What is AI Forecasting?
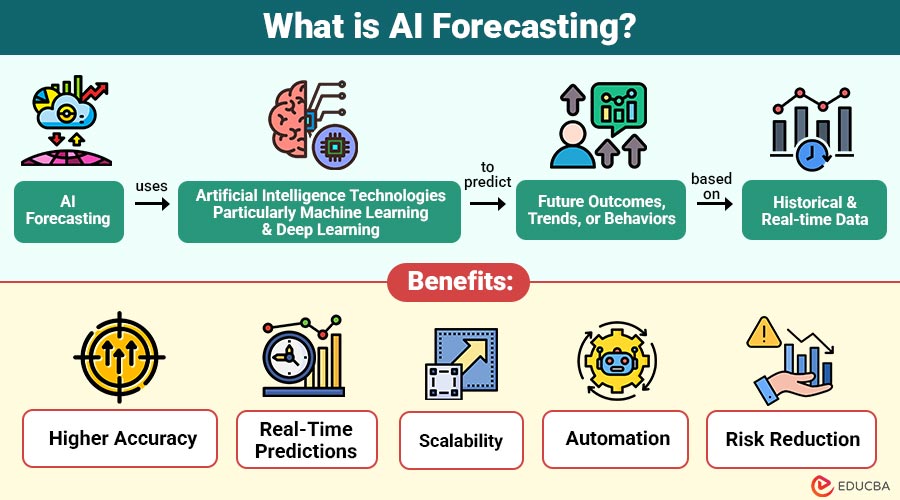
AI Forecasting refers to use of artificial intelligence technologies—particularly machine learning and deep learning—to predict future outcomes, trends, or behaviors based on historical and real-time data.
Unlike traditional forecasting methods that depend on linear statistical models or human intuition, AI forecasting can analyze enormous datasets, uncover hidden patterns, and continuously adapt to changing conditions. With this ability, businesses can make decisions that are more proactive rather than reactive.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- AI forecasting analyzes enormous volumes of data and makes precise predictions about future trends using sophisticated machine learning.
- It enables real-time, data-driven decision-making by continuously learning and adapting to new information.
- Increased productivity, reduced risk, and more precise strategic planning give businesses a competitive edge.
- Technological advancements, including explainable AI and hyperautomation, will redefine forecasting, improving trust, accuracy, and usability across industries.
How AI Forecasting Works?
AI forecasting typically involves several steps:
1. Data Aggregation
Reports, sensors, social media, and market trends are just a few of the types of data that AI systems collect to identify significant patterns.
2. Feature Engineering
Key variables are selected and transformed from raw data to improve prediction accuracy and enhance the forecasting model’s performance.
3. Model Training
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to learn patterns and relationships that enable accurate, efficient forecasting.
4. Prediction Generation
Using learned patterns, the AI model generates forecasts for metrics such as sales, revenue, demand, and healthcare risks.
5. Continuous Learning
AI forecasting models evolve by continuously incorporating new data, refining predictions, and maintaining long-term accuracy and reliability.
Components of AI Forecasting
Here are the key components that form the foundation of an effective system:
1. Data Collection and Integration
AI systems gather and integrate structured and unstructured data from various internal and external sources for comprehensive analysis.
2. Data Preprocessing
Raw data is cleaned, normalized, and transformed to eliminate inconsistencies, ensuring it is accurate, consistent, and ready for analysis.
3. Model Selection and Training
Appropriate AI models, such as neural networks or time-series algorithms, are selected and trained effectively using historical datasets.
4. Prediction and Analysis
Trained models generate accurate forecasts, providing actionable insights that support data-driven strategic, operational, and financial decision-making processes.
Applications of AI Forecasting
It has transformative applications across multiple industries:
1. Finance
- Stock Market Predictions: AI models analyze historical stock prices, trading volumes, and market sentiment to predict future trends.
- Risk Assessment: AI is used by banks and other financial organizations to predict market volatility, credit risks, and loan defaults.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI-driven algorithms can automatically execute trades based on forecasted price movements.
2. Retail and E-commerce
- Demand Forecasting: Retailers predict product demand to optimize inventory, reduce stockouts, and minimize overstock.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI anticipates customer preferences, enabling targeted marketing campaigns that enhance sales.
- Price Optimization: Dynamic pricing strategies are implemented using AI forecasts of market trends and competitor pricing.
3. Healthcare
- Patient Outcome Prediction: AI forecasts patient health risks, potential complications, and disease progression using clinical data.
- Resource Allocation: Hospitals optimize staffing, bed occupancy, and medical equipment usage based on AI forecasts of patient inflow.
