What is API Management?
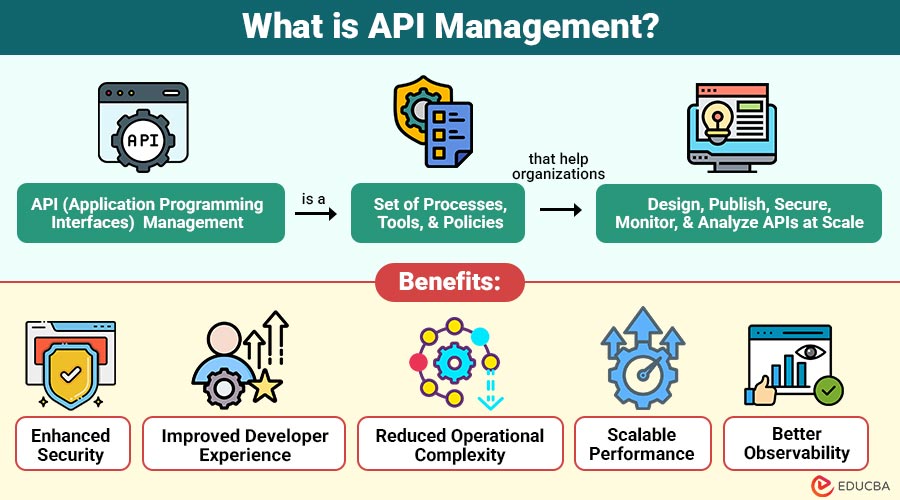
API (Application Programming Interfaces) Management is set of processes, tools, and policies that help organizations design, publish, secure, monitor, and analyze APIs at scale. It provides governance and control across the entire API lifecycle—from creation to retirement—ensuring APIs are reliable, secure, discoverable, and optimized for performance.
API management typically includes:
- API gateways
- Developer portals
- Security and access control
- Analytics and monitoring
- Monetization and documentation
- Policy enforcement
- Lifecycle governance
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Why does API Management Matter?
- Key Components
- Working
- Benefits
- Use Cases
- Real-World Examples
- Tools
- Challenges
Key Takeaways:
- API management ensures secure, governed, and consistent API operations across their entire lifecycle for reliable digital experiences.
- Using gateways, analytics, and portals, organizations enhance performance, security, and developer productivity across all APIs.
- Centralized rules, monitoring, and version control make systems easier to manage and help the whole organization scale and work more efficiently.
- Effective API management accelerates innovation by enabling seamless integrations, microservices communication, and efficient partner collaboration.
Why does API Management Matter?
As businesses grow digitally, they expose more data and functionalities through APIs. Without proper management, APIs can lead to:
1. Security Vulnerabilities
APIs without proper security controls expose sensitive data and increase risks of unauthorized access and breaches.
2. Performance Bottlenecks
Unmanaged APIs can overwhelm backend systems, leading to slow responses, delays, and a worse user experience.
3. Poor Developer Experience
Lack of documentation, standards, and tools makes API usage difficult, slowing integration and frustrating development teams.
4. Governance Issues
Without central control, APIs can be messy, confusing, hard to manage, and may repeat work or have more mistakes.
5. Lack of Visibility and Tracking
Missing analytics reduces insight into API usage, performance issues, failures, and opportunities for optimization.
Key Components of API Management
A fully functional API management platform includes the following:
1. API Gateway
An API Gateway controls all requests to your APIs. It directs traffic, keeps data safe, limits excessive requests, updates data as needed, stores responses for faster access, and balances load across servers.
2. Developer Portal
A Developer Portal offers documentation, testing tools, API keys, and learning materials to make integrations easier and help developers get started faster.
3. API Security
API security protects data and endpoints using OAuth, JWT, TLS, access controls, threat detection, and encryption.
4. API Monitoring and Analytics
Monitoring and analytics keep track of delays, errors, traffic, usage, and revenue data to boost performance and spot problems early.
5. API Lifecycle Management
6. Monetization
API monetization enables revenue models like subscriptions, pay-per-use, tiers, and quotas for commercial API products.
How does API Management Work?
API management architecture typically follows this flow:
1. API Provider
The API provider designs, develops, and publishes APIs, effectively defining functionality, policies, versions, and lifecycle responsibilities.
2. API Gateway
An API Gateway keeps APIs safe by checking who can access them, controlling traffic, directing requests, limiting request rates, and applying consistent rules.
3. Developer Portal
4. API Consumers
API consumers, including applications, partners, and customers, securely access published APIs to perform required operations.
5. Analytics Engine
The Analytics Engine continuously tracks API performance, usage patterns, errors, latency, and operational insights to improve scalability.
