Consensus in AI: Building Reliable Decision-Making Systems
Artificial Intelligence has long promised to be a decision-making partner that is faster, smarter, and more objective than humans. Yet as AI systems expand across industries such as healthcare, finance, and legal analysis, an uncomfortable reality becomes clear: they are not infallible. Even advanced models can produce errors, sometimes with serious consequences. This is where Consensus in AI emerges as a powerful design principle. Rather than relying on a single model, consensus-driven AI systems bring multiple models or agents together to arrive at more reliable, transparent, and trustworthy decisions.
Why Consensus in AI Matters?
At its essence, consensus in AI is about aggregating independent judgments to produce reliable outcomes. Think of it as the computational equivalent of a jury or a scientific peer review panel. Instead of relying on a single model, a system can draw upon multiple sources, approaches, or agents, comparing their outputs and aligning on the most consistent result. This principle addresses a fundamental weakness of traditional AI: fragility.
A single model trained on one dataset may perform brilliantly under ideal conditions but fail catastrophically when faced with edge cases, biases, or adversarial inputs. Consensus offers a safeguard, reducing the probability that a single error compromises the system. The benefits extend beyond technical accuracy: consensus fosters trust, accountability, and interpretability. When multiple models agree, stakeholders have confidence in the decision. When they disagree, the system highlights uncertainty, signaling the need for human intervention. In this sense, consensus is not just a technical choice; it is a design philosophy for responsible AI.
Designing Systems Around Consensus in AI
Implementing consensus in AI requires intentional architecture. Several approaches have emerged as best practices:
1. Ensemble Models
By combining predictions from several models, ensemble approaches like Random Forests and Gradient Boosting produce more reliable results than any single model could. Each model contributes a perspective; collectively, they smooth out individual errors. This is a widely used strategy in both industry and research, consistently improving predictive performance while reducing variance.
2. Multi-Method Cross-Validation
Consensus is most powerful when it spans diverse methodologies. In natural language processing, for example, one could combine rule-based systems, statistical models, and deep learning approaches to generate candidate outputs. Comparing these outputs for consistency allows the system to identify the most reliable result, reducing reliance on a single paradigm and enhancing resilience to unforeseen inputs.
3. Multi-Agent Deliberation
Some advanced AI systems employ multiple agents that iteratively evaluate each other’s outputs. Each agent critiques, scores, or revises proposals from others. This mirrors human deliberation, where debate and review lead to more informed conclusions. Iterative multi-agent systems are particularly promising for high-stakes decision-making, where errors carry severe consequences.
4. Weighted Confidence and Thresholding
Teams can weight outputs based on model confidence, data quality, or historical reliability, and they finalize decisions only after reaching a predefined agreement threshold. This helps the system acknowledge uncertainty instead of hiding it, matching automated decisions with human expectations of responsibility.
Visualizing Consensus
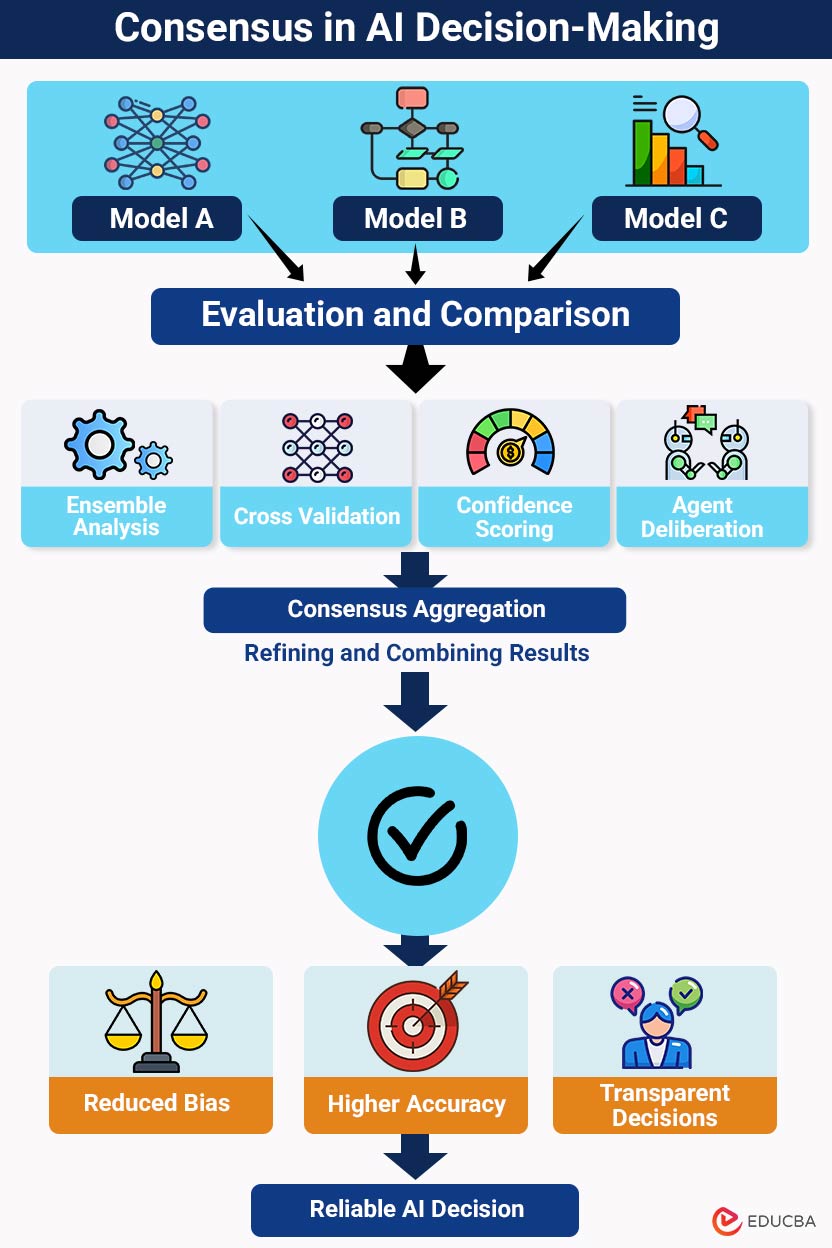
To visualize how multiple models and evaluation strategies combine to produce a reliable AI decision, see the diagram below:
Consensus in AI decision-making, aggregating multiple model outputs to reduce bias, improve accuracy, and produce transparent, reliable decisions.