- Drug Discovery: AI predicts the efficacy of new compounds, accelerating drug development.
4. Supply Chain and Logistics
- Inventory Management: AI forecasts supply and demand, minimizing waste and improving fulfillment rates.
- Route Optimization: Predicting traffic patterns and delivery times enhances logistics efficiency.
- Risk Mitigation: AI predicts disruptions due to weather, geopolitical events, or supplier delays, enabling proactive measures.
5. Energy and Utilities
- Demand Forecasting: Utilities predict energy consumption patterns to manage supply and reduce costs.
- Renewable Energy Management: AI forecasts solar and wind energy generation based on weather and environmental data.
- Predictive Maintenance: Power plants and grids use AI to forecast equipment failures and schedule timely maintenance.
Benefits of AI Forecasting
It offers several key benefits over traditional forecasting methods:
1. Higher Accuracy
AI models detect complex data patterns and correlations that humans often overlook, enabling more reliable, precise predictive forecasts.
2. Real-Time Predictions
It dynamically updates as new data arrives, enabling fast, data-driven decisions and quick responses to market changes.
3. Scalability
AI systems efficiently process massive datasets, handling complex forecasting tasks beyond human capability across various industries and business domains.
4. Automation
Automating forecasting processes reduces manual effort, saves valuable time, minimizes costs, and enhances overall organizational productivity and efficiency.
5. Risk Reduction
Identifies potential risks early, uncovering anomalies and trends to improve preparedness and business continuity planning.
Challenges in AI Forecasting
Despite its advantages, it faces several challenges:
1. Data Quality and Availability
Accurate AI forecasts depend on clean, relevant, and complete data; poor data quality results in misleading and unreliable predictions.
2. Complexity of Models
AI forecasting models, particularly deep learning architectures, are often complex and require advanced technical expertise for proper development and maintenance.
3. Interpretability
Opaque “black box” AI systems make it difficult for people to understand or explain how they generate specific forecasting predictions.
4. Cost of Implementation
Establishing AI forecasting systems demands significant investment in infrastructure, software, and skilled personnel, posing challenges for smaller organizations.
5. Bias in Predictions
If training data contains bias, AI models may reproduce or amplify those biases, leading to unfair or inaccurate forecasting outcomes.
Future Trends
The future is poised for rapid evolution, with emerging trends including:
1. Explainable AI
Explainable AI enhances transparency by making forecasting models interpretable, helping stakeholders understand predictions and build greater trust.
2. Hyperautomation
Combining AI forecasting with robotic process automation enables fully automated, end-to-end workflows that improve efficiency and minimize human intervention.
3. Real-Time Predictive Analytics
AI systems continuously update forecasts using live data streams, enabling instant adjustments and more accurate, dynamic decision-making.
4. AI-Driven Scenario Planning
Simulates diverse “what-if” scenarios, empowering organizations to anticipate outcomes and make informed, data-driven strategic planning decisions.
5. Cross-Industry Applications
It expands across industries, supporting advancements in climate modeling, healthcare personalization, urban development, finance, and resource management.
Real-World Examples
Here are some notable examples of how leading organizations are leveraging AI forecasting across various industries:
1. Amazon
Uses for inventory and demand management, ensuring products are available where and when customers need them.
2. JPMorgan Chase
Applies to predict market trends, optimize trading strategies, and assess credit risks.
3. UPS
Uses artificial intelligence (AI) predictions in logistics to improve delivery times, save fuel usage, and optimize delivery routes.
4. Pfizer
Utilizes in drug discovery to predict compound effectiveness and accelerate clinical trials.
Final Thoughts
AI forecasting is transforming business planning and decision-making by using advanced algorithms and large datasets to deliver accurate, timely predictions. In sectors including banking, healthcare, and retirement, it boosts productivity, reduces risk, and facilitates data-driven initiatives. As technology advances, it will become more transparent, accessible, and essential for achieving sustained growth and competitive advantage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is AI forecasting better than traditional forecasting?
Answer: Yes, AI forecasting generally provides higher accuracy, faster predictions, and scalability that traditional methods cannot match.
Q2. How accurate is AI forecasting?
Answer: Accuracy depends on data quality, model selection, and industry context. Well-trained AI models can significantly outperform traditional methods.
Q3. What skills are needed for AI forecasting?
Answer: Key skills include data analysis, machine learning, statistics, programming (Python, R), and domain expertise in the relevant industry.
Q4. Can AI forecasting predict unexpected events?
Answer: AI is excellent at pattern recognition but may struggle with truly unprecedented events, known as “black swan” events. Combining AI with human judgment is often ideal.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “AI Forecasting” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

