Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to 8085 Architecture
Eighty-eighty-five is an 8-bit microprocessor created in 1971 by Intel. It requires less circuit and makes the computer system to be simpler and easy to be built. It uses 5-volt power supply and has depletion mode transistors. Hence, 8085 could be compared with 8080 derived CPU. Hence these can be used in the systems with CP/M operating system. It has a DIP package with 40 pins. There is a data bus in the processor to fully utilize the functions of pins. There is built in serial I/O and 5 interrupts so that 8085 has long life similar to the controller used.
Architecture of 8085:
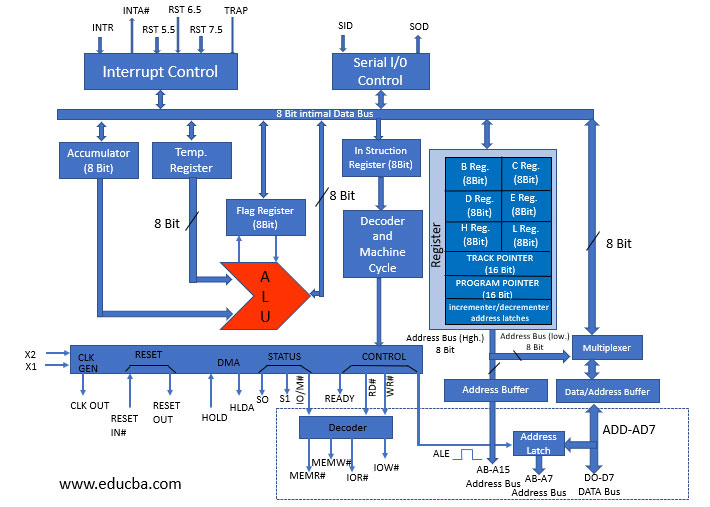
Components of 8085 Architecture
1. It consists of timing and control unit, accumulator, arithmetic and logic unit, general purpose register, program counter, stack pointer, temporary register, flag register, instruction register and decoder, controls, address buffer and address and data bus.
2. The timing and control unit provides proper signals to the microprocessor to perform functions in the system. We have control signals, status signals, DMA signals and RESET signals. This also controls the internal and external circuits in the system.
3. The accumulator is a register that performs all the arithmetic and logic operations in 8-bit processor. It connects the data bus and ALU unit of the processor.
4. ALU performs all the operations that includes arithmetic and logic operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and the logical operations in the system.
5. General purpose registers used in the processor include B, C, D, E, H and L registers. Each register holds the data and also these could be made to work in pairs. Hence these can hold 16-bit data in the processor.
6. The program counter is a 16-bit register that can store memory address locations so that the next instruction is implemented in parallel. This happens in a way such that the processor carries out the instruction to be executed and the program counter gives the address of the instruction to be executed next. This makes the work to be done smoothly.
7. Stack pointer works like a stack with a 16-bit register. It performs push or pop operations and is either incremented or decremented by 2 in the register.
8. Temporary data of the operations in ALU is handled in a temporary register which is 8-bit.
9. The 8-bit register with 1-bit flip-flops is called Flag register. There are 5 flip-flops and it holds logic data from the accumulator register. The logic data can be 0 or 1. The five flip-flops are Sign, Zero, Auxiliary Carry, Parity and Carry.
10. Instruction register and decoder is also an 8-bit register where instructions are stored after taking it from the memory. Decoder encrypts the instruction stored in the register.
11. The signal is given to the microprocessor through the timing and control unit to do the operations. There are different time and control signals to perform the operations. They are control signals, status signals, DMA signals, and RESET signals.
12. Interrupt control interrupts during the process for another request during the main process. Hence, the new request is done before the main process is completed. Different interrupt signals are INTR, RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5.5, and TRAP.
13. Serial data communication is controlled using serial input data and serial output data.
14. Stack pointer and program counter load the data into the address buffer and data buffer so that it communicates with the CPU. The chips are connected here and CPU transfers data via these chips to the data buses.
15. Data to be stored is saved in the data bus and it transfers data to different address services.
Features of 8085 Architecture
- Any 8-bit data could be processed, accepted, or provided in the microprocessor simultaneously. The power supply is a single 5-volt supply and operates on a 50% duty cycle.
- The clock generator in the processor is internal that needs a tuned circuit, either LC or RC or crystal. The frequency is divided by 2 so that the clock signal is generated to synchronize external devices of the system.
- 3 MHz frequency can be used to operate the processor. The maximum frequency in which 8085 operates is 5 MHz
- 16 address lines are provided in the processor so that it can access 64 Kbytes of memory in the system. Also, 8 bit I/O addresses are provided to access 256 I/O ports.
- The address bus and data bus in the processor is multiplexed so that the number of external pins can be reduced. External hardware is needed to separate the address and data lines in the processor. 74 instructions are supported in the processor with different address modes. The address modes are immediate, register, direct, indirect, and implied modes.
Advantages
Below are the prominent advantages of 8085 architecture:
- The general-purpose electronic processing devices in the system to execute various tasks are called the microprocessors. All the logic and arithmetic operations are performed here and the results are stored in the registers. This helps the CPU to fetch information whenever needed in the system.
- Data could be fetched and moved easily to various locations with the help of registers in the microprocessor.
- Operands are delivered easily from the microprocessor and this is easy to do than to restore the operands from the memory. Program variables are stored easily in the registers and hence developers prefer to work with processors in the system.
- Serial communication is provided with serial control and hardware interrupts are available to deliver urgent requests. It handles the interruptions in a skilled manner so that the process is kept on hold until the urgent requests are fulfilled. Control signals are available so that bus cycles are controlled. This rule out the chance of an external bus controller.
- The system bus is shared with Direct Memory Access to transfer huge data from device to memory or vice versa.
Trainer kits are provided in the institutions to learn about microprocessors so that complete documentation is provided to the students regarding the microprocessors. Also, simulators are available for the execution of the codes in the graphical interface. Assembly language programming is added in the microprocessor course so that it helps the students.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to 8085 Architecture. Here we discuss the Introduction and Components of 8085 Architecture and its Features along with its different advantages. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –


