What is a Vector Database?
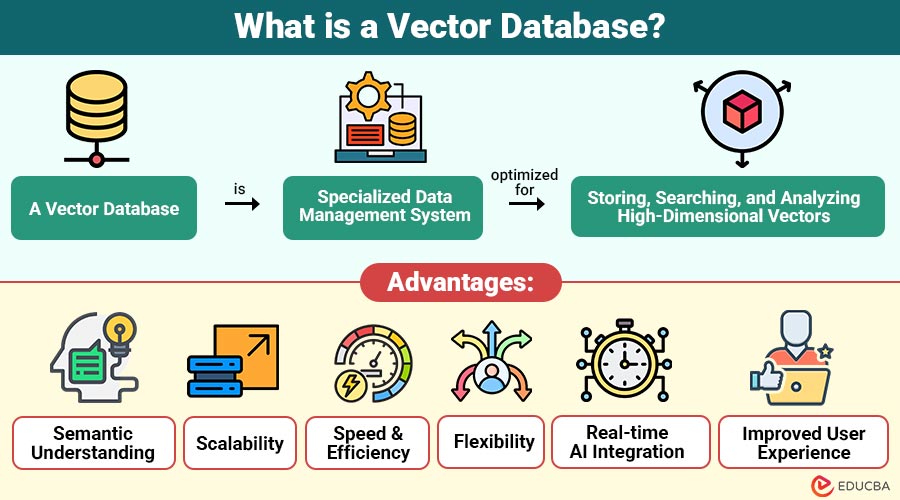
A vector database is specialized data management system optimized for storing, searching, and analyzing high-dimensional vectors. Vectors are numerical arrays representing the semantic meaning of unstructured data. These embeddings are generated using AI models such as OpenAI’s embeddings, BERT, CLIP, or other machine learning algorithms.
For example, in natural language processing, words, sentences, or whole documents can be converted into vectors that capture their semantic meaning. Similarly, images can be transformed into vectors representing visual features. A vector database allows these embeddings to be efficiently stored and retrieved, facilitating AI-driven tasks like semantic search, image recognition, and recommendation systems.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Working
- Key Features
- Popular Vector Databases
- Applications
- Advantages
- Challenges
- Real-World Examples
Key Takeaways:
- Vector databases efficiently transform unstructured data into meaningful numerical representations for advanced AI-driven applications.
- They enable fast similarity searches across high-dimensional embeddings, significantly improving contextual understanding and user experience.
- Integration with AI models allows seamless retrieval and personalized recommendations across diverse industries and platforms.
- Despite resource demands, vector databases provide scalable, intelligent data solutions for search, recommendations, and anomaly detection.
How Vector Databases Work?
Vector databases rely on vector embeddings and similarity search algorithms to match data points. Here is how the process works:
1. Data Conversion (Embedding Generation)
Unstructured data (text, image, or video) is converted into vector embeddings using AI models.
Example:
- Text → Transformer-based models like BERT or GPT embeddings.
- Images → Models like CLIP or ResNet.
Each piece of data becomes a high-dimensional numeric vector representing its semantic meaning.
2. Vector Storage
The vector database stores the embeddings along with metadata such as file names, categories, or timestamps. Unlike relational databases, vector databases organize data in multi-dimensional vector spaces rather than tables.
3. Indexing
To optimize search efficiency, the database uses approximate nearest neighbor (ANN) indexing algorithms such as:
- HNSW (Hierarchical Navigable Small World)
- IVF (Inverted File Index)
- PQ (Product Quantization)
These algorithms enable rapid similarity searches even across millions or billions of vectors.
4. Similarity Search
When a user query is submitted (also converted into a vector), the database measures similarity using metrics like:
- Cosine similarity
- Euclidean distance
- Dot product
Key Features of Vector Databases
Modern vector databases are built to handle scale, speed, and semantic complexity. Their main features include:
1. High-dimensional Data Support
It can efficiently store and process embeddings with hundreds or thousands of dimensions, enabling complex AI-driven similarity searches.
2. Approximate Nearest Neighbor Search
This system provides fast, real-time retrieval of the most similar items, even across massive datasets containing billions of high-dimensional vectors.
3. Hybrid Search
Combines semantic vector-based similarity with traditional keyword search, delivering more accurate and context-aware results for diverse query types.
4. Scalability
By adding more machines, the system may expand and distribute data among them, maintaining speed even as the volume of data grows significantly.
5. Integration with AI Models
Seamlessly works with embeddings generated by models from OpenAI, Hugging Face, Cohere, and other AI platforms for advanced applications.
6. Metadata Filtering
This feature enables the combination of vector similarity searches with metadata filters, such as dates or categories, for more precise and relevant results.
