What is a Business Plan?
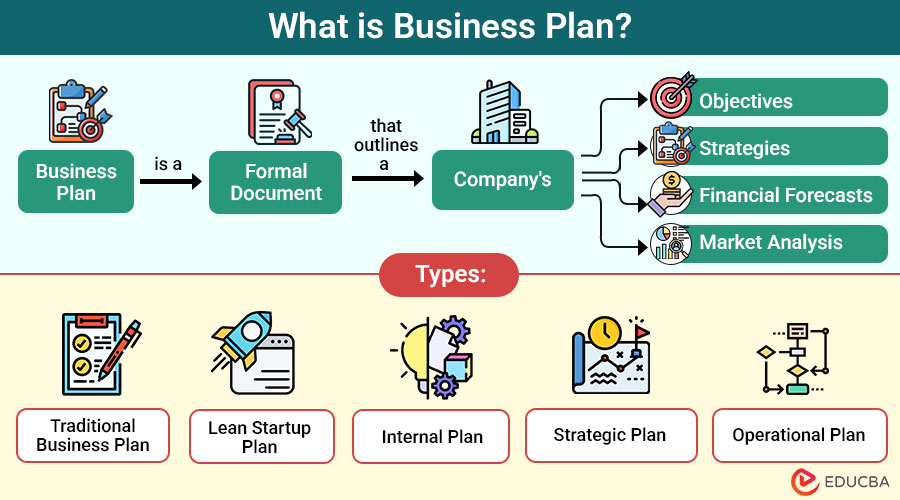
A business plan is a formal document that outlines a company’s objectives, strategies, financial forecasts, and market analysis. It serves as a roadmap to guide the business through each stage of growth, helping stakeholders—including investors, partners, and lenders—understand the business’s vision and goals.
For example, a bakery planning to open in a busy city writes a business plan that includes its menu (cakes, pastries, bread), target market (office workers and families), marketing tactics (social media and local flyers), startup costs, staffing needs, and expected monthly revenue.
Table of Contents:
- Meaning
- Importance
- Types
- Key Components
- Tips for Writing an Effective Business Plan
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Business Plan Tools
Key Takeaways:
- A business plan transforms abstract ideas into structured strategies with measurable action points and priorities.
- Effective plans blend clarity, research, and foresight to drive sustainable growth and informed decisions.
- Investors value transparency, realistic projections, and clear goals presented in a professional, well-organized plan.
- Regularly revisiting your business plan ensures agility in changing markets and evolving customer needs.
Why is a Business Plan Important?
Examine the key reasons a business plan is essential for growth and success, as outlined below:
1. Clarifies Vision and Strategy
A business plan helps define your company’s long-term goals and the strategic path to reach them, ensuring all efforts are focused and consistently aligned with your mission.
2. Attracts Investors and Funding
A clear, detailed business plan demonstrates to potential investors that you understand your market, have realistic financial projections, and a solid strategy, thereby increasing confidence in your ability to deliver returns.
3. Guides Decision Making
A business plan helps you stay on course and assess options that support your company’s objectives by helping you define priorities and goals.
4. Identifies Risks and Opportunities
A good plan includes market analysis, helping you anticipate challenges and capitalize on emerging trends or unmet customer needs, reducing surprises and boosting your competitive edge early on.
5. Improves Operational Efficiency
Through detailed planning of resources, staffing, processes, and timelines, a business plan promotes smoother operations, eliminates redundancy, and enhances productivity with clear roles and measurable performance indicators
Types of Business Plans
Depending on your needs, you might choose from several types:
1. Traditional Business Plan
Use a comprehensive, detailed plan with clear financial projections to attract investors, secure loans, or form partnerships.
2. Lean Startup Plan
A concise plan focusing on essential components like value proposition, target customers, revenue streams, and cost structure—ideal for startups or early-stage businesses.
3. Internal Plan
An internal document designed to align teams, track performance, and communicate goals across departments without the need for external investor-focused details.
4. Strategic Plan
This long-term planning tool outlines major company goals, key initiatives, and strategies to guide growth, expansion, and competitive positioning over a period of several years.
5. Operational Plan
It outlines daily functions, assigns staff responsibilities, and establishes workflows to ensure efficient operation management.
Key Components of a Business Plan
The following sections are commonly found in a strong business plan:
1. Executive Summary
Summarizes your plan with essential information—business name, location, mission, product overview, and financial highlights. Although it appears first, writers usually prepare it last.
2. Company Description
Describe your business structure, ownership, history, and mission. Includes legal status like LLC or sole proprietorship, outlining what your business does, and why it exists.
3. Market Analysis
Presents insights on industry trends, target demographics, competitors, and market gaps. Identifies opportunities, threats, and barriers to entry to validate your business strategy.
4. Organization and Management
Explains the company’s leadership, team structure, and ownership details. Includes management roles, responsibilities, and often a visual organizational chart to clarify internal operations.
5. Products or Services
Describes your product or service, its unique value, customer benefits, development stages, intellectual property, and any future offerings in the pipeline.
6. Marketing and Sales Strategy
Explains your pricing strategy, advertising platforms, promotional tools, sales funnel, long-term strategies for customer engagement and loyalty, and how you will draw in and keep customers.
7. Funding Request
The plan outlines the amount of funding the business requires, its intended use of the funds, preferred financing terms, and the benefits it offers to investors, including projected returns and exit strategies.
8. Financial Projections
Includes future income statements, balance sheets, cash flow analysis, break-even point, and assumptions used to justify your projections for the next 3–5 years.
9. Appendix
An optional section containing supporting materials like licenses, legal documents, resumes, charts, market research, product images, or any other relevant reference documentation.
Tips for Writing an Effective Business Plan
Mentioned below are practical and distinct tips to help you craft a compelling and results-driven plan.
1. Know Your Audience
Tailor your plan’s content, tone, and detail level to suit investors, partners, or internal stakeholders.
2. Keep it Clear and Concise
Avoid technical jargon and complex language. Use straightforward explanations and visual aids, such as graphs and charts, to ensure better understanding and engagement.
3. Be Realistic
Offer grounded financial projections and attainable business goals. Overly ambitious claims can reduce credibility and deter potential investors or partners from supporting your plan.
4. Focus on the Value Proposition
Clearly state what makes your company special. Highlight the unique advantages that your product or service has over rivals in the industry.
5. Update Regularly
Revise your plan periodically to reflect changes in operations, financials, or market trends. Keep it relevant as your business evolves.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Listed below are critical errors that can weaken your plan and impact your chances of success.
1. Overestimating Sales
Inflated sales forecasts damage credibility. Use conservative, data-driven projections to maintain investor trust and realistic expectations.
2. Ignoring the Competition
Failing to address competitors’ signals indicates a poor understanding of the market. Acknowledge and analyze them to show preparedness and strategic positioning.
3. Neglecting Market Research
Relying on assumptions instead of real data weakens your plan. Solid research supports informed decisions and builds investor confidence.
4. Lack of a Clear Strategy
Investors want more than ideas—they expect a clear roadmap showing how you will grow, compete, and achieve long-term success.
5. Missing Financial Details
Incomplete or vague financials raise concerns. Provide comprehensive projections, break-even analysis, and funding requirements to enhance transparency and investor confidence.
Business Plan Tools
Creating a plan can be daunting, but these tools can help:
1. LivePlan
Provides customizable templates, real-time financial forecasting, and performance dashboards to help entrepreneurs create professional, investor-ready business plans easily.
2. Bizplan
A guided platform with a drag-and-drop builder and collaboration tools, making team-based planning structured and efficient.
3. SBA Business Plan Tool
A free, user-friendly online tool from the U.S. Small Business Administration designed to help small businesses build structured plans.
4. Canva or Visme
Design-focused platforms are ideal for creating visually compelling pitch decks, presentations, and business plans with templates and customization options.
5. Google Docs/Sheets
Free, cloud-based tools allowing collaborative editing and sharing of your plan drafts, financials, and related documents in real-time.
Final Thoughts
A well-crafted business plan is more than just a formality—it is your business’s foundation. Whether you are seeking funding, aligning your team, or simply clarifying your vision, your plan serves as a guiding light. It forces you to think strategically, anticipate challenges, and define measurable goals. While drafting a plan may require time and research, the benefits far outweigh the effort. Remember, every successful business started with a single idea—and a solid plan to bring it to life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the ideal time to create a business plan?
Answer: The best time to create a business plan is before launching your business or when introducing a major change, such as a new product, market expansion, or funding round.
Q2. How long should a typical business plan be?
Answer: A typical business plan ranges from 15 to 30 pages, depending on the business type and audience.
Q3. Can a business plan change after starting the business?
Answer: Yes, plans should be revised regularly to reflect new goals, market shifts, or challenges.
Q4. Is a business plan necessary for a sole proprietorship?
Answer: Absolutely. Even solo entrepreneurs benefit from planning to clarify direction and stay organized and accountable.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Business Plan” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.