What Is a Small Business?
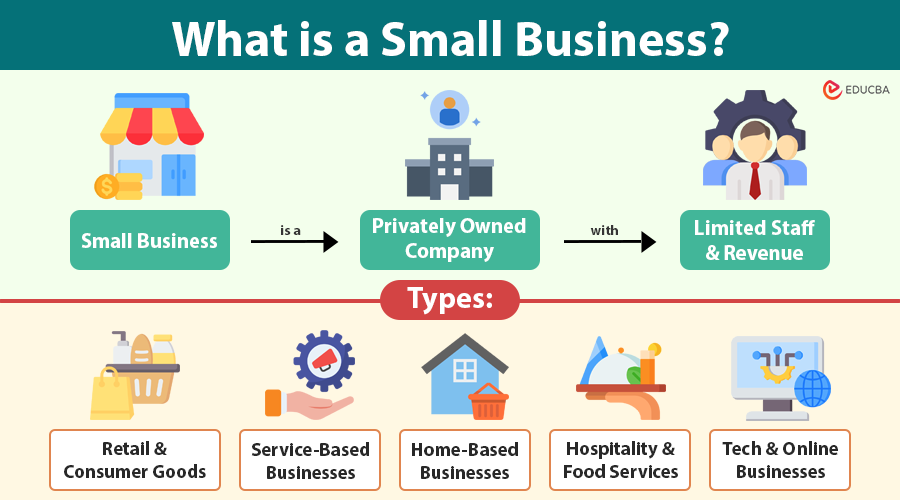
A small business is a privately owned company that operates with a limited number of employees and relatively low revenue compared to larger enterprises. Governments define small businesses differently, but most criteria include factors like employee count, annual turnover, and investment levels.
Small businesses typically include local shops, service providers, startups, freelancers, home-based companies, and specialized niche firms. These businesses often focus on personalized service and community-centric operations.
Table of Content
Key Takeaways
- Small businesses are essential to the economy, providing jobs, supporting communities, and promoting innovation.
- They exist in various forms, such as retail, service-based, home-based, hospitality, and tech-driven models.
- Successful small businesses focus on clear goals, customer satisfaction, financial discipline, adaptability, and effective technology use.
- Common challenges include limited funding, high competition, cash flow issues, hiring difficulties, and restricted marketing budgets.
- The future of small businesses depends on digital adoption, sustainability, customer experience, and growing government support.
Why Small Businesses Matter?
Small businesses are essential for supporting both local communities and the overall economy. Here is why they are so valuable:
1. Job Opportunities for Local People
Small businesses provide many people with their first jobs and support local workers. By hiring from nearby areas, they reduce unemployment and help families earn a stable income.
2. Fresh Ideas and New Solutions
Small businesses often try new things, whether it is a unique product, a fresh service, or a different way of doing business. Because they can make decisions quickly, they easily adapt to what customers want.
3. Boost to the Local Economy
When people buy from small shops or local service providers, the money stays in the community. Business owners then spend that money on local suppliers, workers, and services, which helps the entire area grow.
4. Personal and Trust-Building Service
Small business owners talk directly to their customers, understand their needs, and offer personal attention. This creates trust, loyalty, and a warm customer experience that big companies often can not match.
5. More Choices and Fair Competition
Small businesses offer alternatives to big brands. Because of them, customers get more choices, better quality, and reasonable prices. Their presence prevents any one company from dominating the whole market.
Types of Small Businesses
Small businesses come in many forms, depending on what they sell, how they operate, and the needs they fulfill. Here are some of the most common and important types:
1. Retail and Consumer Goods
These businesses sell physical products that people need in their daily routine. They operate from small shops, kiosks, or local marketplaces. Retail stores help customers by providing quick access to goods without requiring them to travel far. They also improve the local shopping experience through personal attention and convenience.
2. Service-Based Businesses
These businesses earn income by providing services rather than selling products. They depend on skill, expertise, and customer trust. Because service businesses do not require large inventories or heavy investment, they are easier to start and manage.
3. Home-Based Businesses
These businesses run from home or a small workspace. They are affordable to start, offer flexible working hours, and suit individuals who prefer to work independently. Many of these ventures begin part-time and grow into full-time income sources.
4. Hospitality and Food Services
These businesses revolve around serving food, offering accommodation, or improving the travel and stay experience. They depend heavily on service quality, hygiene, and customer satisfaction. Many of them attract tourists and support local culture.
5. Tech and Online Businesses
These businesses use digital tools, apps, and websites to offer products or services. They can operate with small teams and reach customers from anywhere. Tech and online businesses often grow quickly because they can scale operations faster than traditional stores.
Key Characteristics of Successful Small Businesses
Successful small businesses share certain qualities that help them grow, stay competitive, and build strong customer relationships.
1. Clear Vision and Purpose
Successful small businesses know exactly what they want to achieve. They set clear goals, understand their target audience, and define their unique value. This clarity helps them stay focused, make better decisions, and build a strong market identity.
2. Strong Customer Focus
They place customers at the center of everything they do. By delivering consistent service, listening to feedback, and solving problems quickly, these businesses build long-term trust and loyalty. A satisfied customer often returns and recommends the company to others.
3. Effective Financial Management
Money management plays a major role in long-term success. Owners monitor cash flow, avoid unnecessary expenses, and carefully plan their budgets. They also make smart investments that help the business grow, such as training, equipment, or marketing.
