What is Financial Inclusion?
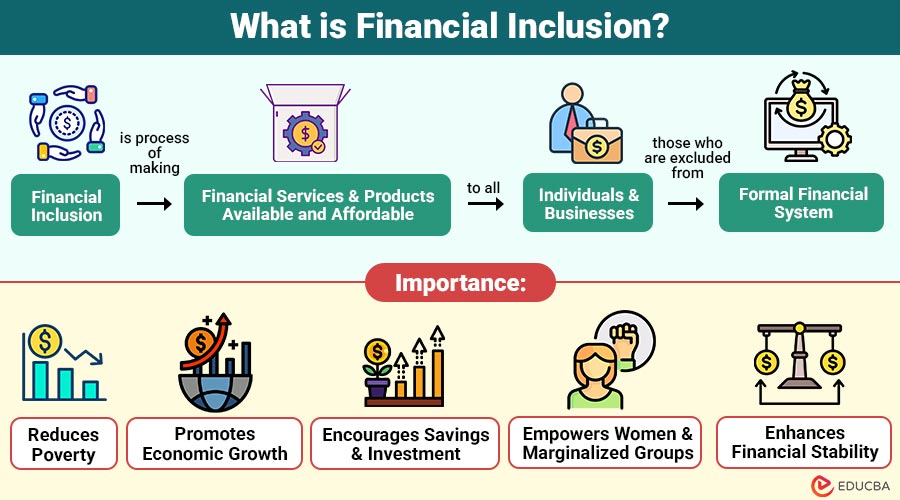
Financial inclusion is process of making financial services and products available and affordable to all individuals and businesses, especially those who are excluded from the formal financial system. It focuses on reaching underbanked and unbanked populations — people who do not have a bank account or access to traditional financial services.
For example, a rural farmer without a bank account gets a small loan and mobile banking access, enabling them to buy seeds and sell produce efficiently. This is financial inclusion.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Financial inclusion ensures equal access to banking, credit, and insurance for all individuals worldwide.
- Digital technology and fintech innovations are driving faster, safer, and more affordable financial accessibility.
- Financial literacy and awareness empower individuals to make informed, responsible, and sustainable financial decisions.
- Global cooperation among governments and institutions is crucial for achieving inclusive and resilient economic growth.
Importance of Financial Inclusion
Financial inclusion plays a crucial role in building an inclusive and stable economy. Here is why it is important:
1. Reduces Poverty
When individuals can save, borrow, and invest, they can improve their standard of living. Access to credit enables them to start small businesses or invest in education and healthcare, thereby helping to lift families out of poverty.
2. Promotes Economic Growth
A financially included population contributes more actively to the economy. With easier access to financial services, entrepreneurs can expand their businesses, create jobs, and drive overall economic development.
3. Encourages Savings and Investment
Having access to formal financial systems motivates people to save regularly and invest wisely. This helps create a culture of financial discipline and long-term financial security.
4. Empowers Women and Marginalized Groups
By providing women with autonomous access to funds and resources, financial inclusion promotes gender equality. It helps them make financial decisions, support their families, and start their own businesses.
5. Enhances Financial Stability
When people rely on formal banking systems rather than informal moneylenders, it reduces financial risks, promotes transparency, and ensures greater financial stability within the economy.
Key Components of Financial Inclusion
To achieve full financial inclusion, several key elements must come together. These include:
1. Access to Banking Services
Basic services, such as savings accounts, credit facilities, and debit cards, are essential for financial inclusion. Banks and other financial institutions help reach the unbanked through various channels, including branches, internet platforms, and microfinance initiatives.
2. Affordable Credit
Access to small, low-interest loans helps individuals and small businesses grow. Microfinance institutions and cooperative banks often serve people who do not qualify for traditional loans.
3. Digital Payments
Digital wallets, UPI (Unified Payments Interface), mobile banking, and online transfers make it easier for people to conduct transactions at any time and from anywhere. This promotes cashless, transparent, and efficient financial operations.