6. Admin Console
Admin Console efficiently manages API configurations, governance, policies, versioning, deployment workflows, and system-wide administrative controls.
Benefits of API Management
Here are some key benefits of API Management in detail:
1. Enhanced Security
Standardized authentication, encryption, threat detection, and access control make APIs safer and protect sensitive organizational data.
2. Improved Developer Experience
Self-service portals, interactive documentation, and testing tools simplify API usage, accelerating development and reducing support needs.
3. Reduced Operational Complexity
Centralized governance makes it easier to set rules, manage updates, track versions, and control APIs, reducing confusion in complex systems.
4. Scalable Performance
API gateways use caching, throttling, and load balancing to manage increasing traffic and maintain performance efficiently.
5. Better Observability
Analytics tools provide visibility into API usage, errors, latency, and trends, helping teams optimize performance effectively.
Use Cases of API Management
Here are the major use cases where API management plays a crucial role:
1. Digital Transformation
Enterprises modernize legacy systems by securely exposing core functionality through API gateways, enabling seamless digital transformation.
2. Microservices Architecture
Microservices use an API gateway to direct requests, enforce security, handle more users, control traffic, and apply rules in a single place.
3. Partner Integrations
Businesses safely share APIs with external partners such as payment processors, shipping companies, and distributors to work together smoothly.
4. Mobile App Backend
Mobile apps use APIs to log in users, fetch data, handle transactions, send notifications, and communicate reliably with backend systems.
5. Banking and Open Finance
Banks use API management to comply with open banking regulations and enable secure financial data sharing across ecosystems.
6. eCommerce Platforms
APIs integrate catalog, checkout, inventory, payments, shipping, and recommendation services to deliver seamless eCommerce customer experiences.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world companies demonstrating effective use of API management:
1. Airbnb
Airbnb leverages API management to integrate booking, payment, and property management systems across multiple platforms and partners.
Outcome: Smooth booking processes, secure payments, and real-time availability updates across web and mobile platforms.
2. PayPal
Manages developer access and payment integrations through an API management platform.
Outcome: Smooth partner onboarding and secure financial transactions.
3. Uber
Uber uses APIs to connect riders, drivers, maps, payments, and real-time tracking across mobile and web applications.
Outcome: Efficient ride-hailing operations with reliable performance, seamless integrations, and accurate location-based services.
Popular API Management Tools
Here are some widely used API management tools that support full lifecycle governance and scalability:
1. Apigee (Google Cloud)
Apigee helps businesses manage APIs effectively, offering tools for analytics, security, revenue tracking, rule enforcement, and flexible setup.
2. AWS API Gateway
AWS API Gateway is fully managed, integrates with Lambda, scales efficiently, and suits serverless or microservices architectures.
3. Azure API Management
Azure API Management effectively supports hybrid environments and provides developer portals, strong policy control, analytics, and enterprise-focused capabilities.
4. Mulesoft Anypoint Platform
MuleSoft combines integration and API management, letting you connect systems via APIs while managing their full lifecycle from one central place.
5. IBM API Connect
IBM API Connect offers secure, scalable API management, designed for industries with strict regulations that require strong governance.
Challenges in API Management
Here are the key challenges organizations commonly face when managing APIs at scale:
1. Complex Governance
Large enterprises manage hundreds of diverse APIs, making consistent governance, policy enforcement, and oversight extremely challenging.
2. Security Vulnerability
Poorly set up API security can leak sensitive data, making it easier for hackers to break in or steal information.
3. Versioning Conflicts
Maintaining backward compatibility becomes difficult as APIs evolve, causing integration issues for existing consumers and applications.
4. Performance Issues
Poorly optimized gateways or heavy policies introduce latency, degrading API response times and overall application performance.
5. High Costs
Enterprise-grade API management platforms are expensive because they need costly licenses, hardware or cloud resources, and ongoing maintenance, which raises overall company costs.
Final Thoughts
API management is essential for modern digital businesses, providing secure, governed, and scalable handling of APIs. APIs enable integrations, microservices, and digital transformation, and effective management ensures they are reliable, fast, and easy to find. API management uses tools like gateways, developer portals, and analytics to make development faster, keep APIs secure, and help technology support business goals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is API Management the same as API Gateway?
Answer: No. A gateway is part of API management, but API management includes many more capabilities, such as portals, analytics, monetization, and governance.
Q2. Who uses API management?
Answer: Developers, architects, product managers, DevOps teams, and enterprise IT teams.
Q3 Can API Management support monetization?
Answer: Yes—many platforms provide billing, usage quotas, and subscription management.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “API Management” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