4. Adaptability and Flexibility
Successful businesses respond quickly to market changes. Whether it is a new trend, customer demand, or economic shift, they adjust their products, pricing, or strategies without delay. This flexibility keeps them competitive and relevant.
5. Smart Use of Technology
They use modern tools to work faster and more efficiently. This includes accounting software, digital marketing tools, online payment systems, automation, and e-commerce platforms. Technology helps small businesses save time, reduce errors, expand their reach to customers, and operate more smoothly.
Common Challenges Small Businesses Face
Small businesses face several obstacles that can make growth and sustainability difficult. Understanding these challenges helps owners plan better and find effective solutions.
1. Limited Access to Funding
Many small businesses find it hard to get loans or attract investors because they may lack collateral, credit history, or a proven track record. Limited funds can restrict expansion, marketing, or even day-to-day operations.
2. Intense Competition
Small businesses often compete with large corporations, online marketplaces, and other local businesses. High competition can make it harder to attract customers, maintain prices, and stand out in the market.
3. Cash Flow Problems
Inconsistent sales or delayed customer payments can cause cash flow issues. High expenses, such as rent, salaries, and inventory costs, make managing daily operations challenging.
4. Difficulty in Finding Skilled Employees
Small businesses may struggle to hire and retain skilled workers. Limited budgets, fewer benefits, and less recognition compared to larger companies can make recruitment challenging.
5. Marketing and Promotion Constraints
Without a large budget or marketing team, small businesses find it difficult to reach their target audience. Limited visibility can slow growth, reduce customer engagement, and affect sales.
Growth Strategies for Small Businesses
Small businesses can grow and succeed by adopting smart strategies that attract more customers, improve operations, and increase revenue.
1. Build a Strong Online Presence
A website, social media accounts, Google Business listing, and online ads help businesses reach more customers. Online visibility allows small businesses to showcase products, share updates, and attract local and global buyers.
2. Focus on Customer Retention
Retaining loyal customers is generally more affordable than attracting fresh customers. By offering excellent service, loyalty programs, and personalized attention, small businesses can maintain steady revenue and encourage repeat purchases.
3. Expand Product or Service Offerings
Adding new products or services can attract more customers and increase sales. Businesses can identify customer needs, explore complementary offerings, and test small additions to grow gradually.
4. Collaborate with Other Businesses
Partnerships, referrals, and joint promotions help small businesses reach a wider audience without heavy investment. Collaborations can include cross-promotions, co-hosted events, or shared marketing campaigns.
5. Invest in Branding
A strong brand identity builds trust and makes a business memorable. Consistent logos, colors, messaging, and customer experience differentiate the company from competitors and attract loyal customers.
6. Use Data to Make Smarter Decisions
Monitoring sales, customer actions, and market patterns helps generate insights that lead to smarter business decisions. Small businesses can analyze what works, identify gaps, and adjust strategies to improve efficiency and growth.
The Future of Small Businesses
Small businesses are changing fast, and the future will bring new opportunities and challenges.
1. Technology Will Shape Business
- Small businesses will use digital tools, AI, automation, and e-commerce platforms to work more efficiently.
- Online marketing and social media will help them reach more customers and compete with bigger companies.
2. Focus on Customers and Sustainability
- Businesses that provide personalized service and care about sustainability will attract loyal customers.
- Using both online and offline methods (a hybrid model) will help small businesses grow.
3. Support from Governments and Banks
- Governments offer grants, training programs, and incentives to help small businesses succeed.
- Easier access to loans and credit will allow entrepreneurs to expand and innovate.
4. Opportunities for Growth
- Small businesses that adopt new technology, respond to customer needs, and use available support will succeed.
- Flexible and forward-thinking companies will contribute more to local and national economies.
Final Thoughts
Small businesses remain vital to local communities and the economy, offering jobs, fresh ideas, and personalized services. Although they face challenges such as limited funding and strong competition, they can overcome these obstacles by using technology, managing finances wisely, and focusing on customer satisfaction.
With increasing support from government programs and digital advancements, the future looks promising for small enterprises. Those who adapt quickly, innovate consistently, and understand customer needs will continue to grow and make a strong impact at both the local and national levels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Q1. How much money do I need to start a small business?
Answer: The amount varies based on the business type. Service and home-based businesses need low investment, while retail or food-related ventures require higher startup and operating costs.
Q2. Do I need to register my small business legally?
Answer: Yes. Depending on your business structure, you may need to register as a sole proprietorship, a partnership, an LLP, or a private limited company. Some businesses also require GST registration and local permits.
Q3. What taxes do small businesses need to pay?
Answer: Small businesses must track income and expenses and file tax returns in accordance with government rules. Some may need to pay GST, income tax, and other applicable local taxes.
Q4. How can I promote my small business on a low budget?
Answer: Using social media, Google Business listing, referrals, partnerships, and word-of-mouth marketing are effective, low-cost ways to reach more customers.
Q5. What documents do I need to keep for my small business?
Answer: Keep records of sales, expenses, invoices, tax filings, employee details, and inventory. Good documentation helps with financial planning, audits, and business growth.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on Small Businesses gave you a clear understanding of their importance, challenges, and growth opportunities. Explore the related articles below to learn more about entrepreneurship, business management, and digital strategies that can help small business owners grow and succeed.