Updated July 5, 2023
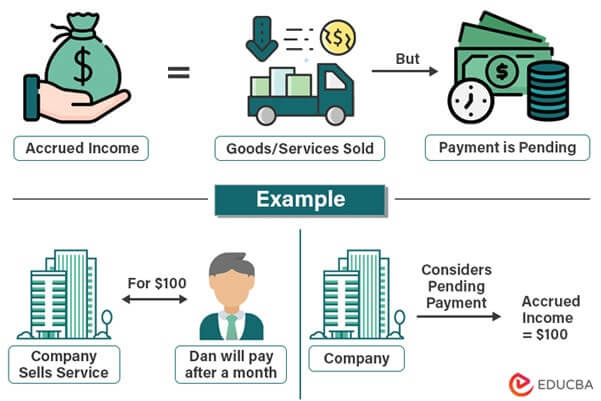
Accrued Income Meaning
Accrued Income in accounting is a crucial concept representing a company’s income during a specific period that it is yet to receive or invoice the customer. It follows the matching accounting principle, which requires companies to record revenues and expenses in the same accounting period they recognize them, regardless of when the business receives or makes the payment.
The concept is not limited to the rental, commission, or interest income but applies to any situation where a company has earned income but has not received payment.
For instance, a company provided consultancy services to a business but did not receive the payment immediately. However, the income still counts as earned, and the company will account for it as accrued income.
Sources
- Product/Service: When a business sells a product or a service, and the customer promises to make the payment in the future, the company documents the data as accrued revenue.
- Investment/loan: When an individual or business expects to receive returns from an investment or interest from a loan, they can consider it as accrual income.
- Real Estate: When property owners collect rent quarterly or yearly, they can record it as accrued revenue even before receiving the capital.
Accrued Income on Balance Sheet
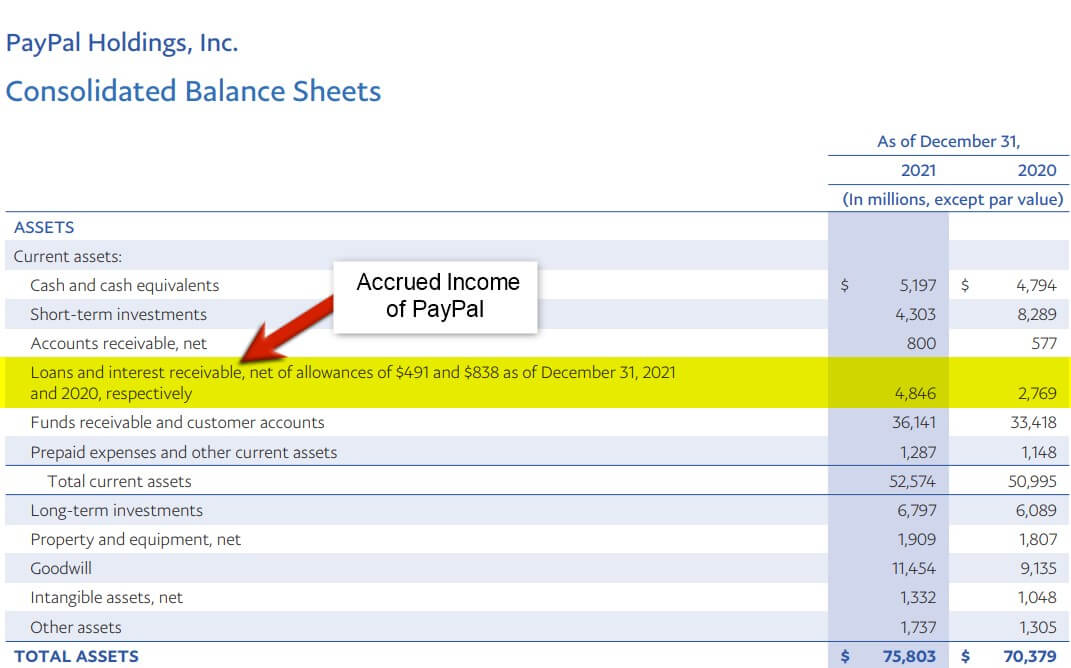
A company records its accrued income on its consolidated balance sheet. It is present under the current asset along with the accounts receivable. For example, in the balance sheet of Paypal Inc. for the financial year 2021, the accrued income (mentioned as net allowance) is $491 million. Similarly, for 2020, the revenue is $838 million.
