What is Geotargeting?
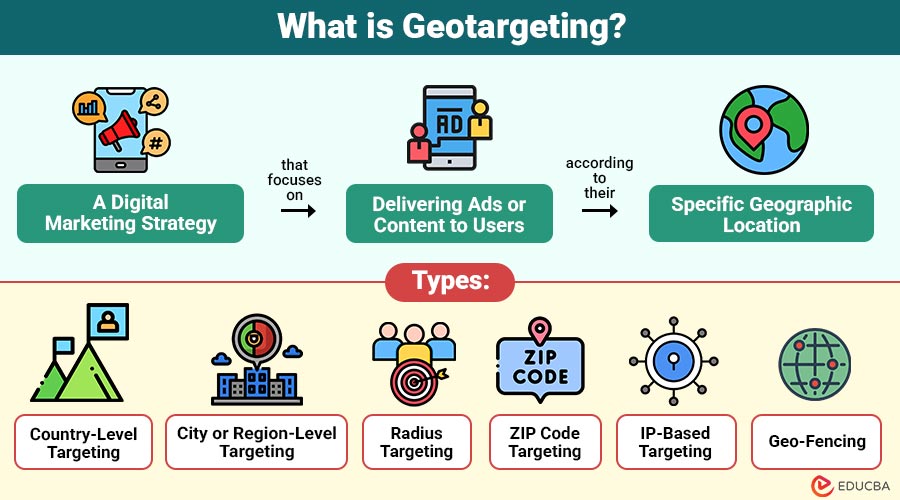
Geotargeting is a digital marketing strategy that focuses on delivering ads or content to users according to their specific geographic location. This location can be determined through technologies like IP addresses, GPS data, Wi-Fi connections, and mobile device tracking.
For example, if you own a restaurant in Mumbai, you can use geotargeting to show ads only to users located within Mumbai. This helps you avoid wasting cash on far-off customers by concentrating your marketing efforts on those who can really visit your restaurant.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Geotargeting enables marketers to deliver personalized ads based on precise user location data.
- It improves marketing ROI by focusing ad spend on audiences within specific, high-potential geographic areas.
- Combining geotargeting with demographic and behavioral filters creates more accurate and impactful campaigns.
- Despite its benefits, geotargeting requires careful planning to overcome privacy, accuracy, and regulatory challenges.
How does Geotargeting Work?
Geotargeting uses location-detection technologies to identify where a user is accessing digital content. Once the system detects the location, it matches the user’s geographical data with the predefined criteria set by the advertiser or marketer.
Here is a breakdown of how it works:
1. Location Detection
The user’s location is determined using sources such as:
- IP address
- GPS data (from mobile devices)
- Cell tower triangulation
- Wi-Fi positioning
2. Data Processing
The system matches this location data with the marketer’s targeting rules. For instance, if you target a campaign at “New York City,” only users in that area will see the ad.
3. Ad or Content Delivery
The user receives customized ads, offers, or web content relevant to their current location.
4. Performance Tracking
Marketers analyze performance metrics such as impressions, clicks, and conversions based on geographic regions to optimize future campaigns.
Types of Geotargeting
Geotargeting can be implemented in various ways, depending on the campaign goal and the technology used. The main types include:
1. Country-Level Targeting
This involves targeting users in a specific country. Businesses commonly use it for international campaigns, e-commerce platforms, and brands targeting global audiences.
2. City or Region-Level Targeting
Businesses can target specific cities, states, or regions. This is ideal for companies with localized services, such as car rentals or regional retailers.
3. Radius Targeting (Proximity Targeting)
This technique targets users within a specific radius from a business location — such as 5 km around a retail store or restaurant.
4. ZIP Code Targeting
Ads are shown only to users within specific ZIP or postal codes. This approach is particularly useful for hyperlocal businesses, such as salons or repair services.
5. IP-Based Targeting
This targets users based on their IP address. Although less precise than GPS, it is effective for desktop campaigns.
6. Geo-Fencing
Geo-fencing surrounds a physical site with a virtual barrier. When users enter or exit that boundary, they receive specific notifications or ads.
Benefits of Geotargeting
Implementing geotargeting in marketing campaigns brings several benefits. Here are the most impactful ones:
1. Higher Relevance
Geotargeting ensures users see location-relevant ads or content, increasing engagement, interest, and the likelihood of making a purchase.
