What is Meta Learning?
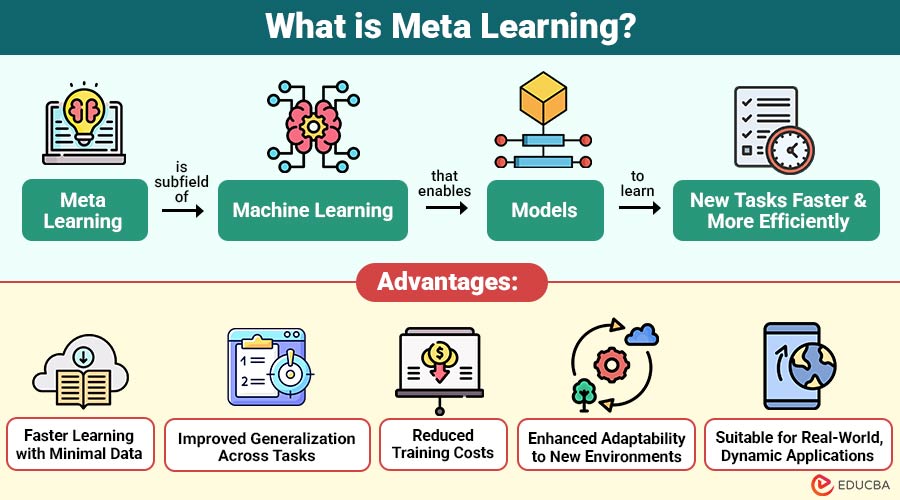
Meta learning is subfield of machine learning that enables models to learn new tasks faster and more efficiently. It focuses on optimizing the learning process itself, rather than just solving a specific problem.
In simple terms:
- Traditional ML: Learns to solve one task using data.
- Meta Learning: Learns how to learn tasks in general, enabling adaptation to unseen tasks quickly.
Meta learning typically involves two levels of learning:
- Base-level Learning: The model learns a specific task using task-specific data.
- Meta-level Learning: The model learns patterns or strategies across multiple tasks to improve future learning efficiency.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Meta learning enables models to quickly adapt to new tasks by learning general learning strategies.
- It focuses on improving the learning process itself, not just solving individual tasks efficiently.
- Base-level learning handles task-specific data, teaching the model how to solve particular problems effectively.
- It captures patterns across tasks, enhancing the model’s performance on unseen, future tasks.
Why is Meta Learning Important?
Here are the key reasons why it plays a important role in modern AI systems:
1. Faster Adaptation to New Tasks
Reduces the time and effort needed for retraining and fine-tuning by enabling models to swiftly adapt to previously unforeseen challenges.
2. Reduced Training Data Requirements
By leveraging prior knowledge, it minimizes the amount of labeled data needed, making learning efficient even in data-scarce environments without compromising performance.
3. Better Generalization Across Domains
Equips models to generalize effectively across different domains, allowing them to perform well on tasks that differ from their original training environments.
4. Improved Efficiency and Scalability
Increases computational efficiency and scalability by reusing learned strategies, enabling models to tackle multiple tasks without retraining from scratch.
5. Closer Resemblance to Human Learning Behavior
Mimics human cognitive processes by learning how to learn, allowing AI systems to acquire new skills and knowledge more naturally and flexibly.
How does Meta Learning Works?
Here’s a breakdown of how it functions, combining task-specific learning with overarching guidance:
1. Base Learner
The base learner is responsible for learning specific tasks.
- By concentrating on fixing the present problem, it functions similarly to a traditional machine learning model, like a decision tree or neural network.
- For example, if the task is image classification, the base learner learns to distinguish cats from dogs using the available training data.
- The base learner’s performance on individual tasks is crucial, as it provides the feedback the meta learner uses to improve overall learning strategies.
2. Meta Learner
The meta learner oversees and guides the base learner.
- Its goal is to learn how the base learner should learn, rather than solving tasks directly.
- It optimizes learning strategies, model parameters, or representations so that the base learner can adapt efficiently to new tasks.
- For instance, the meta learner might identify which features are most important or suggest optimal ways to update the base learner’s weights.
- Over time, the meta learner builds experience across multiple tasks, enabling faster adaptation and better generalization when encountering completely new tasks.
3. Interaction Between Base and Meta Learners
The base learner focuses on task-specific learning.
- The meta learner monitors the base learner’s progress and provides guidance, adjusting its learning process for efficiency and accuracy.
- This two-level approach allows the system to generalize to unseen tasks, even with limited data, quickly.
Types of Meta Learning
Meta learning methods can be broadly classified into three main types:
1. Model-Based Meta Learning
Model based meta learning leverages models with internal memory, such as recurrent networks or attention mechanisms, enabling rapid task-specific learning and efficient adaptation in few-shot learning scenarios.
Key Characteristics:
- Learns task-specific information rapidly
- Uses recurrent neural networks or attention mechanisms
- Suitable for few-shot learning scenarios
2. Metric-Based Meta Learning
Metric-based meta learning learns similarity or distance measures between data points, enabling efficient classification of new examples, especially when training data is limited, and often uses Siamese or Prototypical Networks.
Key Characteristics:
- Focuses on distance or similarity functions
- Effective for classification problems
- Works well with limited data
3. Optimization-Based Meta Learning
Optimization-based meta learning focuses on learning optimal model initialization or learning strategies that enhance gradient-based adaptation and enable models to quickly fine-tune for new tasks, as exemplified by MAML approaches.
Key Characteristics:
- Improves gradient-based learning
- Quickly fine-tunes models for new tasks
- Widely used in research and applications
Real-World Applications
Meta learning is transforming multiple industries by enabling AI systems to learn efficiently and adapt quickly. Here are some key applications:
1. Few-Shot Image Recognition
Enables image recognition systems to classify new objects with only a few labeled images, which is useful in medical imaging and satellite analysis.
2. Natural Language Processing
Used for language translation, text classification, and sentiment analysis when labeled data is scarce for new languages or domains.
3. Robotics
Robots use to adapt quickly to new environments, tasks, or objects without extensive retraining.
4. Healthcare
Helps build diagnostic models that adapt to different hospitals, patient demographics, or rare diseases.
5. Recommendation Systems
Personalized recommendations improve as systems learn user preferences faster with minimal interaction data.
Advantages of Meta Learning
It offers several key advantages that make AI systems more efficient, adaptable, and practical for real-world applications:
1. Faster Learning with Minimal Data
Allows models to quickly grasp new tasks using very limited data, significantly reducing training time and effort.
2. Improved Generalization across Tasks
By leveraging prior experience, meta-learning helps models perform effectively on diverse tasks beyond their original training domain.
3. Reduced Training Costs
Minimizes the computational resources and time required for retraining models, lowering overall deployment costs for AI systems.
4. Enhanced Adaptability to New Environments
Models trained with meta-learning can adapt seamlessly to changing conditions, tasks, or domains without extensive retraining or manual tuning.
5. Suitable for Real-World, Dynamic Applications
Ideal for real-world problems where tasks frequently change, requiring AI systems to adapt efficiently and reliably.
Limitations of Meta Learning
While it offers powerful benefits, it also comes with certain limitations and constraints:
1. Computationally Expensive During Meta-Training
Often demands high computational resources and time during the meta-training phase, making large-scale implementation challenging.
2. Complex Model Design and Tuning
Designing and fine-tuning meta-learning models is complex, requiring expertise in architecture selection, hyperparameter tuning, and optimization strategies.
3. Requires Diverse Task Distributions
Effective meta learning requires a wide variety of tasks during training to generalize well to unseen tasks.
4. Difficult to Interpret Learning Behavior
Understanding how meta learners make decisions is challenging, often limiting the transparency and interpretability of the learning process.
5. Not always Suitable for Simple Problems
For straightforward tasks, it can be unnecessary overhead, as traditional models may solve them more efficiently.
Final Thoughts
Meta Learning represents a significant shift in how machines acquire knowledge. By focusing on learning how to learn, models can adapt faster, generalize better, and perform more efficiently in data-scarce environments. Although complex and resource-intensive, its growing applications across industries highlight its importance in the future of artificial intelligence. As AI systems move toward autonomy and lifelong learning, it will remain a cornerstone technique for building smarter, more adaptable machines.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is meta learning the same as transfer learning?
Answer: No. Transfer learning reuses knowledge from one task, while meta learning focuses on learning the learning process itself across many tasks.
Q2. Does meta learning require large datasets?
Answer: Meta training may require many tasks, but each task usually has very little data.
Q3. Is meta learning used in deep learning?
Answer: Yes. It is often combined with deep neural networks to improve adaptability and performance.
Q4. Is meta learning suitable for beginners?
Answer: Meta learning is an advanced topic and requires prior knowledge of machine learning and deep learning fundamentals.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Meta Learning” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.