Updated June 21, 2023

Introduction to addAll() in Java
In Java ArrayList, a method addAll() helps append every element available in the argument collection to the list present at the end. The appended elements will be ordered using the iterator of argument collection. In addition to that, this method first makes sure that there is enough space on the list. If enough space is unavailable, it will be grown by adding spaces in the existing array. After this only, elements will be added to the end of the list. Even though it is possible to add any element in the array list, it is best to add elements of a particular type available in the given instance.
Syntax with parameters:
Below is the syntax of the addAll() method:
addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)Parameters:
1. index: Index where the first element has to be inserted in the collection mentioned.
2. c: Collection containing the elements that must be added to the list.
3. Return Value: True will be returned if the particular list has changed on calling this method.
4. Exception: There may occur two types of exceptions, such as:
- NullPointerException occurs when the collection mentioned is null.
- IndexOutOfBoundsException, which occurs when the index is out of range.
How does the addAll() method work in Java?
addAll() method appends the elements at the end of the array list. If a new element comes, it will check whether there is space for that element. If there is no space, then the ArrayList will add spaces. Once the spaces are added, the element will be added to its end.
Given below are the examples of addAll() in Java:
Example #1: addAll(Collection c)
This method helps in adding elements of the collection mentioned to an ArrayList.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class AddAllExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> A1 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 1
//add elements to arraylist 1
A1.add("Anna Sam");
A1.add("Izanorah Denan");
A1.add("Adam Sam");
A1.add("Annamu S");
A1.add("Naasy D");
A1.add("Thukidi D");
A1.add("Kuffi D");
A1.add("Samcha T");
ArrayList<String> A2 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 2
//add element to arraylist 2
A2.add("Anabeth Denan");
//Combine the arraylist 1 and arraylist 2
A1.addAll(A2);
//print the combined list
System.out.println(A1);
}
}Output:
![]()
Explanation:
Create an ArrayList A1 and add elements. Similarly, create an arraylist A2 and add elements to it as well. Then, add elements of A2 to A1 and print the arraylist A1.
Example #2: addAll (int fromIndex, Collection c)
Unlike the previous method, this method is an overloaded variant. An argument ‘fromIndex’ is added here, which inserts the beginning element from the collection mentioned. Usually, the starting index is ‘0’.
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class AddAllExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> A1 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 1
//add elements to arraylist 1
A1.add("Izanorah Denan");
A1.add("Adam Sam");
A1.add("Annamu S");
A1.add("Naasy D");
A1.add("Thukidi D");
A1.add("Princy v");
A1.add("Kuffi D");
A1.add("Samcha T");
ArrayList<String> A2 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 2
//add element to arraylist 2
A2.add("Anabeth Denan");
//Combine the arraylist 1 and arraylist 2
A1.addAll(A2);
//print the combined list
System.out.println("Combined A1 and A2 list :"+ A1);
ArrayList<String> A3 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 3
//add element to arraylist 3
A3.add("Riyan Jaykar");
A3.add("Kukku Chikku");
//Combine the arraylist 1 and arraylist 3 starting from 2nd position
A1.addAll(2, A3);
//print the combined list
System.out.println("Combined A1 and A3 list :"+ A1);
}
}Output:

Explanation:
Create an arraylist A1 and A2. Then, add elements of A2 to A1 and print the arraylist A1. Once you have completed that, create an ArrayList called A3 and add elements to it. After that, add elements of A3 to A1 starting from index two and print the arraylist A1. This program will help you understand how to insert elements from a particular index.
Let us see some more examples of the addall() method.
Example #3
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class AddAllExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> A1 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 1
ArrayList<String> A2 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 2
//add element to arraylist 2
A2.add("Anabeth Denan");
//Combine the arraylist 1 and arraylist 2
A1.addAll(A2);
//print the combined list
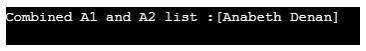
System.out.println("Combined A1 and A2 list :"+ A1);
}
}Output:
Explanation:
Create an arraylist A1 and A2. Then, add elements to A2 only. Print the elements after combining A1 and A2. Even if ArrayList A1 is empty, we can add elements of ArrayList A2 to A1.
Example #4
Code:
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
ArrayList<String> A1 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 1
//add elements to arraylist 1
A1.add("Izanorah Denan");
A1.add("Adam Sam");
A1.add("Annamu S");
A1.add("Naasy D");
A1.add("Thukidi D");
A1.add("Princy v");
ArrayList<String> A2 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 2
//add element to arraylist 2
A2.add("Anabeth Denan");
//Combine the arraylist 1 and arraylist 2
A1.addAll(A2);
//print the combined list
System.out.println("Combined A1 and A2 list :"+ A1);
ArrayList<String> A3 = new ArrayList<>(); //Array list 3
//add element to arraylist 3
A3.add("Riyan Jaykar");
A3.add("Kukku Chikku");
//Combine the arraylist 2 and arraylist 3 starting from first position
A2.addAll(1, A3);
//print the combined list
System.out.println("Combined A2 and A3 list :"+ A2);
}
}Output:

Explanation:
Create an arraylist A1 and A2. Then, add elements of A2 to A1 and print the arraylist A1. Once you have done this, create an ArrayList A3 and add elements to it. After that, add elements of A3 to A1 starting from index 1 and print the arraylist A1. Unlike the second program in this document, this program combines the ArrayList A2 and A3. While combining ArrayList A2 with A1, the original ArrayList A2 remains unchanged, as demonstrated in the provided sample output.
Conclusion
addAll() is a method in the arraylist of Java that helps append every element available in the argument collection to the list present at the end.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “addAll() in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