2. Cost Efficiency
By focusing on target regions only, marketers reduce wasted ad spend, optimize budgets, and achieve higher returns on investment (ROI).
3. Improved Conversion Rates
Localized campaigns connect more effectively with users’ needs, resulting in higher click-through rates, increased customer engagement, and improved overall conversion success in marketing efforts.
4. Enhanced Customer Experience
Delivering personalized, location-based offers enhances user satisfaction, creating meaningful interactions and stronger connections between customers and brands.
5. Effective Local Marketing
Geotargeting drives store visits, strengthens community presence, and helps brick-and-mortar businesses effectively engage nearby audiences through tailored promotions.
Use Cases of Geotargeting
Geotargeting is used across industries. Some common examples include:
1. Retail and Restaurants
Geotargeting helps retail stores and restaurants attract nearby customers by sending location-based promotions, offers, or real-time push notifications.
2. E-commerce
Online retailers utilize geotargeting to display region-specific pricing, local shipping options, and personalized product recommendations tailored to each customer’s location.
3. Tourism and Hospitality
Travel companies, hotels, and resorts use geotargeting to promote nearby accommodations, attractions, and travel deals to tourists in specific destinations.
4. Event Marketing
Event organizers use geotargeting to advertise concerts, festivals, or sports events to people located near the event venue or city.
5. Real Estate
Real estate agents effectively leverage geotargeting to reach potential buyers or renters in specific neighborhoods, cities, or property investment zones.
6. Healthcare
Hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies use geotargeting to promote healthcare services, vaccination drives, or emergency care options to nearby residents.
How to Implement Geotargeting?
Here are some practical tips for marketers:
1. Define Clear Location Goals
Identify the exact geographic areas—countries, cities, or neighborhoods—you want to target to align campaigns with specific audience locations.
2. Use Location-Based Keywords
Incorporate relevant local search terms, such as “best pizza in New York,” to attract potential customers searching within specific regions.
3. Leverage Google Ads and Meta Ads Tools
Utilize advanced geotargeting features on Google Ads and Meta Ads to deliver highly localized campaigns and track performance efficiently.
4. Customize Content for Each Location
Create location-specific visuals, messaging, and offers that reflect regional preferences, language, and culture to enhance audience connection and engagement.
5. Monitor Analytics
Continuously track engagement, click-through rates, and conversion metrics for different regions to measure success and refine targeting strategies effectively.
6. Combine with Other Targeting Methods
Blend geotargeting with demographic, behavioral, and device-based filters to improve ad precision and overall campaign effectiveness across various audience segments.
Challenges in Geotargeting
While effective, geotargeting comes with certain limitations:
1. Privacy Concerns
Users may disable or limit location access due to privacy worries, making it harder for marketers to deliver personalized ads effectively.
2. Data Accuracy
IP-based targeting can be inaccurate, particularly for mobile users, resulting in misplaced ads or irrelevant promotions in unintended regions.
3. Complexity
Managing multi-location campaigns requires strategic planning, continuous optimization, and technical expertise to ensure consistent performance across different regions.
4. Ad Fatigue
Excessive targeting in a specific area can cause audience burnout, resulting in reduced engagement and declining ad performance over time.
5. Limited Reach in Rural Areas
Geotargeting may underperform in rural or low-data regions where limited connectivity reduces location tracking accuracy and audience targeting potential.
6. Regulatory Restrictions
Certain regions have strict data protection or advertising laws, limiting the extent to which location-based marketing can be implemented effectively.
Final Thoughts
Geotargeting is a game-changing tool that bridges the gap between digital marketing and physical presence. By understanding user location and behavior, businesses can create meaningful connections, increase conversions, and optimize their marketing spend. Whether you are running a local campaign or managing a global brand, geotargeting ensures that your message reaches the right people — in the right place, at the right time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What tools are used for geotargeting?
Answer: Common tools include Google Ads, Facebook Ads Manager, LinkedIn Ads, and programmatic ad platforms that support location targeting.
Q2. How accurate is geotargeting?
Answer: Accuracy depends on the method used. GPS-based data is highly accurate, while IP-based targeting is approximate.
Q3. Is geotargeting suitable for small businesses?
Answer: Yes. Small businesses can benefit significantly from geotargeting by focusing their marketing efforts on local customers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Geotargeting” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