(Source: PayPal Inc. Annual Report 2021)
How Does Accrued Income Work?
To better understand how accrued income works in business transactions, let’s explore the various steps involved in the process.
#1: Business Sells Product/Service:
A company produces and provides consumers with a product or service.
Example: A clothing business makes menswear, including suits, formals, and casuals.
#2: Customer Purchases From the Business:
The consumer either buys the product or receives the service from the business.
Example: An IT company purchases $500,000 worth of suits in March 2023 for an annual company meeting.
#3: Customer Does Not Make Immediate Payment:
After purchasing/receiving the goods or services from the company, the consumer promises to pay the bill at a future date.
Example: The IT company assures to pay the $500,000 to the clothing business by the beginning of June 2023.
#4: Business Records as Revenue:
The business has to recognize the pending payment as accrued income on the financial statement.
Example: The clothing company records the $500,000 as accrued revenue on its balance sheet, quarter ending March 2023.
Accrued Income Journal Entry
For recording the journal entry, the business debits the “Accrued Income” account and credits the “Income” account. Here is how companies register double journal entries:
Step #1: Determine the Income Amount
The business must first calculate the accrual receivable amount.
Example: A digital marketing agency generated $150,000 in March but received only $100,000. Thus, its yet-to-receivable amount is $50,000.
Step #2: Debit and Credit the Respective Accounts
The company records a debit of the receivable amount to the accrual account. Next, credit the same amount to a corresponding account. For instance, the related account for accrued rent will be accounts receivable.
Example: The agency records the $50,000 in the accounting book as follows:
$50,000 debit to Accrued Income and credit to Accounts Receivable.
|
Date |
Account | Debit |
Credit |
| 31 March 2023 | Accrued Income | $50,000 | |
| 31 March 2023 | Accounts Receivable | $50,000 |
Step #3: Record Final Entry for Received Capital
After the firm receives the pending payment, they make a journal entry, by debiting the accounts receivable and crediting the final receiving account, such as income or cash.
Example: The agency will receive the remaining balance by the end of May. So it will record the received amount as follows:
Credit the income account and debit the accounts receivable.
|
Date |
Account | Debit |
Credit |
| 31 May 2023 | Accounts Receivable | $50,000 | |
| 31 May 2023 | Income Account | $50,000 |
Accrued Income Examples
#1: Housing Company
Homes & Homes Pvt. Ltd. is a housing company that has several apartments in Dallas and gives apartments to its tenants on a rental basis. The company collects rent on a bi-monthly basis. Record a journal entry for the accumulated rental income.
Solution:
As Homes & Homes Pvt. Ltd collects rent bi-monthly, and the payment for the first month will count as accrued revenue since the amount is accounting for the first month. However, the company will get its payment in the next month only.
To record the rental income collected by Homes & Homes Pvt. Ltd., the accountant will need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the rental income for the first month
Homes & Homes Pvt. Ltd. rents apartments for $1,000 monthly. Thus, the rental income for the first month will be $1,000.
Step 2: Record the rental income
The rental income for the first month is accrued income. Thus, the entry will be as follows:
The company debits the Accrued Rental Income account for $1,000, representing the income for the first month. Then they credit the Rental Income Account for the same amount.
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| End of Month | Accrued Rental Income | $1,000 | |
| End of Month | Rental Income | $1,000 |
Step 3: Record the actual receipt of rental income
When Homes & Homes Pvt. Ltd. receives the payment for the first month in the next month, the accountant records it as an actual receipt of income. The journal entry will be as follows:
The business credits the Bank Account and debits the rental income account for $1,000.
| Date | Account | Debit | Credit |
| Mid of Month | Rental Income | $1,000 | |
| Mid of Month | Bank Account | $1,000 |
#2: Accounting Firm
Masterpay Ltd. receives interest on $300,000 from the bank every month at an interest rate of 2%. Masterpay’s account gets the current month’s payment in the first week of the following month. For instance, the interest income of March will come in April, and so on. Record a journal entry for the interest income.
Solution:
To record the interest income received from the bank, the accountant at Masterpay Ltd. will need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Determine the interest for the month
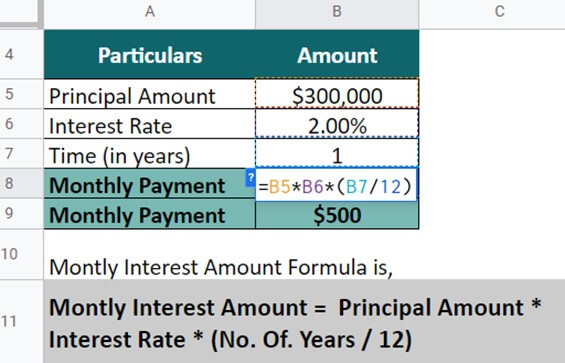
The bank offers a 2% interest rate per annum on a deposit of $300,000. Therefore, let’s calculate the monthly interest:
Monthly interest = Principal Amount * Interest Rate * (No. Of. Years / 12)
= $300,000 * 2 * (1/12)
= $500
The monthly interest amount is $500.
Step 2: Record the interest income in the books of accounts
As the interest income of the month gets credited in the first week of the next month, it records the payment as accrued. The entry for March will be as follows:
The accountant debits the Accrued Interest Income account for $500 and credits the Interest Income account.
|
Date |
Account | Debit |
Credit |
| 31 March 2023 | Accrued Interest Income | $500 | |
| 31 March 2023 | Interest Income | $500 |
Step 3: Record the journal entry for the final receipt of interest income
When Masterpay gets the interest income in April, the accountant records it as an actual receipt of payment. The entry for recording the receipt of interest income for March will be as follows:
The accountant debits the Interest Income Account for $500 and credits the bank account for the same amount.
|
Date |
Account | Debit |
Credit |
| 07 April 2023 | Interest Income | $500 | |
| 07 April 2023 | Bank Account | $500 |
Accrued Vs. Deferred Income
|
Particulars |
Accrued Income |
Deferred Income |
| Definition | It is the income that comes before payment and receipt. | The income comes after the amount or receipt of the revenue. |
| Payment Status | The income payment is still incomplete. | The income payment is already complete. |
| Advance Payments | It does not involve any advance payments. | It involves advance cash payments. |
| Impact | It leads to a decrease in the company’s expenses and an increase in revenue. | It leads to an increase in the company’s expenses and a decrease in revenue. |
| Financial Reporting | The company reports it at the time of sale but still awaits the payments. | These are first received and then reported in the later accounting period. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Differentiate between prepayments and accrued income.
Answer: Accrued income is primarily different from prepayments as it comes from already occurred events where the parties are yet to settle the cash transaction. On the contrary, prepayment income is from advanced cash payments for events yet to happen.
Q2. What is accrued income also known as?
Answer: Another accounting term for accrued income is outstanding income or accrued revenue.
Q3. Is accrued income an asset or liability?
Answer: Accrued income represents the future benefits of the company in the form of future cash flow. Therefore, it comes under the asset section of the balance sheet.
Q4. Is accrued income taxable?
Answer: Yes, accrued income is taxable. IRS states that revenue from accruals is taxable in the year it is recorded in the financial statement, regardless of when the business receives the payment.
Q5. What is the difference between accrued expenses and income?
Answer: Accrued income is the revenue a business recognizes on the balance sheet before it receives the payment. On the other hand, the accrued expense is the expense the company records while the company is yet to pay the amount.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Accrued Income. Here we also discuss the definition, how to record it, and its advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –