Updated July 4, 2023

Introduction to Abstraction in C#
Abstraction is an important part of Object-Oriented Programming. C# supports abstraction, a process of hiding implementation details and providing only essential information to the user. In C# we can achieve abstraction with the help of abstract classes and methods.
Following are some important points regarding abstract classes:
- We can define abstract classes and methods by prefixing the class name and the method name with the keyword abstract.
- We cannot create an object of an abstract class.
- An abstract class can contain abstract and non-abstract methods.
- An abstract class cannot be declared as a sealed class.
Syntax with Explanation:
We can declare abstract class and method with the help of the keyword abstract, as shown in below syntax:
//abstract class
abstract class class_name
{
//abstract method
public abstract <return_type> method_name();
}In the above syntax, we can see that the abstract method does not have anybody. The derived class provides an implementation of the abstract methods of an abstract class. We can access the abstract class by the class inherited from it.
We cannot declare abstract methods outside the abstract class, but an abstract class can contain non-abstract methods, as shown in the below syntax:
abstract class class_name
{
//abstract method
public abstract <return_type> method_name();
//non-abstract method
public <return_type> method_name()
{
//user code
}
}Examples of Abstraction in C#
Sometimes the user needs to create a generalized form of methods and properties in a superclass that can be shared by its entire subclasses, which can use these methods and properties according to their requirements by providing implementations to the methods accordingly.
Example #1
Code:
using System;
namespace abstraction
{
//abstract class
abstract class Shape
{
//abstract methods
public abstract double calculateArea();
public abstract void displayDetails(double area);
}
//Rectangle class inheriting Shape class
class Rectangle : Shape
{
//private data members
private double length;
private double breadth;
public Rectangle(double length, double breadth)
{
this.length = length;
this.breadth = breadth;
}
//overriding abstract methods of Shape class using 'override' keyword
public override double calculateArea()
{
return (length * breadth);
}
public override void displayDetails(double area)
{
Console.Write("Length of rectangle: "+length);
Console.Write("\nBreadth of rectangle: "+breadth);
Console.Write("\nArea of rectangle: "+area);
}
}
//Square class inheriting Shape class
class Square : Shape{
//private data members
private double side;
public Square(double side)
{
this.side = side;
}
//overriding abstract methods of Shape class using 'override' keyword
public override double calculateArea()
{
return (side * side);
}
public override void displayDetails(double area)
{
Console.Write("Length of a side of square: "+side);
Console.Write("\nArea of square: "+area);
}
}
public class AbstractionDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
double area;
//creating reference of Shape class using Rectangle class
Shape shapeRec = new Rectangle(5,6);
area = shapeRec.calculateArea();
shapeRec.displayDetails(area);
Console.WriteLine("\n");
//creating reference of Shape class using Square class
Shape shapeSquare = new Square(4);
area = shapeSquare.calculateArea();
shapeSquare.displayDetails(area);
}
}
}Output:
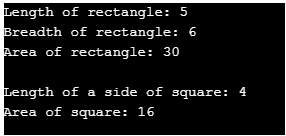
In the above example, both the methods defined under the abstract class ‘Shape’ are abstract methods. Thus, Shape is a pure abstract base class, and the derived class must provide an implementation for both methods of the Shape class.
Example #2
Code:
using System;
abstract class Mobile
{
public abstract void mobileDetails();
}
class Apple : Mobile
{
public override void mobileDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("Model: IphoneX");
Console.WriteLine("Screen size: 5.8 inch");
Console.WriteLine("Processor: A11 Bionic Processor");
}
}
class Motorola : Mobile
{
public override void mobileDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("Model: G5 plus");
Console.WriteLine("Screen size: 5.2 inch");
Console.WriteLine("Processor: octa-core Snapdragon");
}
}
public class AbstractionDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Mobile mobileApple = new Apple();
mobileApple.mobileDetails();
Console.WriteLine("");
Mobile mobileMoto = new Motorola();
mobileMoto.mobileDetails();
}
}Output:
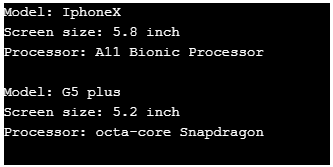
Example #3
An abstract class can also contain non-abstract methods, as shown in the below example.
Code:
using System;
namespace abstraction
{
abstract class Birds
{
//abstract method
public abstract void birdDetails();
//non-abstract method
public void canFly(bool canFly, string name)
{
if(canFly)
Console.WriteLine(name+" can fly");
else
Console.WriteLine(name+" cannot fly");
}
}
class Parrot : Birds
{
public override void birdDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("Parrots have different colours and size");
}
}
class Ostrich : Birds
{
public override void birdDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("Ostrich is the largest living bird");
}
}
public class AbstractionDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Birds birdParrot = new Parrot();
birdParrot.birdDetails();
birdParrot.canFly(true, "Parrot");
Console.WriteLine("");
Birds birdOstrich = new Ostrich();
birdOstrich.birdDetails();
birdOstrich.canFly(false, "Ostrich");
}
}
}Output:

Example #4
Apart from abstract classes and methods, we can achieve abstraction in C# using private access modifiers as shown in the below example.
Code:
using System;
namespace abstraction
{
public class Bank
{
private string name;
private string branch;
private string ifscCode;
public string Name
{
get { return name; }
set { name = value; }
}
public string Branch
{
get { return branch; }
set { branch = value; }
}
public string IfscCode
{
get { return ifscCode; }
set { ifscCode = value; }
}
public void bankDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("Bank name: " + Name);
Console.WriteLine("Branch name: " + Branch);
Console.WriteLine("IFSC code: " + IfscCode);
}
public void bankAddress()
{
Console.WriteLine("Address: Andheri, Mumbai");
}
private void numberOfAccounts()
{
Console.WriteLine("Account Information");
}
private void numberOfLockers()
{
Console.WriteLine("Locker Information");
}
}
public class AbstractionDemo
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Bank bank = new Bank();
bank.Name = "ABC";
bank.Branch = "XYZ";
bank.IfscCode = "ABC123";
bank.bankDetails();
bank.bankAddress();
//Error -'Bank.numberOfAccounts()' is inaccessible due to its protection level
//bank.numberOfAccounts();
//Error - 'Bank.numberOfLockers()' is inaccessible due to its protection level
//bank.numberOfLockers();
}
}
}Output:
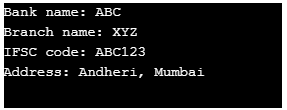
The above example shows that public methods can be accessed from other classes, but we cannot call private methods from other classes. Thus it helps achieve abstraction by providing the only necessary information and hiding other details.
Conclusion – Abstraction in C#
Abstraction in Object-Oriented Programming provides security by hiding implementation details and providing only necessary information to the user. We use an abstract class in which, with the help of abstract methods, we can hide implementation details. Abstraction can also be achieved using Interfaces.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Abstraction in C#” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


