What is Email Encryption?
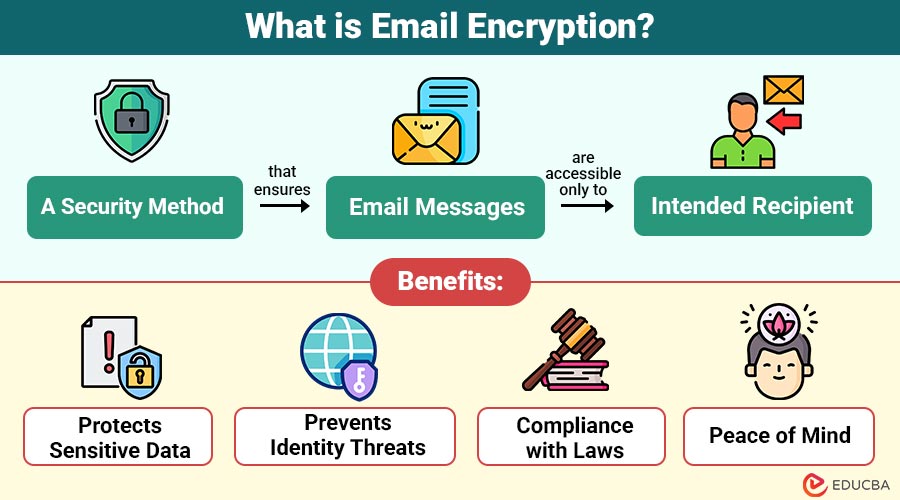
Email encryption is a security method that ensures email messages are accessible only to the intended recipient. It works by converting the original readable message (plaintext) into an unreadable format (ciphertext) using specialized cryptographic techniques. This scrambled content can only be decoded and understood by someone who has the correct decryption key.
Example:
Without Encryption (Plaintext Email):
- Hi John, here’s the bank account number: 1234567890.
- Anyone intercepting this email can read the sensitive information.
With Encryption (Ciphertext Email):
- 9x$3s@!kd892#&klmqz=+34sd…
The message is scrambled and unreadable during transmission. Only John, who has the correct private decryption key, can convert it back to:
- Hi John, here’s the bank account number: 1234567890.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Working
- Popular Protocols
- Benefits
- Challenges
- How to Encrypt Emails?
- Best Practices
- Industries that Rely on Email Encryption
Key Takeaways:
- Email encryption protects sensitive email content, ensuring only the intended recipient can read the message securely.
- Using strong encryption methods like S/MIME and PGP prevents unauthorized access and data breaches.
- It plays a crucial role in industries handling confidential data, supporting secure workflows and ethical data management.
- Despite some complexity, encryption boosts confidentiality, builds trust, and defends against phishing and cyber threats.
Why is Email Encryption Important?
Here are key reasons why email encryption is essential in today’s digital communication landscape:
1. Protection Against Data Breaches
Encryption keeps intercepted emails unreadable, protecting sensitive data from hackers, breaches, and unauthorized third-party access.
2. Maintaining Confidentiality
Protects sensitive information from disclosure by limiting access to the email to the intended recipient.
3. Regulatory Compliance
Meets legal standards like GDPR and HIPAA by safeguarding personal and sensitive data shared via email.
4. Trust and Professionalism
Secure emails demonstrate responsibility, building trust with clients and enhancing your brand’s image and professional credibility.
How Does Email Encryption Work?
Email encryption relies on cryptographic algorithms. There are two main types:
1. Symmetric Encryption
- Employs the same key for data encryption and decryption.
- Sender and recipient must both have access to the same key.
- The difficulty of safely exchanging the key makes it less secure for large-scale transmission, despite its speed.
2. Asymmetric Encryption
- Uses a pair of keys—a public key to encrypt and a private key to decrypt.
- While the private key is kept private, the public key can be freely disseminated.
- More secure and widely used in email communication.
Popular Email Encryption Protocols
Here are the most widely used protocols that help secure email communication from interception and unauthorized access:
1. S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)
- Built into many email clients like Microsoft Outlook and Apple Mail.
- Makes use of digital certificates that have been granted by a Certificate Authority (CA).
- Relies on both sender and receiver supporting TLS.s encryption and digital signing.
2. PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) / OpenPGP
- An open standard.
- Users create their key pairs.
- Popular with individuals and organizations that prioritize data privacy.
3. TLS (Transport Layer Security)
- Encrypts the email transmission (not the email itself).
