What is Geofencing?
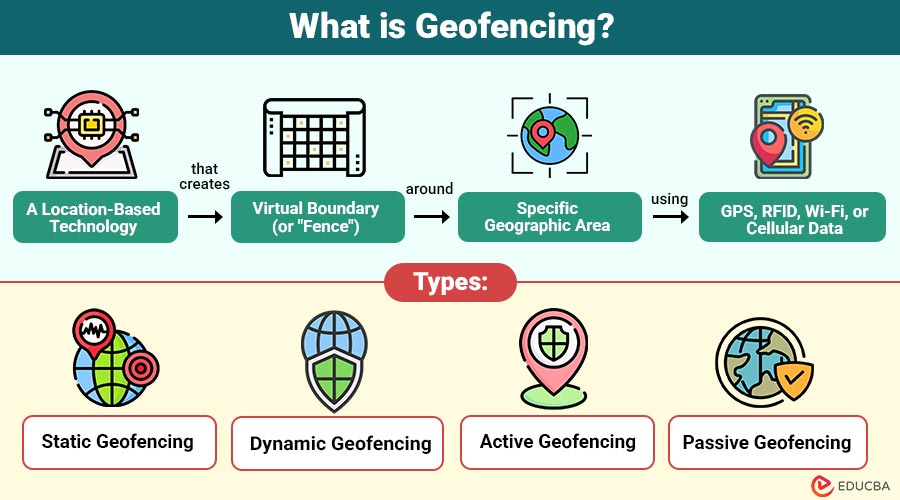
Geofencing is location-based technology that creates virtual boundary (or “fence”) around specific geographic area using GPS (Global Positioning System), RFID (Radio Frequency Identification), Wi-Fi, or cellular data. When a device, such as a smartphone or a GPS-enabled tracker, enters or exits this boundary, a predefined action is triggered automatically.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Geofencing bridges digital intelligence with real-world actions through automated, location-triggered responses.
- It empowers businesses to deliver context-aware engagement, improving customer experience and operational visibility.
- Effective geofencing relies on ethical data practices and transparent user consent for location tracking.
- From marketing to security, geofencing transforms industries by merging mobility insights with automation precision.
How Does Geofencing Work?
The functioning involves three main components—location data, defined boundaries, and triggers.
1. Setting the Virtual Boundary
A boundary or perimeter is digitally defined around a real-world area using tools like Google Maps, mapping APIs, or GPS coordinates. The boundary can be a radius (e.g., 500 meters around a store) or a polygon covering a custom area.
2. Device Detection
Mobile devices or tracking systems use location-tracking technologies (like GPS or cellular data) to monitor when they enter or leave the designated boundary.
3. Triggering an Action
When a device crosses the virtual fence, the system performs a predefined action, such as sending a notification, alerting security personnel, logging entry/exit, or initiating marketing campaigns.
Types of Geofencing
It can be categorized based on its trigger type and purpose.
1. Static
A fixed virtual boundary around a physical location (e.g., a store or warehouse). The location does not change.
2. Dynamic
Boundaries change dynamically based on the user’s movement or location data (used in ride-hailing apps or delivery tracking).
3. Active
Requires users to keep location services or GPS turned on, ensuring real-time tracking accuracy.
4. Passive
Uses cellular or Wi-Fi data and consumes less power, but provides less precision compared to active tracking.
Applications of Geofencing
It has widespread applications across industries.
1. Marketing and Advertising
Enables businesses to send location-based offers or alerts to customers in the vicinity, thereby enhancing engagement and conversions.
2. Transportation and Fleet Management
Fleet operators track vehicle routes and receive alerts for deviations or arrivals, improving logistics efficiency and delivery accuracy.
3. Security and Access Control
Helps restrict access to secure areas and automates safety measures when users enter or exit predefined zones.
4. Employee Management
Organizations use geofencing for workforce tracking, verifying employee attendance, and ensuring staff operate within assigned geographic boundaries.
5. Smart Homes and IoT
Connected devices adjust automatically based on user location, enhancing comfort, energy efficiency, and home automation convenience.
6. Healthcare
Safeguards patients by alerting caregivers when individuals, especially those with dementia, move beyond designated safe areas.
7. Education
Schools enhance safety and communication by tracking buses and notifying parents when students arrive or leave school premises.
Benefits of Geofencing
Here are the key benefits that make geofencing a powerful tool for businesses and organizations:
1. Enhanced Personalization
Enables highly targeted marketing by sending offers or messages based on a user’s location, thereby improving engagement and conversion rates.
2. Operational Efficiency
Businesses can monitor field workers, deliveries, or assets in real time, ensuring better control and resource optimization.
3. Improved Security
By defining restricted zones, organizations can prevent unauthorized access and enhance workplace safety.
4. Data Collection and Analytics
Provides valuable insights into consumer behavior, traffic patterns, and movement trends.
5. Increased Customer Engagement
Timely notifications and location-based offers boost customer interaction and brand loyalty.
Limitations of Geofencing
Despite its numerous advantages, it has certain limitations:
1. Privacy Concerns
Continuous location tracking raises privacy issues and may lead to user distrust if not handled transparently.
2. Battery Consumption
Active geofencing requires GPS usage, which can quickly drain mobile device batteries.
3. Accuracy Issues
Environmental factors, such as tall buildings or weak GPS signals, can affect tracking precision.
4. Cost and Technical Complexity
Developing and maintaining geofencing systems can be expensive, particularly for small businesses.
5. User Permission
Geofencing relies on user consent for location sharing; without it, the system cannot function effectively.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable real-world examples that showcase the effectiveness of geofencing technology:
1. Burger King’s “Whopper Detour” Campaign
Burger King launched a campaign that offered customers a one-cent Whopper when they entered a geofence set around McDonald’s locations. The campaign was a viral success, driving massive app downloads and engagement.
2. Uber
Uber uses geofencing at airports and event venues to streamline pickup zones and notify drivers of available passengers in specific areas.
3. Home Automation
Smart home systems, such as Google Home or Amazon Alexa, can utilize geofencing to automate actions—turning lights on when users arrive home or activating security when they leave.
Final Thoughts
Geofencing revolutionizes how businesses engage with customers, employees, and assets by combining digital precision with real-world context. It enables targeted promotions, enhanced security, and efficient logistics through real-time location insights. To fully leverage its power, organizations must strike a balance between personalization and privacy. As location intelligence advances, it emerges as a cornerstone of smart automation and contextual marketing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main purpose of geofencing?
Answer: The main purpose of geofencing is to create virtual boundaries around physical locations to trigger automated actions based on movement within or outside the area.
Q2. How accurate is geofencing?
Answer: Geofencing accuracy depends on the technology used. GPS-based geofencing can be accurate within 5–20 meters, whereas Wi-Fi or cellular-based systems may have varying accuracy.
Q3. Is geofencing legal?
Answer: Yes, geofencing is legal, but it must comply with privacy laws such as CCPA or GDPR, and users must give explicit consent for location tracking.
Q4. What industries use geofencing the most?
Answer: Marketing, logistics, transportation, real estate, and security are the most common industries using geofencing technology.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Geofencing” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
