Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction to Ansible Install
This is an outline of Ansible Install. Ansible is a software provisioning tool, and it is available as open-source. It can be executed on both UNIX systems and Windows. Additionally, it serves as orchestration management, enabling automatic deployment in various environments. You can execute it on both UNIX systems and Windows. Additionally, it serves as orchestration management, allowing automatic deployment in various environments. It automates the process of application deployment, configuration management, orchestration, and other IT processes. You can see the process of installing Ansible in a different environment here.
Installation of Ansible
The management systems of Ansible should not imply added dependencies on the environment, and it is consistent. It should be able to develop refined and secured environments where Ansible doesn’t enable implementing agents to nodes. To manage the nodes, only Python and OpenSSH are required. The careful composition of Ansible is crucial to ensure reliability and prevent unwanted malware attacks. Ansible is not a tough part; it is easy to learn and implement. Many playbooks use Ansible as descriptive language, purely dependent on Jinja templates and YAML.
To install Ansible, it is mandatory to have dual machines. One is the server, and the other is a node. The server behaves like the user’s managed node, and the node behaves like a controller one.
- As a first step, it is advisable to update the control node.
- It is mandatory to check the existing operating system; its version is updated.
- Give the command to initiate the task.
Code:
Yum update
- To install the EPEL repository, you need to execute the following command. This command installs the most commonly used packages on the system.
Code:
Yum, install epel – release.
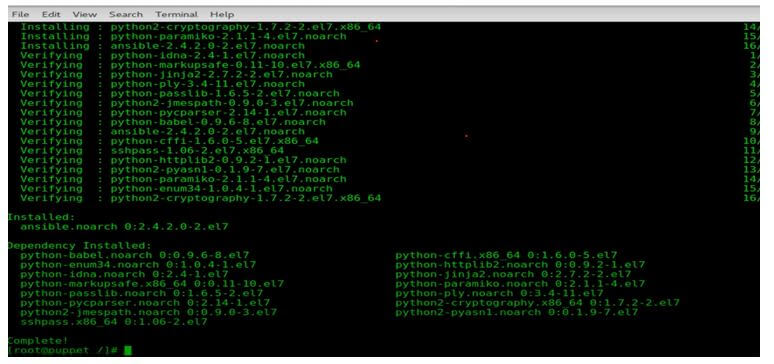
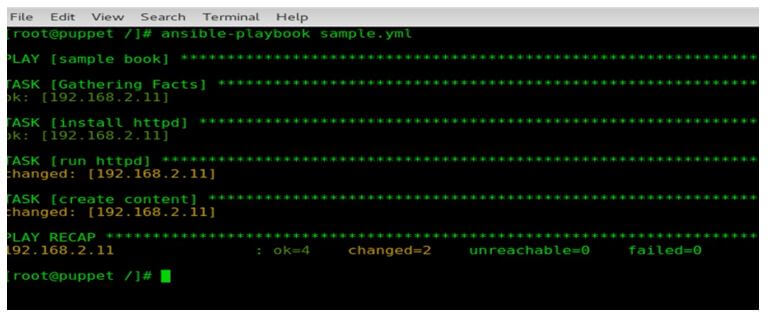
- After installing the repositories, the installation of Ansible begins. The below screen shows the different package installations from yum and Ansible.
Output:
Code:
yum install ansible
- You can download Ansible from the EPEL repository.
Output:
- A user for Ansible should be created. Then we should create a user who is non-root on both ends, which can be executed on the Ansible playbook. Here, you can provide the username as “Educba” (or any preferred username), but use the same username for both the managed node and controller node.
- The controller node adds the user and creates a password for them.
Useradd_Educba
Passwd Educba@123
- To gain access to the managed node, it is necessary to add the admin user and provide the corresponding password.
User add Educba
Passwd Educba@123
- Then it is mandatory to set the admin user as an Educba user, as he can easily work on the managed node without any password. Then check on the setup of the key pair of SSH to the user Educba. In the control node, execute the SSH pair by using the command.