4. Financial Literacy
The capacity to understand and use financial tools successfully is known as financial literacy. Educating people about savings, credit management, and investment options enables them to make informed financial decisions.
5. Insurance and Social Security
Reasonably priced insurance products protect individuals against unforeseen circumstances, such as illness, accidents, or loss of income. Social security schemes ensure that vulnerable populations receive support during emergencies.
Global Efforts to Promote Financial Inclusion
Many international organizations and governments are collaborating to promote financial inclusion globally.
1. World Bank Initiatives
The World Bank created the Global Findex Database to monitor global progress in financial inclusion. By aiding developing nations, it seeks to guarantee that everyone has access to financial services.
2. United Nations and SDGs
Financial inclusion is linked to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)—especially Goal 1 (No Poverty), Goal 5 (Gender Equality), and Goal 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth).
3. G20 Global Partnership for Financial Inclusion
The G20 countries have created partnerships to promote financial literacy, digital inclusion, and affordable financial services for all.
4. Mobile Money Revolution
In countries like Kenya, mobile payment systems like M-Pesa have revolutionized how people manage their finances. These innovations make banking possible even without traditional infrastructure.
Challenges in Achieving Financial Inclusion
While progress has been made, several challenges still limit the success of financial inclusion programs.
1. Lack of Financial Literacy
Many people, particularly in rural and underprivileged areas, lack understanding of how to utilize financial products effectively.
2. Limited Infrastructure
In remote areas, banks and ATMs are often not easily accessible. Internet connectivity issues also make digital banking difficult.
3. Gender Inequality
Women in some societies face cultural and social barriers that restrict their financial independence and access to credit.
4. Low Income and Irregular Earnings
Many people in the informal sector have unpredictable incomes, making it difficult for them to maintain regular savings or qualify for loans.
5. Cybersecurity Risks
As digital transactions increase, so does the risk of fraud, data breaches, and scams. Building confidence requires ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity.
Future of Financial Inclusion
Innovation and technology are directly related to the future of financial inclusion. The following trends will influence the future:
1. Fintech Growth
Financial technology (Fintech) companies are revolutionizing banking with mobile apps, digital wallets, and AI-powered credit systems. They make services faster, cheaper, and more accessible.
2. Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
Blockchain technology can facilitate secure, transparent, and efficient financial transactions, particularly in cross-border payments.
3. Artificial Intelligence
AI helps banks analyze customer data, design personalized financial products, and assess credit risk more accurately.
4. Digital Identity Systems
People can conveniently and securely open bank accounts and access financial services with biometric identification, such as Aadhaar in India.
Final Thoughts
Financial inclusion is essential for equitable and sustainable growth. Providing people with access to financial resources enables them to enhance their quality of life, make informed investments for the future, and contribute to economic growth. Governments, institutions, and tech firms must unite to remove barriers, promote digital literacy, and ensure everyone can participate fully in the financial ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1. Can financial inclusion help reduce reliance on informal lenders?
Answer: Yes, by providing access to affordable banking and credit options, individuals are less dependent on informal lenders who frequently charge high interest rates. This creates safer and more transparent financial practices.
Q2. How does technology improve access to financial services in remote areas?
Answer: Technologies like mobile banking, digital wallets, and online payment systems allow people in rural or underserved regions to access financial services without physically visiting banks, bridging the gap created by limited infrastructure.
Q3. Is financial inclusion only about opening bank accounts?
Answer: No, financial inclusion encompasses more than just accounts. It also involves access to credit, insurance, pensions, digital payment systems, and financial education that enables informed money management.
Q4. How can small businesses benefit from financial inclusion?
Answer: Small businesses gain access to loans, digital payment systems, and business accounts, which help them expand their operations, manage cash flow efficiently, and reach new customers, thereby contributing to economic growth.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Financial Inclusion” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.