What is a Holographic Display?
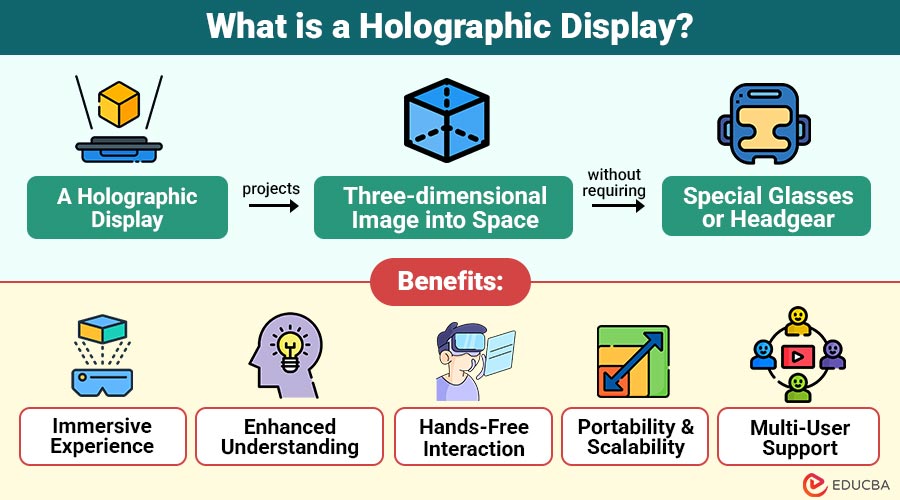
A holographic display is a device or system that projects a three-dimensional image into space without requiring special glasses or headgear. Unlike traditional 2D displays, which show only height and width, holographic displays add depth perception, creating a volumetric and lifelike viewing experience.
Table of Contents:
Key Takeaways:
- Holographic displays project realistic 3D images without the need for glasses, enhancing visualization across various industries and environments.
- They work by capturing and reconstructing light wavefronts using lasers, interference patterns, and spatial modulators.
- Applications span healthcare, education, entertainment, defense, and retail through immersive, interactive, and multi-user experiences.
- Despite high costs and complexity, advancements in AI, 5G, and wearables promise a transformative future.
How Does Holographic Display Work?
Holographic displays utilize light diffraction and interference to reconstruct the three-dimensional light field of an object. Here is how the process generally works:
- Holography captures the light wavefront from an object using a laser, splitting it into an object beam and a reference beam.
- After reflecting off the subject, the reference beam and the object beam cross paths, producing an interference pattern.
- The system records this pattern onto a medium such as photopolymer or digital sensors.
- When illuminated, the recorded interference pattern diffracts light in a way that recreates the original light field, forming a floating 3D image.
Types of Holographic Displays
There are several variations of holographic displays based on technology and application:
- Laser Plasma Displays: These displays ionize air molecules using lasers to form bright, floating 3D points of light visible without any physical screen.
- Digital Holography: Computer-generated holograms and spatial light modulators (SLMs) work together to display 3D content on screens or transparent materials in real-time.
- Integral Imaging: It uses several 2D images from different angles to create a 3D-like view, giving depth without needing 3D glasses.
- Holographic Projection: Projects 3D visuals onto glass or transparent panels, often used in exhibitions, marketing events, and concerts to simulate real-life presence.
- Volumetric Display: These displays create 3D images in real space by lighting up precise points using carefully controlled light techniques.
Key Components of Holographic Display
A fully functional holographic display system includes multiple critical components, each playing a different role in creating and displaying 3D holograms:
- Laser Source: This component provides the coherent light necessary for forming holograms. Coherent light ensures uniformity and precision in wave interference.
- Beam Splitter: The beam splitter divides the laser light into two separate beams—known as the object beam and the reference beam—which are essential for creating the interference pattern.
- Spatial Light Modulator (SLM): The SLM creates dynamic holograms, frequently in real-time, by varying the phase and, in some situations, the amplitude of light waves.
- Holographic Medium: This is the recording surface (such as a photopolymer film or LCD panel) where the interference pattern is stored or displayed.
- Projector or Diffuser: These components make the final 3D holographic image visible to the viewer by scattering or directing the modulated light into a holographic form.
- Computational Unit: A powerful processor or GPU handles the complex mathematical operations and rendering tasks needed to process holographic data in real time.