Code:
Ssh-keygen ( implied to generate keys)
- After generating the keys, copy and paste the public key to the managed node by using the command.
Code:
Ssh-copy-id node.kb.educba.com
- To locate the managed nodes, the admin user needs to create an inventory and establish a connection between the inventory and managed node by logging in to the control node.
Code:
vim\home\admin\inventory
- To choose the insert mode, you can use the “I” command and then add the hostname.
- Then save the file by giving: wq command.
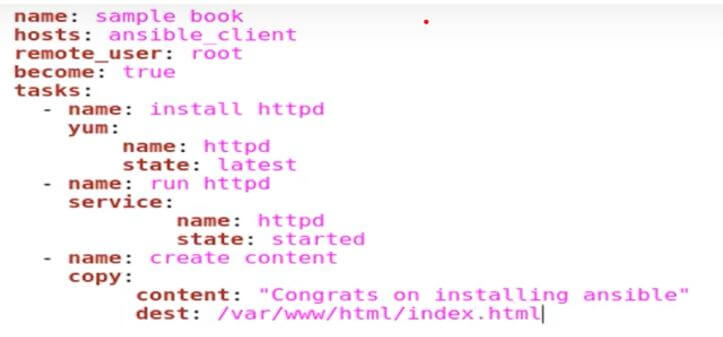
- We’ve prepared a playbook for Ansible that requires installing Nginx on the managed node. Please log in to the controller node using the username “Educba” and create a file with a unique name.
Vim\home\Educba\install-Nginx.yml
-
To create the playbook, use YAML and make sure it is easy to read for humans by formatting it correctly.
You can add the text to the playbook by entering the insert mode.
Output:
Code:
Host : app server
Become: yes
Tasks:
Educba (name of the task)
Educba: install nginx webserver
Apt: Educba: nginx state: start: update_cache: yes: true
Notify: - start nginx
Handlers: start nginx
Service: Educba: nginx
State: initiated
YAML gives multiple files to be present in one or multiple documents and can be placed separately. The YAML file describes a hierarchy composed of hosts, handlers, and tasks. The image below provides the sample playbook, and the user can customize their playbook by using the commands provided below.
We can create multiple tasks, hosts, and handlers in the playbook.
Code:
Host: Name of the app server
Tasks:
Educba: install webserver –nginx
Apt: Educba: nginx: init updated_cache: yes
Notify
- Run nginx
-
Output:
The executed task perform all the essential operation in the file. The code above contains a “notify” section that has a list with just one labeled item – “run nginx.” Although it doesn’t explicitly state that “run” is an internal command, one can infer that it refers to the handler. Handlers are responsible for executing a function when triggered by a task. They act as tasks or hosts that only execute when instructed by the user or the task running on the client system.
Code:
Handlers:
Educba: start nginx
Service:
Educba: run nginx
State: initiated
- The above code states that run the nginx handler. It will execute only after the Nginx web server is downloaded. The user can run the playbook into the file called nginx.yml.
- Then save the code and exit by using the command: wq.
- Try to use space instead of tab and ensure that spacing should be consistent with the YAML file to prevent bugs.
- Execute the playbook.
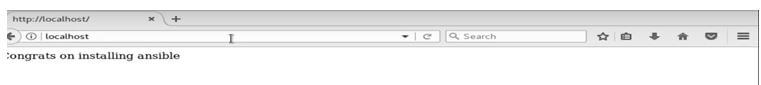
- After executing the playbook, you should copy the link into the created web server. Then, you can create a playbook in the command-line interface. Next, execute any tasks, hosts, and handlers on the webserver hosted on the machine.
Output:
The image above shows the home page of the web server. After copying the link, it will display all the tasks created.
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen Ansible and its installation. notifyIt serves as an orchestrated management tool that significantly aids the automation process. You can see more about Ansible and Excel in DevOps, which helps you connect the bridge between operations and developers.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Ansible Install. Here we discuss the introduction and installation of Ansible for a better understanding. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –