armstrong Number
This section will discuss how to check Armstrong’s number using various methods.
Example #1 – Using a while loop
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num, r, sum=0, temp_num;
cout << "Enter number to check Armstrong number ";
cin >> num;
temp_num = num;
while(num > 0)
{
r = num % 10;
sum = sum + (r * r * r);
num = num / 10;
}
if(temp_num == sum)
cout << "Entered number is Armstrong Number." << endl;
else
cout << "Entered number is not Armstrong Number." << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
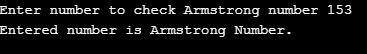
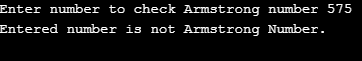
Here we have written a program to check Armstrong’s number using a while loop; first, it asks a user to enter a value. Then the entered number is copied into temp_num. Here, we use ‘temp_num’ to compare the result with the original number. While condition checks whether the number is greater than 0 or not. If the number is greater than 0, it executes the statements following a while. The last digit is separated from num by performing num%10. Then the digit is cubed and stored as the sum. Then we discard the last digit by dividing the number by 10 (i.e., num/10). We perform the process for all digits in the number. Then temp_num and num are compared; if both are equal, it will print Entered number as Armstrong Number. If both are not equal, it will print Entered number is not Armstrong Number.
Example #2 – Using a do-while loop
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num, r, sum=0, temp_num;
cout << "Enter number to check Armstrong number ";
cin >> num;
temp_num = num;
do
{
r = num % 10;
sum = sum + (r * r * r);
num = num / 10;
} while(num > 0);
if(temp_num == sum)
cout << "Entered number is Armstrong Number." << endl;
else
cout << "Entered number is not Armstrong Number." << endl;
return 0;
}Output:
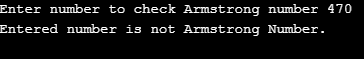
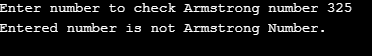
Using the do-while loop, we have written a program to check Armstrong’s number. The work is the same as we have discussed in example 1. The only difference is in 1st example if first checks the condition, i.e., num > 0. In this example, we test the same condition at the end of the loop.
Example #3 – Using for loop
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int lower_limit, upper_limit, i, r, sum, temp_num;
cout << "Enter lower limit ";
cin >> lower_limit;
cout << "Enter uppee limit ";
cin >> upper_limit;
cout << "List of Armstrong numbers between " << lower_limit << " and " << upper_limit << endl;
for(i = lower_limit; i <= upper_limit; i++)
{
sum = 0;
temp_num = i;
for(; temp_num >0; temp_num /= 10)
{
r = temp_num % 10;
sum = sum + (r * r * r);
}
if(sum == i)
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}Output:
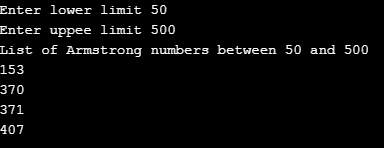
Here we have written a program to print the Armstrong number between two numbers entered by the users. The lower limit takes the minimum number, and the upper limit takes the maximum number. If the upper limit number is small, then the lower limit throws an error. The upper limit number should be greater than the lower limit. We store each number between the interval in the variable ‘temp_num.’ Then we retrieve each digit of the number in variable ‘r’ and find its cube. We then add the result of cubing the digit to the result of the last digit. Likewise, we traverse each digit, and when the traversal is complete, we compare the sum with the original number, i.e., i. If they are equal, then it prints the number.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Armstrong Number in C++. Here we discuss the introduction and algorithm of Armstrong Number in C++, along with examples and code implementation. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