Consensus as an Ethical Safeguard
Beyond improving accuracy, consensus is a powerful ethical tool. In applications like healthcare or criminal justice, decisions affect human lives. A single flawed model may inadvertently embed bias or misinformation. Consensus mitigates this risk by diluting individual model biases and flagging disagreements for review.
Moreover, consensus promotes transparency. Developers can trace which models agreed, which diverged, and why. Clear insight into how AI makes decisions is vital for regulators, auditors, and users to trust that outcomes are accurate and easy to explain.
A Practical Example: Consensus in AI Translation
Even in specialized domains, consensus proves its value. Consider AI-assisted language translation. Some modern AI translation tool, such as MachineTranslation.com, leverage consensus across multiple AI models to improve reliability. Their SMART feature, for instance, compares the outputs of 22 independent translation models and selects the version that most systems agree on. By aligning on the majority consensus at the sentence level, the system dramatically reduces the risk of errors, cutting translation mistakes by roughly 90%.
This illustrates a broader principle: consensus allows AI to self-validate. Instead of relying on a single model’s judgment, the system weighs multiple independent outputs, highlighting areas of agreement and uncertainty. The result is more robust, trustworthy decision-making across language translation, predictive analytics, and other high-stakes AI applications.
Challenges and Trade-Offs
Consensus is not a panacea. Implementing it can increase computational cost and complexity, particularly when combining many large models or iterative agents. There is also a risk of false consensus, in which models converge on a systematic error, leading to a misleading sense of certainty. Careful monitoring, validation, and integration of human oversight are crucial to ensure that consensus truly enhances decision quality.
Additionally, designers must thoughtfully structure consensus to balance speed, efficiency, and interpretability. In real-time systems, excessive deliberation among models may slow decision-making, while insufficient consensus can undermine reliability. The key is strategic integration, designing systems that are resilient, agile, and accountable.
The Future: Consensus as a Foundational AI Principle
Consensus represents a paradigm shift in AI design. Instead of pursuing singular, “superior” models, we embrace collective intelligence, leveraging diversity in models, data, and methods to achieve dependable outcomes. This philosophy mirrors the best practices in human knowledge production: debate, peer review, and collaborative validation.
Consensus may emerge as a benchmark for moral, reliable AI as well as a technical optimization as AI systems grow increasingly integrated into important facets of society. It is a principle that addresses accuracy, bias, and transparency in one integrated framework, providing a blueprint for AI that can be relied upon, understood, and held accountable.
Final Thoughts
Consensus in AI is more than an engineering technique it is a design philosophy that aligns artificial intelligence with human standards of judgment, reliability, and ethics. By enabling AI systems to reason collectively, weigh multiple perspectives, and transparently signal uncertainty, consensus-driven approaches address many of AI’s most persistent challenges. In a world where AI influences decisions that shape lives and societies, embracing Consensus in AI may be the most important design choice we can make.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide on Consensus in AI helps you understand how collective intelligence enables reliable, ethical decision-making. Explore these recommended articles for more insights and strategies on building trustworthy AI systems.