Popular Vector Databases
Several vector databases are leading the industry with specialized features and performance optimizations. Some of the most popular include:
| Database | Key Highlights | Use Case |
| Pinecone | Fully managed, high-performance, cloud-native | Semantic search, personalization |
| Weaviate | Open-source, hybrid search (vector + keyword) | Knowledge graphs, enterprise AI search |
| Milvus | Scalable open-source vector DB with GPU acceleration | Image & video retrieval |
| Qdrant | Rust-based, memory-efficient, open-source | Recommendation systems |
| FAISS | Library for efficient similarity search | ML research, custom deployments |
| Chroma | Open-source, local-first, easy to use with LLMs | AI chatbots, RAG applications |
| Redis Vector Similarity | Integrated with Redis for hybrid queries | Real-time search and caching |
Applications of Vector Database
Vector databases are revolutionizing how businesses and developers interact with unstructured data. Some of the key use cases include:
1. Semantic Search
Vector databases enable search engines to understand the meaning behind queries, retrieving results based on context rather than simple keyword matches.
2. Recommendation Systems
By measuring vector similarity between users or products, these systems suggest items or content that closely match user preferences or behavior.
3. Chatbots and Conversational AI
In RAG systems, chatbots query vector databases for relevant knowledge to generate more accurate, contextually appropriate, and informative responses.
4. Image and Video Retrieval
Vector embeddings of visual data allow systems to find and rank images or videos similar to a given reference efficiently.
5. Anomaly Detection
Comparing vectors representing typical behavior with new data points helps accurately detect unusual activity, potential fraud, or system anomalies.
6. Personalization Engines
Vector-based similarity helps platforms customize recommendations, content, and user experiences based on individual preferences, interactions, and behavioral patterns.
Advantages of Using a Vector Database
Here are some key advantages of using a vector database:
1. Semantic Understanding
Vector databases interpret the meaning and context of data, allowing retrieval based on concepts rather than mere keyword matching, improving accuracy.
2. Scalability
Vector databases are made for very big datasets and are capable of processing and storing billions of vectors for use in research and enterprise applications.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Using advanced Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) algorithms, vector databases perform rapid similarity searches even on massive, high-dimensional datasets without performance loss.
4. Flexibility
They support multiple data types, including text, images, audio, and video, within a single unified framework for diverse applications.
5. Real-time AI Integration
Vector databases integrate seamlessly with AI and machine learning pipelines, enabling instant updates, retrievals, and interaction with evolving datasets.
6. Improved User Experience
Vector databases help apps understand meaning and similarity in data, which makes search smarter, recommendations personal, and content more relevant, keeping users happy and engaged.
Challenges of Vector Database
Despite their powerful capabilities, vector databases come with certain challenges:
1. High Computational Requirements
2. Storage Costs
Vector embeddings, especially in massive datasets, consume large amounts of disk and memory, leading to increased infrastructure and operational expenses.
3. Complex Index Management
Selecting and maintaining the optimal indexing strategy requires balancing speed, accuracy, and resource usage, which can be technically challenging.
4. Integration Complexity
Integrating vector databases involves understanding embeddings, AI models, APIs, and data pipelines, requiring specialized expertise and careful system design.
5. Limited Standardization
Different vector databases adopt varied architectures and formats, causing interoperability challenges when switching platforms or integrating with other systems.
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of vector databases in the real world:
1. Spotify
Spotify uses vector analysis to understand songs’ sounds and moods, giving users personalized music suggestions that fit their taste.
2. eBay & Amazon
These online shopping sites use image data to let customers search by pictures, helping them find products that look similar to the images they upload or see.
3. Google Photos
Google Photos uses vector embeddings to recognize faces and objects, helping users find visually similar photos easily in their libraries.
4. LinkedIn
Final Thoughts
A vector database goes beyond simple storage—it powers modern AI by interpreting meaning and similarity in data. By enabling semantic search, smarter recommendations, and accurate generative AI, it transforms raw data into actionable insights. Organizations using vector databases gain a competitive edge, delivering faster, more intuitive, and contextually aware user experiences across industries.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How is a vector database different from a traditional database?
Answer: Traditional databases handle structured data and exact matches, while vector databases handle unstructured data and similarity-based searches.
Q2. Are vector databases suitable for real-time applications?
Answer: Yes, most modern systems like Pinecone and Qdrant are optimized for real-time, low-latency search.
Q3. Can vector databases work with LLMs like GPT or BERT?
Answer: Absolutely. They are commonly paired with LLMs for RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) and AI-powered knowledge retrieval systems.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Vector Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
