Introduction to Access Specifiers in C++
Access specifiers in C++ are basically used in OOPs concepts. In classes, we start their use, they are mainly used in inheritance. They set the range for the usage of the variable and the functions of a particular class. Access specifiers are used for data hiding purposes also.
What is Access Specifiers in C++?
Here we will discuss some basic concept of access specifier in C++ that you should know:
- The access specifiers used in C++ are Private, Protected and Public. The data members and member functions of a class declared as public are available to everyone and other classes can also access them. The public members of a class are accessible from everywhere in the program using the dot operator (.) which is called a direct member access operator along with the object of the same class.
- The data members and member functions of a class declared as private are accessible only by the inside functions of the class and are restricted to be accessed directly by any object or function outside the class. The private data members of a class can be accessed using the member functions of the class or the friend functions.
- Protected access modifier is similar to that of private access modifiers, the difference is that the class member declared as Protected cannot be accessed outside the class however they are accessible by any derived class or subclass of that class.
- The main difference between private and protected is that protected inheritance allows continued access to base class members whereas private inheritance prohibits the access of those members.
How Does Access Specifiers Work in C++?
The accessibility of access specifiers in classes during inheritance is shown in Table.
| Access Specifiers | Private | Protected | Public |
| Access in same class | √ | √ | √ |
| Access in derived class | × | √ | √ |
| Access outside the class | × | × | √ |
Working of access specifiers in inheritance is as discussed below:
1. Private
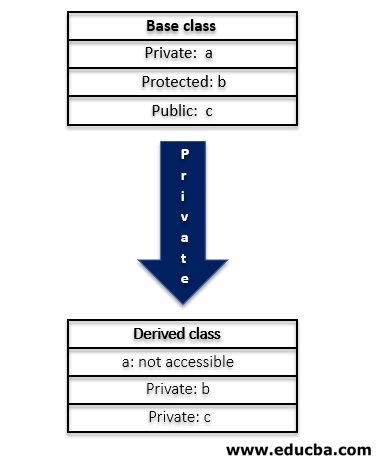
While creating a class using access specifier as private, the base class’ public and protected data members become the derived class’ private member and base class’ private member stays private. Hence, the members of the base class can be used only inside the derived class but are inaccessible through the object created for the derived class. The other way to access them is to create a function in the derived class. The below figure depicts the inheritance of data members of the base class when the access mode of the derived class is private.
2. Protected
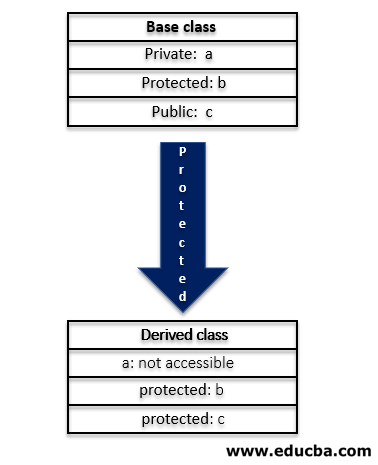
In derived class, when protected access specifier is used, the public and protected data members of the base class becomes the derived class’ protected member and base class’ private member are not accessible. Hence, the members of the base class can be used only inside the derived class as protected members. The below figure depicts the inheritance of data members of the base class when the access mode of the derived class is protected.
3. Public
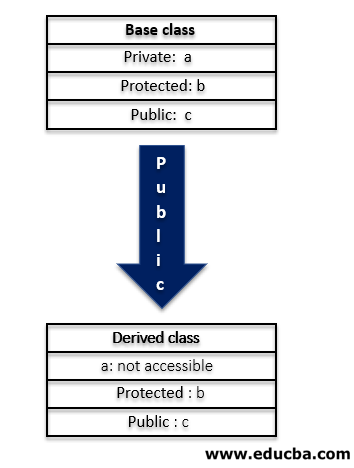
While derive class is created, if public access specifier is used, the public data members of the base class become the public member of the derived class and protected members become the protected in the derived class but the private members of the base class are inaccessible. The following figure depicts the inheritance of data members of the base class when the access mode of the derived class is public.
Examples of Access Specifiers in C++
Here are some of the examples of access modifiers in C++ which are explained below:
Example #1: Private
This is the example of a private modifier in C++.
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class baseclass
{
private:
int s;
protected:
int t;
public:
int u;
baseclass()
{
s = 11;
t = 12;
u = 13;
}
};
class deriveclass: private baseclass
{
//t and u becomes private members of deriveclass and s will remain private
public:
void show ()
{
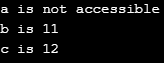
cout << "s is not accessible";
cout << "\nt is " << t;
cout << "\nu is " << u;
}
};
int main()
{
deriveclass l; //object created
l.show();
//l.s = 11; not valid : private members are inaccessible outside the class
//l.t = 12; not valid
//l.u = 13; not valid : t and u have become derived class’ private members
return 0;
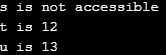
}Output:
Example #2: Protected
This is the example of a protected modifier in C++.
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class baseclass
{
private:
int a;
protected:
int b;
public:
int c;
baseclass()
{
a = 10;
b = 11;
c = 12;
}
};
class deriveclass: protected baseclass
{
//b and c becomes protected members of deriveclass
public:
void show ()
{
cout << "a is not accessible";
cout << "\nb is " << b;
cout << "\nc is " << c;
}
};
int main()
{
deriveclass d; // object created
d.show();
//d.a = 10; not valid : private members are inaccessible outside the class
//d.b = 11; not valid
//d.c = 12; not valid : b and c have become derived class’ private member
return 0;
}Output:
Example #3: Public
This is the example of a public modifier in C++.
Code:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class baseclass
{
private:
int u;
protected:
int v;
public:
int w;
baseclass()
{
u = 3;
v = 4;
w = 5;
}
};
class deriveclass: public baseclass
{
//v becomes protected and w becomes public members of class derive
public:
void show()
{
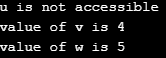
cout << "u is not accessible";
cout << "\nvalue of v is " << v;
cout << "]\nvalue of w is " << w;
}
};
int main()
{
deriveclass c;
c.show();
//c.u = 3; not valid: private members are inaccessible outside the class
//c.v = 4; not valid: v is now protected member of derived class
//c.w = 5; valid: w is now a public member of derived class
return 0;
}Output:
Conclusion
Whenever data needs any kind of restriction of accessibility that can be set as private or protected so that only the authorized functions can access them. Otherwise, the data can be set as public which can be accessed from anywhere in the program by any class in inheritance.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Access Specifiers in C++. Here we discuss what is access specifiers in C++ its working along with their examples and implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more-