Applications of Holographic Displays
Holographic displays have vast potential across industries:
- Healthcare: Holographic displays help doctors plan surgeries, train, and diagnose by showing lifelike 3D images of organs and guiding procedures with augmented reality.
- Education: They enhance learning with interactive 3D models, virtual labs, and historical recreations, making abstract concepts and past events visually engaging.
- Entertainment & Media: Enable immersive concerts, realistic gaming, and 3D cinema without glasses, offering audiences lifelike visual experiences across diverse media formats.
- Retail and Marketing: Used for virtual fitting rooms, interactive ads, and holographic product showcases, transforming customer engagement and personalizing the shopping experience.
- Defense and Aerospace: Help with mission planning and training by using 3D maps and virtual environments, making it easier to understand situations and be prepared.
Benefits of Holographic Displays
Holographic technology offers several key benefits across various applications:
- Immersive Experience: It provides a realistic 3D depth that enhances user engagement without the need for headsets or glasses.
- Enhanced Understanding: This technology improves spatial awareness and comprehension, particularly in technical fields such as engineering, architecture, and medicine.
- Hands-Free Interaction: Holographic systems let users control and interact with 3D content using hand gestures, allowing real-time teamwork without touch.
- Portability and Scalability: Contemporary holographic systems are becoming more portable and lightweight, which facilitates their scalability for various applications.
- Multi-User Support: Multiple viewers can simultaneously observe and interact with the same hologram from different angles, enhancing group experiences and collaboration.
Limitations and Challenges
Despite its potential, holographic display technology faces several limitations:
- High Cost: The hardware and development costs associated with holographic systems remain high, making them less accessible for widespread consumer or educational use.
- Computational Complexity: Real-time holographic rendering demands powerful processors and high-end GPUs, which can limit the technology’s integration into smaller or mobile platforms.
- Limited Field of View: Many current holographic displays offer narrow viewing angles, which can restrict the immersive experience for multiple viewers or when dynamic movement is involved.
- Brightness and Resolution: Achieving sufficient brightness for outdoor visibility and maintaining high-definition image quality are still significant technical hurdles.
- Content Creation: Developing holographic content is complex, time-consuming, and often requires specialized skills and tools, which can slow adoption in industries without dedicated resources.
Real-World Examples
Several companies and organizations are pioneering holographic display technology:
- Looking Glass Factory: Developed light field displays like Looking Glass Portrait, enabling interactive 3D content for creators and developers.
- Holoxica Ltd.: Specializes in medical and scientific holographic visualizations.
- Microsoft HoloLens: Although not a traditional holographic display, it combines augmented reality and holography for enterprise use.
- Voxon Photonics: Offers volumetric 3D displays for education, simulation, and healthcare.
Future of Holographic Displays
The future of holographic display technology looks promising with developments in:
- AI-Powered Holograms: Future systems will use AI to create lifelike, responsive 3D avatars for real-time interaction.
- 5G Integration: High-speed 5G networks will enable seamless, real-time streaming and sharing of complex holographic content globally.
- Wearable Holography: Future wearable gadgets will show 3D holograms you can interact with anywhere, changing how we use mobile devices.
- Holographic Telepresence: Real-time holographic communication will simulate face-to-face meetings, dramatically improving virtual collaboration and remote presence.
Final Thoughts
Holographic displays represent a groundbreaking shift in visual communication, turning science fiction into everyday reality. From transforming education and healthcare to revolutionizing entertainment and collaboration, this technology has boundless potential. Holography has the potential to completely change how we view and engage with digital content as developments in light modulation, data processing, and user interaction continue.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are holographic displays the same as 3D displays?
Answer: No. 3D displays typically require glasses and simulate depth using stereoscopy. Holographic displays create true 3D images using light interference and can be viewed without special equipment.
Q2. What are some common uses of holography today?
Answer: Holography is used in data storage, medical imaging, product marketing, education, military simulations, and entertainment.
Q3. What skills are needed to work on holographic display development?
Answer: Skills in optics, physics, computer graphics, signal processing, and software engineering are essential.
Q4. Will holographic displays replace traditional screens?
Answer: Not entirely, but they will complement them in specialized fields where immersive visualization is valuable.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Holographic Display” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.
