Updated May 29, 2023
Introduction to Aggregation in Java
Aggregation can be termed as an association between two classes in a way that member functions and data members can be utilized in other classes. This association is one way so-called “directional association”. This relationship is the “HAS-A” relationship. That means in case we have a class Student and the student has subjects. In this case, we define subject class separately with its own characteristics and member functions, while student class has its own member functions and data members. In this case, these classes are associated with a “HAS-A” relationship. In this topic, we are going to learn more about aggregation in JAVA.
Syntax of Aggregation in Java
The syntax for aggregation can be described as Structure of code:
class Student{
int rollnumber;
String firstname;
String lastname;
Subjectsubject;//Here subject is a different class containing its own members functions and data members.
...
//**..Code snippet..**
…
}Explanation: In the above syntax, we can see that there are two classes named “student” and “subject”. These two are linked via an aggregation relationship. Students have subjects, and so this justifies a “HAS-A” relation as any student has a subject. So all the member functions of the subject can be called under student class. This further propagates the feature of data reusability.
Why do we need Aggregation in Java?
The major use of this feature in JAVA is for “Code Reusability”. An example can well understand this.
For example, there are two classes named “customer” and “car”. There are some predefined properties of a car that is stored in the “car” class like engine power, color, power steering, dimensions and many more. While the class “customer” is to store the characteristics of customers like customer name, phone number, address, etc. So, in case any customer arrives to buy a car in the store, then the store holder will only have to make use of the “car” class. This way, we can have on code reused for multiple customers arriving in the store.
This feature reduces the code complexity and improves code visibility by using a modular approach.
How does Aggregation work in Java?
Aggregation is basically an association between two classes, as explained above. This is achieved by defining two classes in the JAVA program. Out of these two classes, one will be reused. For instance, “Class A” and “Class B” are the classes. “Class B” is to be reused, so this class will be instantiated in “Class A”.
- Ques: How to instantiate?
- Ans: Using ClassBcb;
We can then use the object “cb” to invoke member functions of “Class B” in “Class A”. This feature allows one to follow an object-oriented feature of modularity, encapsulation and data re-use.
Steps to Implement Aggregation in Java
Below are the steps mentioned:
Step #1
class Application{
int finding_square(int number){
return number*number;
// refer step 1 in explanation section.
}
}
class Square{Step #2
Application app;
//aggregationfeature is initiated by instantiating a class defined above which needs to be re used.
double area_of_square(int side){Step #3
app=new Application();
int area=app.finding_square(side);//code reusability (i.e. delegates the method call)Step #4
return area;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
Square sq=new Square();
double result=sq.area_of_square(5);Step #5
System.out.println(result);Step #6
}
}Explanation
- Step 1: We defined a function in here which can be used in multiple places like. If we want to find out the area of a square, circle or need to find out a square of a number, we can use this single function again and again in all the mentioned cases. This explains the feature of code reusability.
- Step 2: This is the carrier class that will be used to implement the code of class defined above. This is done with the help of aggregation. Aggregation is implemented in the below statement.
- Step 3: In this, we defined a function to calculate the area of a square. This function is making use of the previous class. We created a new object called “app” and assigned a default constructor in the below statement.
- Step 4: In this step, we call the member function of the previous class and pass the value as well to It called “side”. Since we extract the function from the application class, we have used the “app” and then given the function name.
- Step 5: We are sending 5 as an aside. Using this 5, the area of the square will be calculated by the function defined above and will be captured under a variable named “result”.
- Step 6: Finally, we are printing the “result” variable containing the area of the square. In this case, the area of the square is 25. Hence 25 will be printed on the output screen. Since we declared the “result” variable in float data type, we should get a result in float, i.e. 25.0, instead of 25.
Output:
We will compile the JAVA code using the command “javac” along with the file name followed by the extension of .java. After compilation, the object of this class is created. This object file contains intermediate code understood by JRE (JAVA run time environment), which then is converted into machine language. This stream of machine language code is passed to the system to generate an output in return.
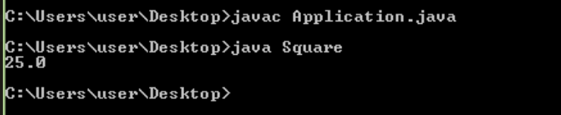
In case we make any changes to the code, then we will have to recompile the code to generate another object file. We then execute the file using the command “java” along with the file name. Here we do not have to give an extension as we are calling executable file here, not the JAVA file. The default name of the executable (object) file is the same as the JAVA file. Hence we obtained the area of the square in float data type.
Conclusion
Hence aggregation in the JAVA language is one of the key features used abundantly by developers. As it supports the feature of code reusability, thereby reduces the bulkiness of the code. Code looks clearer, and implementation along with maintenance becomes much easier. It is well-advised to use this concept while working on JAVA projects.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Aggregation in Java. Here we discuss the introduction to Aggregation and how it works in java with a sample program and some respective step for better understanding. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