- Prevents interception between email servers.
Benefits of Email Encryption
Below are some benefits that make email encryption a useful technique for individuals and organizations alike:
1. Protects Sensitive Data
Encryption protects confidential data like medical records and business documents from being accessed, read, or stolen by unauthorized users.
2. Prevents Identity Threats
Digital signatures verify the sender’s identity, reducing the chances of phishing and email spoofing.
3. Compliance with Laws
Helps meet legal data protection requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, avoiding fines and reputational damage.
4. Peace of Mind
Ensures communication safety, allowing users and businesses to operate confidently without constant fear of data leaks or cyberattacks.
Challenges of Email Encryption
While encryption is crucial, there are several hurdles users may face when implementing it effectively:
1. Complexity for Non-Technical Users
Many users struggle with installing certificates, managing keys, and configuring settings without technical knowledge or dedicated IT support.
2. Compatibility Issues
Some email clients and services do not support all encryption protocols, leading to errors, unreadable messages, or failed secure communication.
3. Cost
High-quality encryption tools and digital certificates often come with subscription fees, making them less accessible for small businesses or individuals.
4. Enhanced Control Over Information
Encryption features like expiration dates, restricted access, and no-forwarding controls empower senders to control how recipients use sensitive data.
How to Encrypt Emails? (Step-by-Step Guide)
Here is a breakdown of how to encrypt emails using popular platforms and tools:
1. With Gmail (TLS Encryption)
- Gmail automatically uses TLS when possible.
- You can not manually enable end-to-end encryption unless using a plugin.
To enhance Gmail encryption:
- Use browser extensions like FlowCrypt or Mailvelope to add PGP support.
- Compose your message, encrypt, and send securely.
2. With Microsoft Outlook (S/MIME)
- Install a digital certificate.
- Navigate to File → Options → Trust Center → Email Security.
- Under Encrypted Email, select Encrypt contents and attachments.
- Compose and send as usual.
3. With ProtonMail
- The system includes encryption by default.
- Emails between ProtonMail users are automatically encrypted.
- For external users, you can send a password-protected link.
Best Practices for Secure Email Communication
To protect sensitive information and maintain email security, follow these essential practices:
1. Strong Passwords & 2FA
To provide an additional layer of protection against unwanted access to your email accounts, create complicated passwords and turn on 2FA.
2. Encrypted Services
Choose reliable encrypted email providers to ensure attackers cannot intercept confidential information during transmission and that it remains secure.
3. Employee Awareness
Conduct regular training to help employees identify suspicious emails and avoid falling victim to phishing, spoofing, or social engineering attacks.
4. Regular Updates
Keep encryption tools, certificates, and email software updated to fix vulnerabilities and maintain strong protection against modern cyber threats.
5. Delete Old Emails
Delete outdated emails containing sensitive data to minimize exposure risks in case your email account is ever breached or compromised.
Industries that Rely on Email Encryption
Here are key sectors where email encryption is vital to protect sensitive information and meet regulatory requirements:
1. Healthcare
Healthcare providers must encrypt emails containing Protected Health Information (PHI) to comply with HIPAA regulations and prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
2. Finance & Banking
Banks and financial institutions use email encryption to secure sensitive transactions, account details, and personal financial data from cyber threats and fraud.
3. Legal Firms
Law firms rely on encryption to protect privileged communications between clients and attorneys, ensuring confidentiality and compliance with legal privacy requirements.
4. Government & Defense
Government agencies and defense sectors enforce strict encryption standards to safeguard classified information, national security data, and sensitive internal communications.
Final Thoughts
Email encryption is no longer optional—it is a necessity in a digital landscape riddled with cyber threats. Whether you are a student sending assignments, a business executive negotiating contracts, or a doctor sharing patient reports, encrypted emails ensure that your information is safe, private, and compliant with global standards.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is Gmail encrypted by default?
Answer: Yes, Gmail uses TLS encryption, but it does not provide end-to-end encryption unless you use third-party tools.
Q2. Can I encrypt emails on my phone?
Answer: Yes. Apps like ProtonMail, Tutanota, or encrypted plugins support mobile encryption.
Q3. What happens if someone intercepts an encrypted email?
Answer: Without the decryption key, the intercepted email appears as gibberish and is unusable.
Q4. Is email encryption 100% foolproof?
Answer: While no system is entirely invulnerable, strong encryption severly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Email Encryption” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
